Wavetronix Click 510 (communication tester) (CLK-510) - Quick-reference Guide User Manual
Click 510 comm. tester, Installer quick-reference guide, Wire power and communication
Click 510 Comm. Tester
INSTALLER QUICK-REFERENCE GUIDE
2
Wire power and communication
If you are using a Click 200 surge protector with the Click 510, power and communication are provided to
the Click 510 through the T-bus (see the Click 200 Quick-Reference Guide). If you don’t have a Click 200
surge protector, use the following steps to wire power and communication into the Click 510:
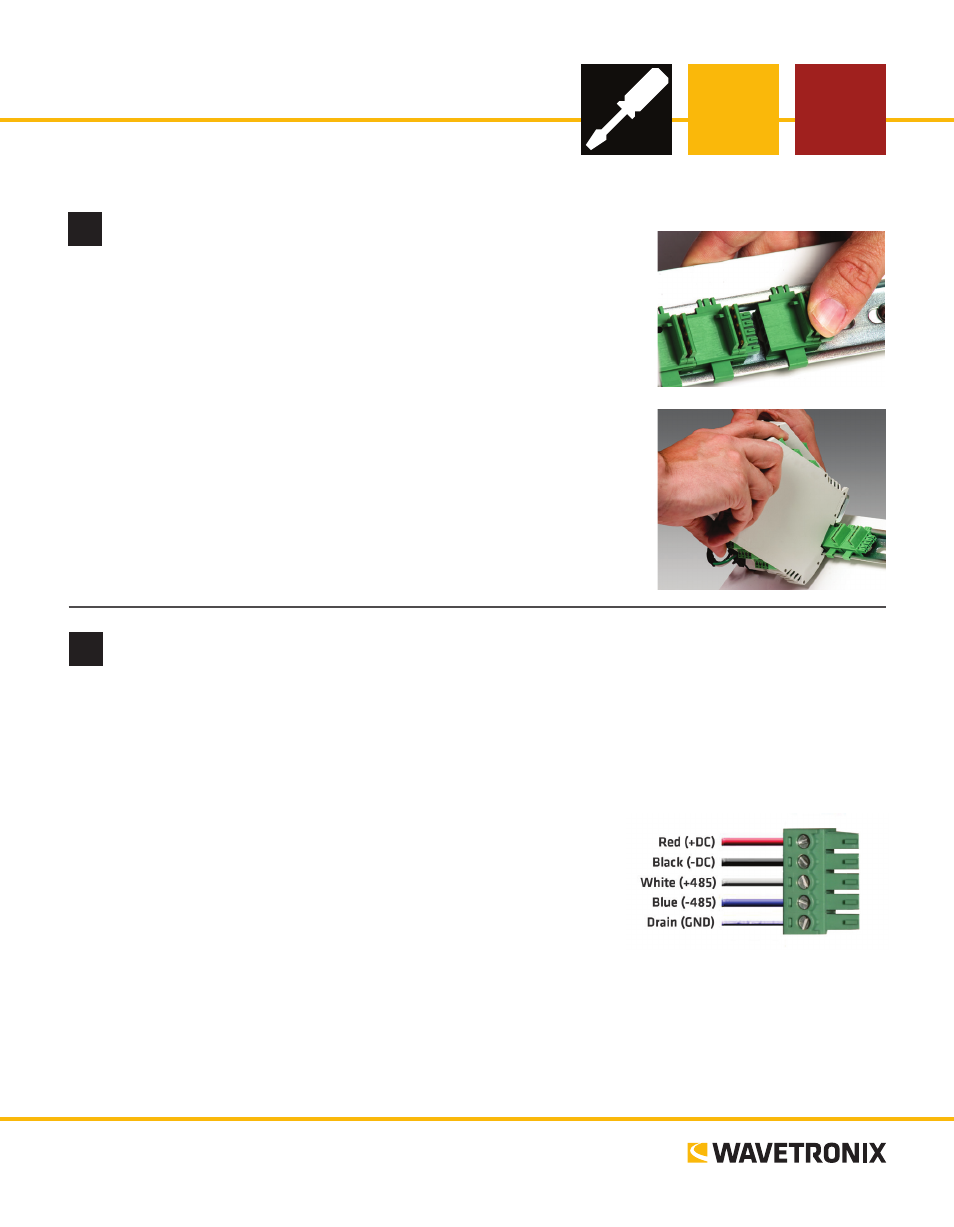
1 Plug a T-bus 5-screw terminal block into the first T-bus connector.
2 Wire DC power (10–30 V) from the power supply into the first
screw terminal on the 5-screw terminal block; wire -DC into the
second screw terminal.
3 Connect RS-485 communication (+485, -485 and GND) to either
the remaining three screw terminals on the 5-screw terminal block
or to the screw terminals in the pluggable screw terminal block on
the top of the Click 510 (see labels for correct wiring).
The Click 510 has three other communication ports.
˽
RJ-11 jack – Connect a jumper cable here for RS-485 communication
˽
DB-9 connector – Connect a straight-through cable here for RS-232 communication
˽
RS-232/RS-485 terminals – On top of device; usually not used
www.wavetronix.com
801.734.7200
1
Mount the device
The Click 510 mounts over a T-bus for power and communication:
1 If the Click 510 was shipped with the T-bus connector attached, re-
move the connector from the module.
2 Snap the connector onto the DIN rail by positioning it over the rail
with the male connector pointing to the right. Hook one arm over the
edge of the DIN rail and press down on the other arm until it snaps
into place.
3 Connect the T-bus connector to the rest of the T-bus by sliding them
together until you hear them snap into place.
4 Mount the Click 510 onto the DIN rail: position it properly over the
T-bus connector, hook the lip over the lower edge of the DIN rail, and
use a rocking motion to snap the module into place.
