Twincat ads, Ads routes, A.2. twincat ads – BECKHOFF IPC-Security User Manual
Page 34: A.2.1. ads routes
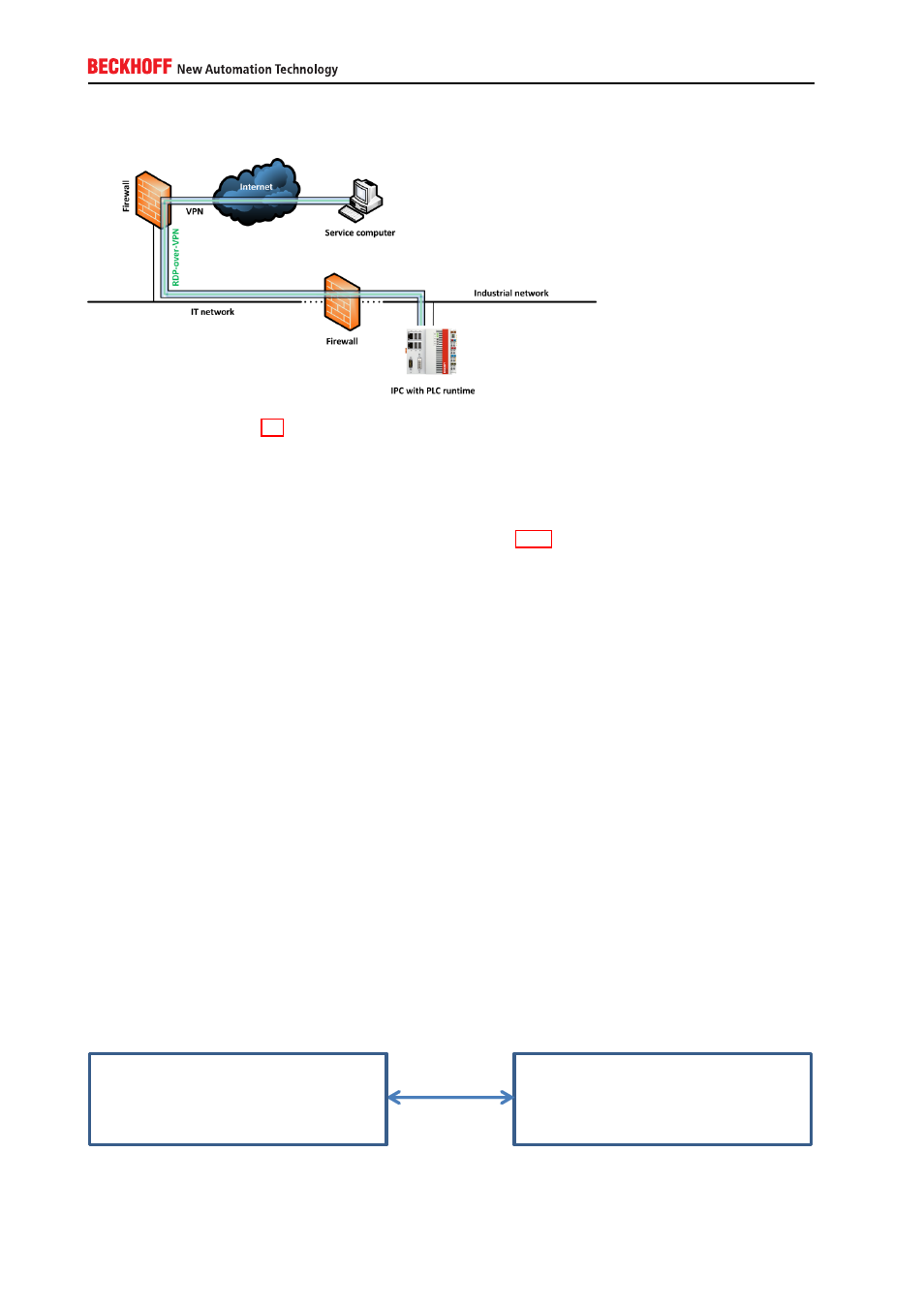
A.1.4. Remote maintenance via VPN server on IPC
As described in chapter 5.2, Windows CE and Windows XP/7 operating systems provide all necessary
functionalities to create an own VPN-Server directly on the embedded device. Therefore, in this scenario
the VPN connection only needs to be routed through both firewalls, e.g. by configuring a port-forwarding
on these firewalls. The advantage of this setup is that the communication is encrypted during the whole
transition from service computer to IPC.
Please note that this setup could also be relevant for scenario A.1.2, e.g. to wrap the RDP communication
into a secure VPN / IPSec channel.
A.2. TwinCAT ADS
Connectivity in TwinCAT is generally based on the ADS communication protocol, which ensures a fast
transport of data between ADS devices, e.g. between TwinCAT PLC and TwinCAT I/O. ADS is a propri-
etary communication protocol developed by Beckhoff Automation. ADS has been developed to maximize
throughput and data flow between TwinCAT components and to enable communication via different trans-
port protocols, e.g. to transmit ADS over a TCP or even a serial communication channel. Because of this
goal, ADS has not been designed to achieve security purposes and therefore does not include any encryp-
tion algorithms because of their negative effect on performance and throughput. However, ADS implements
user authentication when establishing an ADS route between two TwinCAT devices.
A.2.1. ADS routes
To enable connectvity between ADS devices, a one-time creation of corresponding ADS routes is required.
Each ADS device has an identifier, the so-called ADS-NetID. Each ADS application has its own port, the so-
called ADS-Port. The ADS communication is independent of the transport protocol, e.g. ADS pakets could
be transmitted via a TCP channel. The internal ADS routing table then maps the corresponding transport
address to the ADS-NetID. Ín the following scenario two ADS devices should communicate with each other
via a TCP/IP network. Each device has its own IP-address and ADS-NetID.
Hostname: Device1
IP: 192.168.1.1
ADS-NetID: 192.168.1.1.1.1
Hostname: Device2
IP: 192.168.1.2
ADS-NetID: 192.168.1.2.1.1
34
