6 calculating power consumption – Westermo RM-505U-K User Manual
Page 16
505K Radio Telemetry Module
User Manual
ELPRO Technologies Pty Ltd 2008
Page 16
2.6 Calculating Power Consumption
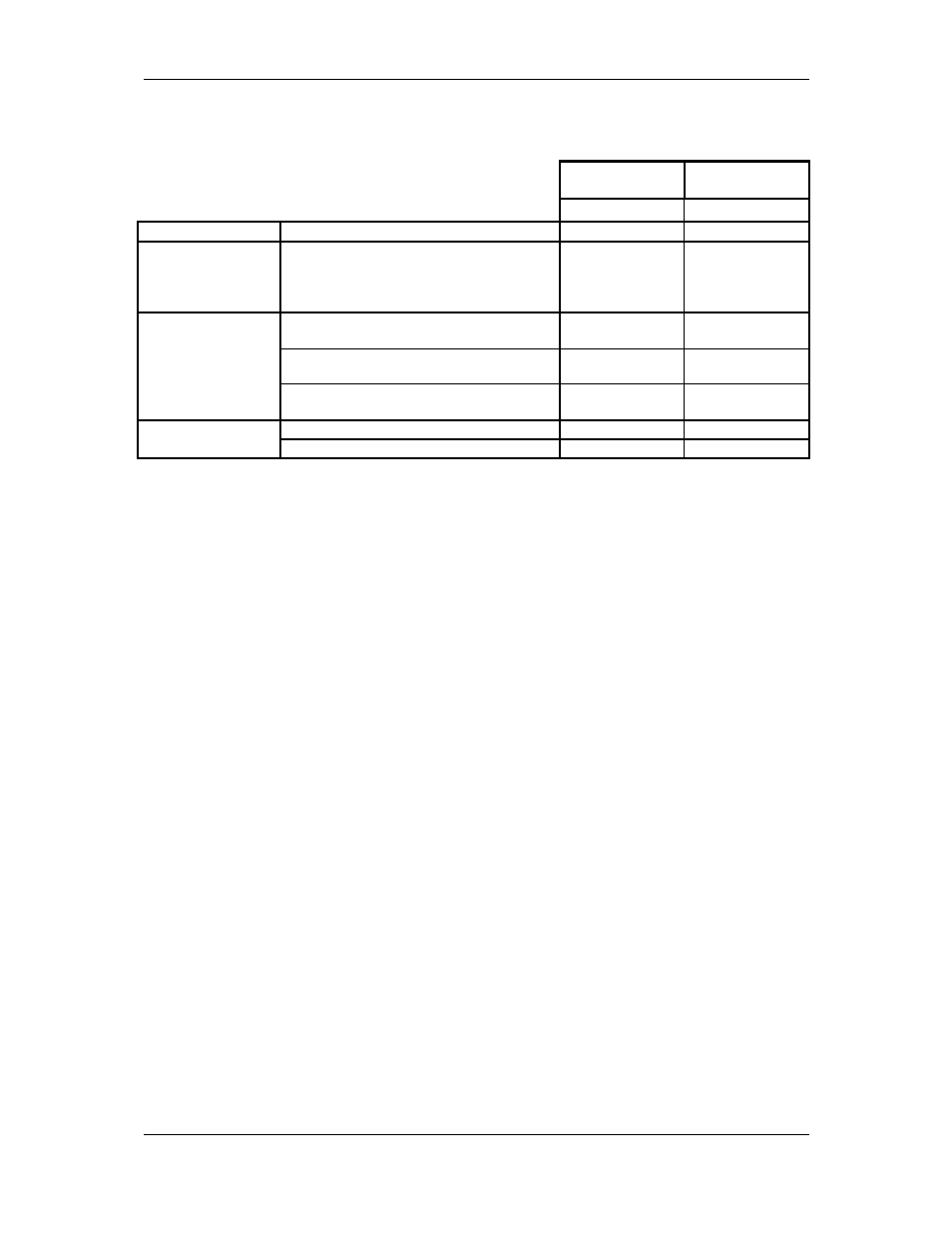
The following information may be used for calculating power consumption.
Voltage Supply
∆ volts (6 – 30)
BU-5-2 Battery
Pack
mA
mAHr
Quiescent
constant regardless of voltage
0.14
3.4 per day
Each radio
transmission
Transmission time 42msec 6V
12V
24V
30V
700
300
180
150
0.005
per transmission
Analogue input
measurement
Externally powered transducer - constant
regardless of voltage
10
Not applicable
(per measurement)
Loop Powered Transducer - 12 mA average
355 / ∆
0.012 x w-time
per measurement
Loop Powered Transducer - 20 mA average
576 / ∆
0.020 x w-time
per measurement
Pulse Input
0 - 10 Hz (Slow Pulse Inputs)
0.0025 x f
0.06 x f per day
> 10Hz (Fast Pulsed Inputs)
0.2
4.8 per day
w-time = warm up time in seconds
f = average pulse frequency in Hz ∆ = supply
volts
The overall current or energy requirements may be calculated by using the above figures.
Total energy per day = Quiescent
+
Pulse input (if used)
+
Analogue input per measurement x number of measurements per day
+
Radio transmission x number of radio transmissions per day
There is no additional power required for digital inputs.
Where the BU-5-2 battery pack is used, these figures can be used to determine the expected
battery life. A BU-5-2 with new batteries has a capacity of 1.7 amphours (1700 mAHr). If
two BU-5-2’s are connected, the second pack provides an additional 1200 mAHr.
Example:-
An application has one digital input, one pulse input and one analogue input. It is powered by a single BU-5-2
battery pack. Each radio message is configured to transmit two times.
The total power consumed = power for transmissions + power for analogue loop supply + pulse input + quiescent
Power for radio transmissions:-
The configuration parameters, and estimated activity data, for each input are:
Digital input
Update time, off state
1 day
Update time, on state
15 minutes
Input is expected to be on twice per year for 4 hours
No. of change messages per year
=
2 (twice per year) * 2 (on to off and off to on)
=
4
No. of “off” update messages per year
=
364 (approximately)
No. of “on” update messages per year
=
2 (twice per year) * 16 (4 hours @ 15 min update)
