Route target attributes – H3C Technologies H3C S5820V2 Series Switches User Manual
Page 9
3
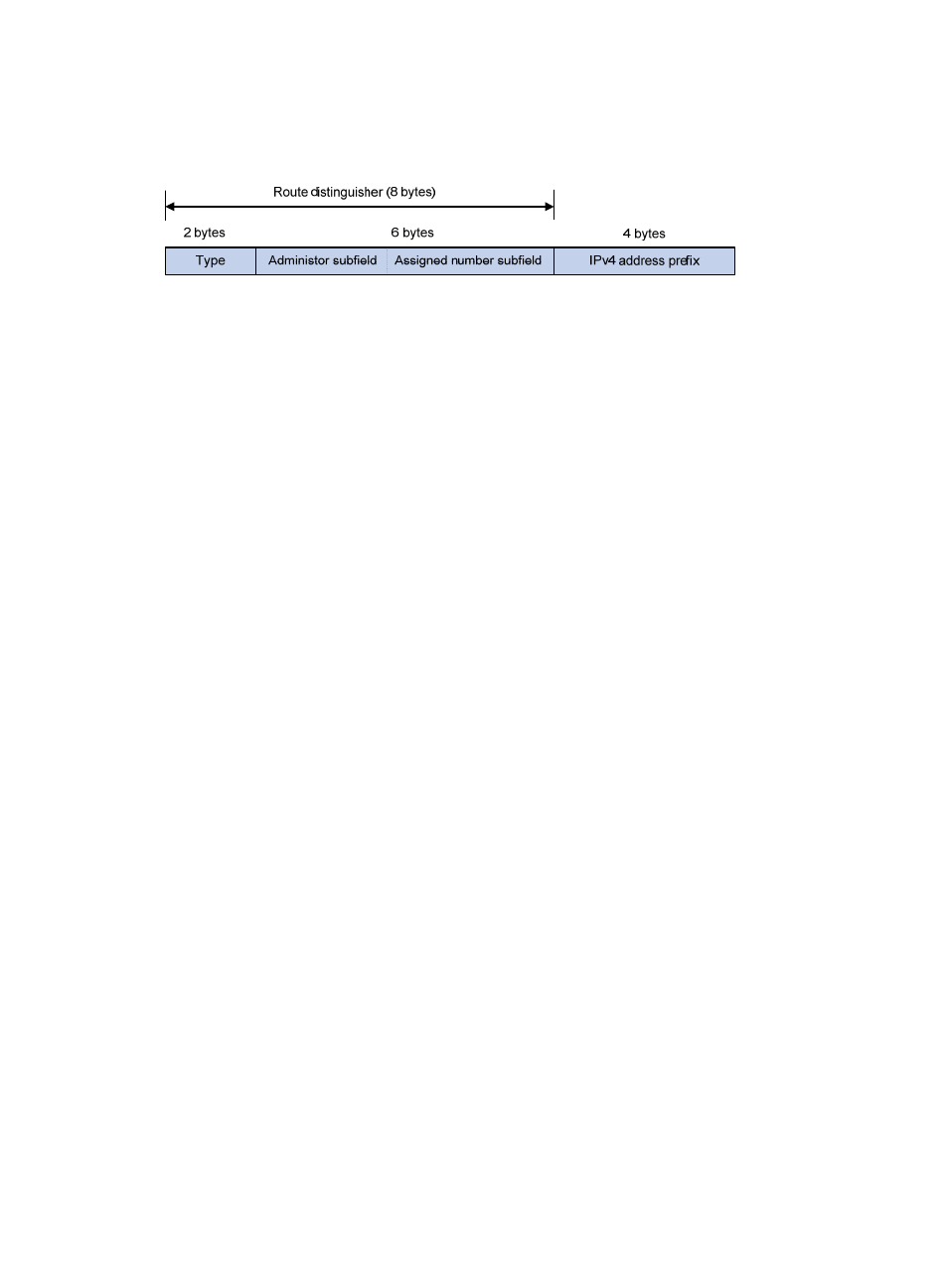
A VPN-IPv4 address consists of 12 bytes. The first eight bytes represent the RD, followed by a four-byte
IPv4 address prefix.
Figure 2 VPN-IPv4 address structure
Upon receiving an IPv4 route from a CE, a PE changes the route to a VPN route by adding an RD and
then advertises the VPN route to the peer PE. The RD ensures the uniqueness of the VPN route.
Each service provider can independently assign unique RDs. A PE can advertise routes for VPNs even if
the VPNs are from different service providers and are using the same IPv4 address space.
Configure a distinct RD for each VPN instance on a PE, so that routes to the same CE use the same RD.
A VPN-IPv4 address with an RD of 0 equals a globally unique IPv4 address.
By prefixing a distinct RD to a specific IPv4 address prefix, you get a globally unique VPN IPv4 address
prefix.
An RD can be related to an autonomous system (AS) number, in which case it is the combination of the
AS number and a discretionary number; or it can be related to an IP address, in which case it is the
combination of the IP address and a discretionary number.
An RD can be in one of the following formats distinguished by a 2-byte Type field:
•
When the value of the Type field is 0, the Administrator subfield occupies two bytes, the Assigned
number subfield occupies four bytes, and the RD format is 16-bit AS number:32-bit user-defined
number. For example, 100:1.
•
When the value of the Type field is 1, the Administrator subfield occupies four bytes, the Assigned
number subfield occupies two bytes, and the RD format is 32-bit IPv4 address:16-bit user-defined
number. For example, 172.1.1.1:1.
•
When the value of the Type field is 2, the Administrator subfield occupies four bytes, the Assigned
number subfield occupies two bytes, and the RD format is 32-bit AS number:16-bit user-defined
number, where the minimum value of the AS number is 65536. For example, 65536:1.
To guarantee global uniqueness for an RD, do not set the Administrator subfield to any private AS
number or private IP address.
Route target attributes
MPLS L3VPN uses the BGP extended community attributes called route target attributes or route target
attributes, to control the advertisement of VPN routing information.
A VPN instance on a PE supports the following types of route target attributes:
•
Export target attribute—A PE sets the export attribute for VPN-IPv4 routes learned from directly
connected sites before advertising them to other PEs.
•
Import target attribute—A PE checks the export target attribute of VPN-IPv4 routes received from
other PEs. If the export target attribute matches the import target attribute of the VPN instance, the
PE adds the routes to the VPN routing table.
In other words, route target attributes define which sites can receive a VPN-IPv4 route, and from which
sites that a PE can receive routes.
Similar to RDs, route target attributes can be one of the following formats:
