B.3 802.1q vlan support, B.4 section packing – Comtech EF Data CME-5000 Manual User Manual
Page 75
Digicast Micro Encapsulator (MENCAP)
Revision A
IP Routing Support
MN/MENCAPEDC.IOM
Several examples of the relationship are:
• Received IP: 239.1.1.10 = MAC: 0x01 00 5E 01 01 0A
• Received IP: 224.10.10.10 = MAC: 0x01 00 5E 0A 0A 0A
• Received IP: 228.63.10.10 = MAC: 0x01 00 5E 3F 0A 0A
Note that the upper 5 bits of the multicast IP address are ignored in the MAC so that 32
Multicast group IP addresses map to a single MAC address. This implies further filtering
is required at the end device.
B.3 802.1Q
VLAN
Support
802.1Q VLAN support allows the MENCAP to route traffic based on the VLAN tags.
The configuration of the VLAN tag is done on the Advanced Routing page on the
terminal interface and is also available on the web interface.
VLAN tags are supported when LLC_SNAP Ethernet frames are being used. Normal
Ethernet frames utilize IEEE 802.3 framing with a maximum frame size of 1,518 bytes;
however, LLC_SNAP frames contain four extra bytes (on the frame header) that may be
used for VLAN tags, so the Ethernet frame size is up to 1,522 bytes.
The VLAN tag allows the MENCAP to route packets based on the presence of a route
that matches the VLAN tag. The VLAN tag is 12 bits in length and valid values from
0 to 4095 are accepted.
B.4 Section
Packing
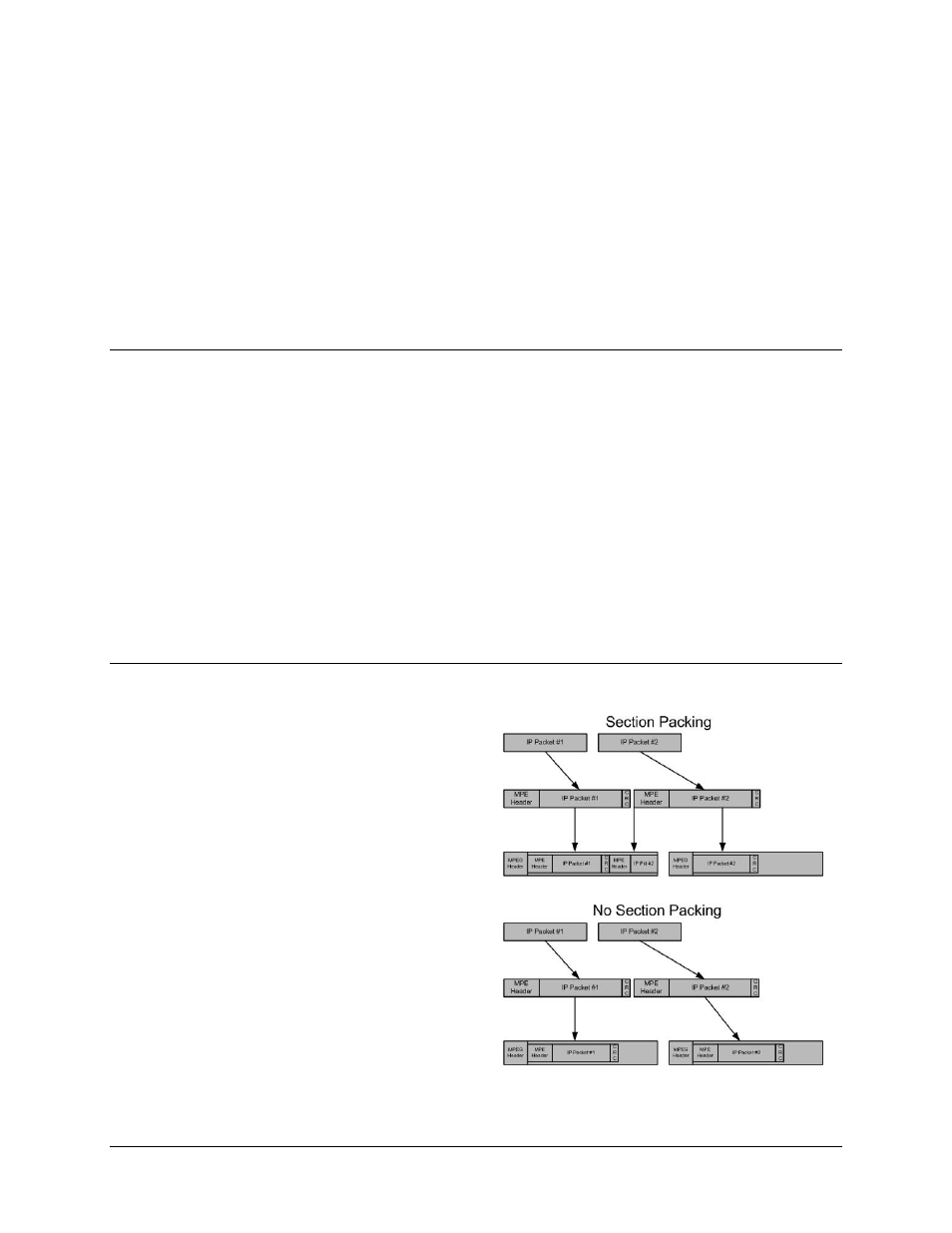
Section packing is a technique to
provide better utilization of the
MPEG-2 Transport Stream (TS)
packet structure. When section
packing is not used, each TS
packet (containing the MPE
section) can carry no more than a
single section. This often results in
wasted payload capacity when the
sections are less than 184 bytes.
The section packing feature allows
more than a single MPE section to
be carried by an MPEG-2 TS
packet, thereby minimizing wasted
payload capacity. In the case of a
large MPE section that spans
multiple MPEG-2 packets, the
ending of an MPE section may
Figure B-2. Section Packing
B-3
