Signal connections, Input isolation, Analog/tc input – Measurement Computing USB-2408 Series User Manual
Page 12
USB-2408 Series User's Guide
Functional Details
12
Signal connections
Input isolation
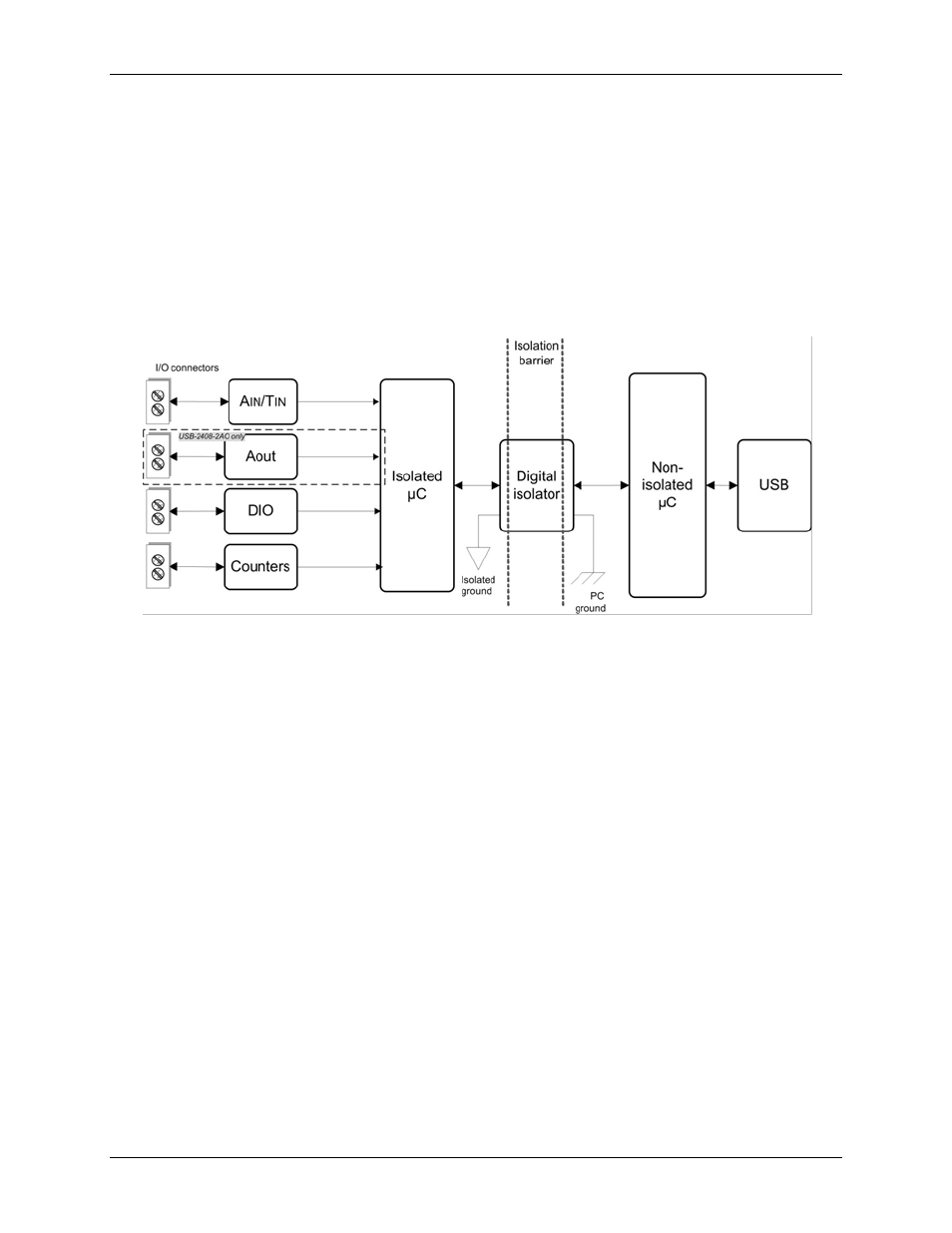
USB-2408 Series devices are isolated data acquisition devices. The analog I/O, digital I/O, counters, and all the
digital control/timing are referenced to an isolated ground as shown in the figure below. This ground is
physically and electrically separate from the ground used by the circuit connected to the system bus interface.
Isolation provides a barrier between the host computer and potentially hazardous voltages by physically and
electrically separating two parts of the measurement device.
The non-isolated ground is common to the chassis ground of the computer, while the isolated ground is not.
All analog measurements are made relative to the isolated ground. See Figure 5 for details.
Figure 5. USB-2408 Series input isolation diagram
When making measurements in industrial environments, DAQ devices can encounter hazardous voltages,
transients, large common mode voltages and fluctuating ground potentials. Any one of these issues can
seriously degrade the measurement accuracy of the device and possibly damage the measurement instrument.
To overcome these issues, some DAQ devices provide physical and electrical isolation. Some of the benefits of
isolation include:
Safety: A DAQ device employing physical and electrical isolation helps to keep high voltages and
transients from damaging the system-side host computer.
Ground loops: Improper grounding of the signal source that the DAQ device is measuring is one of the
most common sources of noise and measurement inaccuracies. Isolation improves the measurement
accuracy by physically preventing ground loops. Ground loops – a common source of noise and error – are
the results of a measurement system having multiple grounds at different potentials.
Common mode rejection: With isolation, a DAQ device can measure small signals in the presence of large
common mode voltages. Isolation increases the ability of the measurement system to reject common mode
voltages. The common mode voltage is the signal that is common to both the positive and negative inputs
of the measurement device, but is not part of the signal to measure.
Analog/TC input
Each analog input channel has the following measurement parameters:
Voltage input range
TC type J, K, T, E, R, S, B, or N
You can select a unique input range or signal type for each channel. For example, one channel could be used for
volts and another for temperature.
