Appendix a: raid concepts, Disk striping – OpenEye G4 GraniteRack User Manual
Page 24
24
APPENDIX A: RAID CONCEPTS
The purpose of RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is to combine multiple inexpensive disk
drives into an array of drives to obtain performance, capacity, and reliability that exceeds the capability
of a single large drive. The array of drives is recognized by the recorder as a single logical drive.
Six types of array architectures, RAID 1 through RAID 6 provide disk fault tolerance with different
compromises in features and performance. IN addition to these five redundant array architectures, it
has become popular to refer to a non-redundant array of disk drives as a RAID 0 array.
DISK STRIPING
Striping is fundamental to RAID technology. This is a method of combining multiple drives into one
logical storage unit. Striping partitions the storage space of each drive. These stripes can be as small as
one sector (512 bytes) or as large as several megabytes. These stripes are then interleaved in a
rotating sequence, so that the combined space is composed of stripes from each drive, alternately. The
specific type of operating environment determines whether large or small stripes should be used.
Most current operating systems support concurrent disk I/O operations across multiple drives. However,
in order to maximize throughput for the G4 GraniteRack, the I/O load must be balanced across all the
drives, so that each drive can be kept busy as much as possible. In a multiple drive system without
striping, the disk I/O load is never perfectly balanced. Some drives contain data files that are frequently
accessed and some drives are rarely accessed.
By striping the drives in the array with stripes large enough for each record to be contained within one
stripe, most records can be evenly distributed across all drives. This keeps all drives in the array busy
during heavy load situations. This situation allows all drives to work concurrently on different I/O
operations, and thus maximize the number of simultaneous I/O operations that can be performed by the
array.
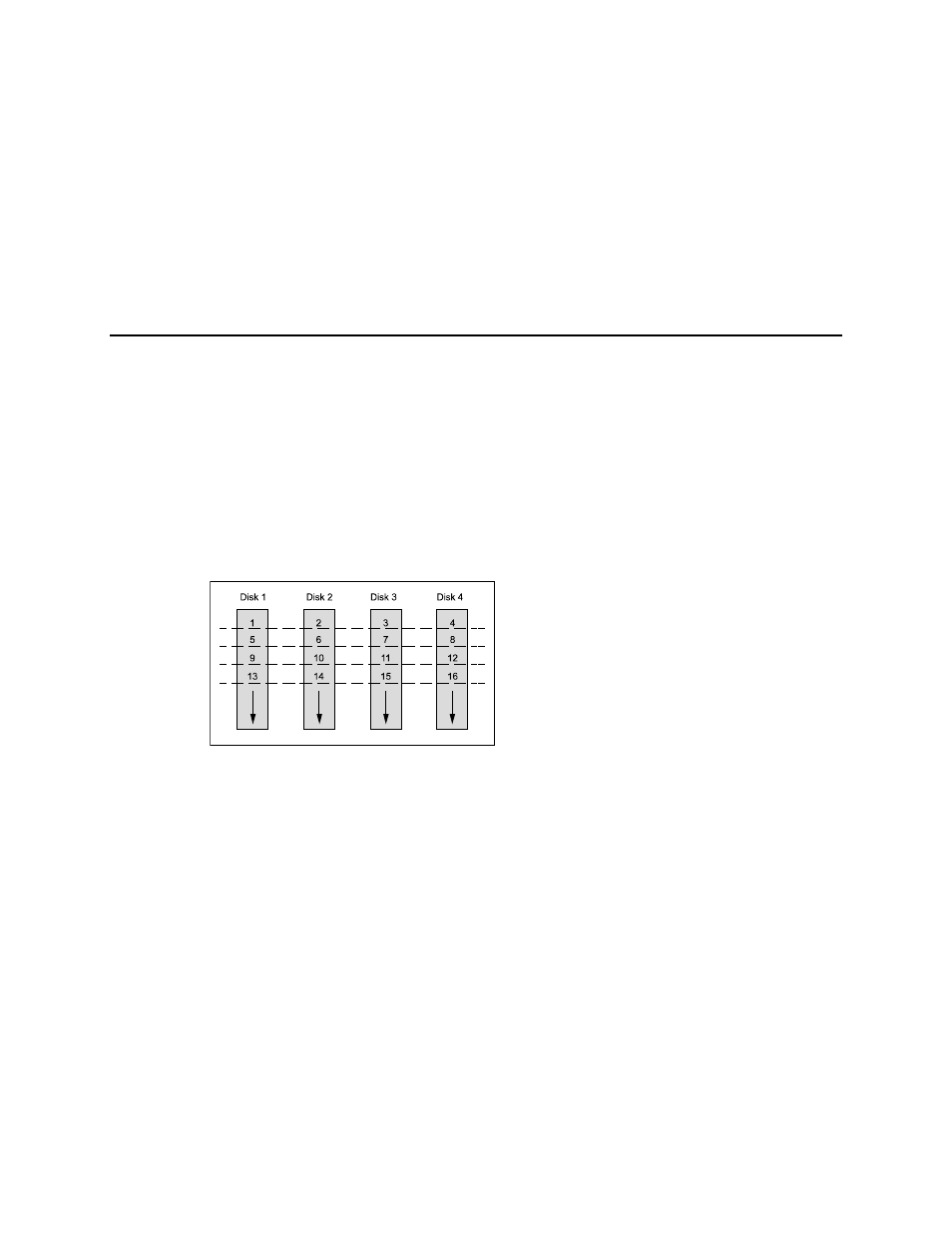
STRIPING DISK DRIVES
Data stripes from each drive are interleaved
to create one logical drive
