Hanna Instruments HI 96711 User Manual
Page 4
6
7
PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION
Absorption of Light is a typical phenomenon of interaction between electromagnetic radiation and
matter. When a light beam crosses a substance, some of the radiation may be absorbed by
atoms, molecules or crystal lattices.
If pure absorption occurs, the fraction of light absorbed depends both on the optical path length
through the matter and on the
physical
-chemical characteristics of the substance according to the
Lambert-Beer Law:
-log
I
/
I
o
=
ε
λ
c d
or
A
=
ε
λ
c d
Where:
-log
I
/
I
o
=
Absorbance (A)
I
o
=
intensity of incident light beam
I
=
intensity of light beam after absorption
ε
λ
=
molar extinction coefficient at wavelength
λ
c
=
molar concentration of the substance
d
=
optical path through the substance
Therefore, the concentration "c" can be calculated from the absorbance of the substance as the
other factors are known.
Photometric chemical analysis is based on the possibility to develop an absorbing compound
from a specific chemical reaction between sample and reagents. Given that the absorption of a
compound strictly depends on the wavelength of the incident light beam, a narrow spectral
bandwidth should be selected as well as a proper central wavelength to optimize measurements.
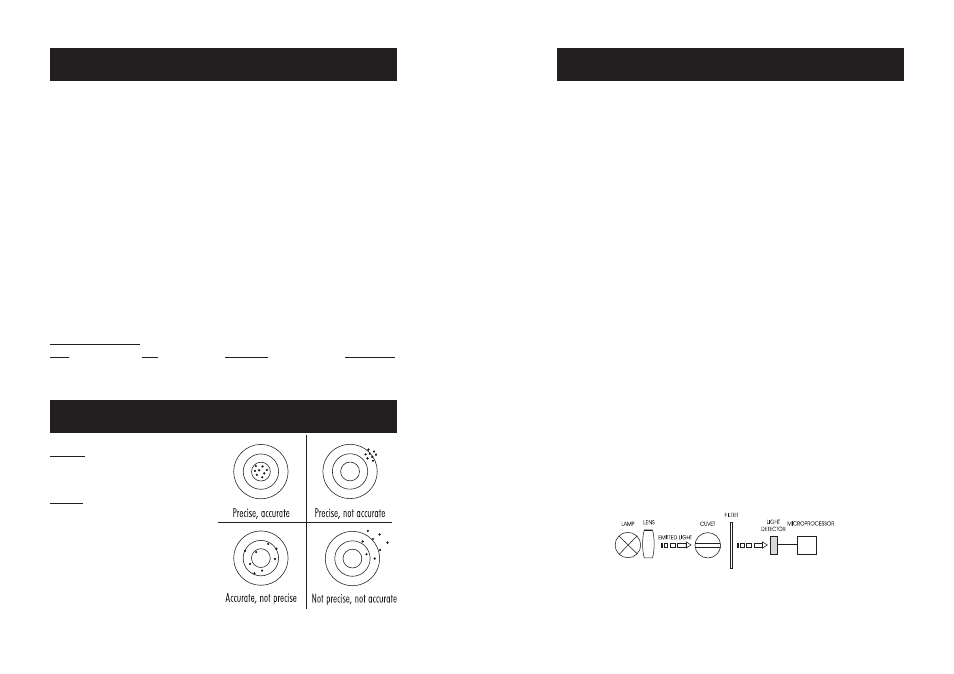
The optical system of Hanna's HI 96 series colorimeters is based on special subminiature
tungsten lamps and narrow-band interference filters to guarantee both high performance and
reliable results.
HI 96 series block diagram (optical layout)
SPECIFICATIONS
PRECISION AND ACCURACY
Range
Free Cl
2
0.00 to 5.00 mg/L
Total Cl
2
0.00 to 5.00 mg/L
Resolution
0.01 mg/L from 0.00 to 3.50 mg/L; 0.10 mg/L above 3.50 mg/L
Accuracy
±0.03 mg/L ±3% of reading @ 25°C
Typical EMC Deviation
±0.01 mg/L
Light Source
Tungsten lamp
Light Detector
Silicon Photocell with narrow band interference filter @ 525nm.
Method
Adaptation of the USEPA method 330.5 and Standard Method 4500-Cl G.
The reaction between chlorine and the DPD reagent causes a pink tint
in the sample.
Environment
0 to 50°C (32 to 122°F); max 95% RH non-condensing
Battery Type
1 x 9 volt
Auto-Shut off
After 10' of non-use in
measurement mode;
after 1 hour of non-use in
calibration mode;
with last reading reminder.
Dimensions
192 x 104 x 69 mm (7.6 x 4.1 x 2.7")
Weight
360 g (12.7 oz.).
REQUIRED REAGENTS
Code Unit
Description
Quantity/test
HI 93701-0
Free Cl
2
DPD Powder Reagent
1 packet
HI 93711-0
Total Cl
2
DPD Powder Reagent
1 packet
Precision
is how closely repeated measurements
agree with each other. Precision is usually
expressed as standard deviation (SD).
Accuracy
is defined as the nearness of a test
result to the true value.
Although good precision suggests good accuracy,
precise results can be inaccurate. The figure
explains these definitions. In a laboratory using
a standard solution of 1.00 mg/L chlorine and a
representative lot of reagent, an operator obtained
with a single instrument a standard deviation of
0.02 mg/L.
