Advanced operation, Adjusting the line input trim pots – Studio Technologies 220 2013 User Manual
Page 29
Model 220 User Guide
Issue 5, February 2013
Studio Technologies, Inc.
Page 29
Advanced
Operation
Adjusting the Line Input
Trim Pots
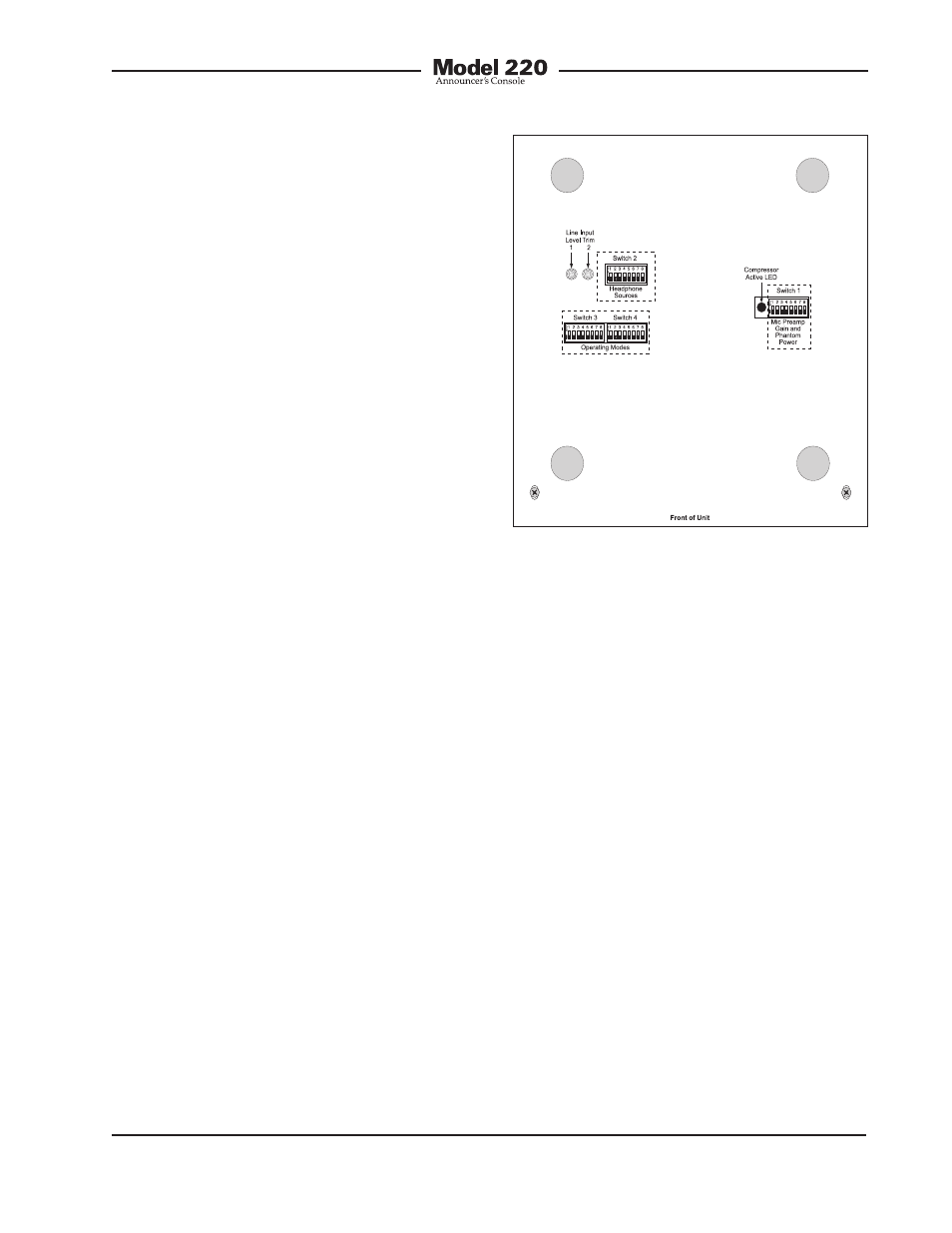
As has been previously mentioned, as-
sociated with the line inputs are trim pots
that allow the input levels to be adjusted.
The two trim pots are accessible by way
of round openings in the bottom of the
Model 220’s enclosure. By adjusting these
trim pots, signals with a nominal level of
–12 dBV to +6 dBu can be effectively used
as cue sources. Unfortunately, there are
no definitive rules regarding how best to
adjust the trim pots, but some suggestions
may prove to be valuable. Depending on
how the line inputs are utilized, the trim
pots can be used to either adjust the ab-
solute level of each line input signal, or to
adjust the relative level of the signals when
compared to other sources. The following
examples may provide some clarification.
Let’s begin with an application that has a
stereo cue source connected to the line
inputs. The source selection DIP switches
are configured to create a stereo head-
phone output with line input 1 assigned to
the left channel and line input 2 assigned
to the right channel. Begin the trim pot
adjustment process by moving the user
level controls (located on the front panel)
to their detent (50% of rotation) positions.
Then, with the stereo cue source provid-
ing signal at its normal level, adjust the
trim pots to provide a comfortable level
to the connected headphones. The user
can now, in response to changing condi-
tions, adjust the front-panel level controls
as desired. Returning the controls to their
detent positions will always provide the
“reference” level to the headphone output.
A second example has the IFB input and
line input 1 both providing cue sources.
Channel 1 of the IFB circuit supplies pro-
gram-with-interrupt audio that is routed
to the headphone output’s left channel.
Channel 2 of the IFB circuit supplies
program-only audio that is routed to the
right channel. Line input 1 is connected to
an audio source associated with a sports-
event “spotter” position. This source is
routed to the headphone output’s right
channel. The input trim pot associated
with line input 1 can now serve a critical
role—adjusting the relative level of the
“spotter” audio as compared to the level
of IFB channel 2. The trim pot allows the
desired “mix” to be created, providing the
user with an effective cue signal.
Figure 18. Bottom view showing line input
trim pots
