Hanna Instruments HI9126 User Manual
Page 12
22
23
EEEEELECTRODE CONDITIONING & MAINTENANCE
LECTRODE CONDITIONING & MAINTENANCE
LECTRODE CONDITIONING & MAINTENANCE
LECTRODE CONDITIONING & MAINTENANCE
LECTRODE CONDITIONING & MAINTENANCE
PREPARATION PROCEDURE
Remove the electrode protective cap.
DO NOT BE ALARMED IF ANY SALT DEPOSITS ARE PRESENT. This is
normal with electrodes and they will disappear when rinsed with water.
During transport tiny bubbles of air may have formed inside the glass
bulb. The electrode cannot function properly under these conditions.
These bubbles can be removed by "shaking down" the electrode as you
would do with a glass thermometer.
If the bulb and/or junction are dry, soak the electrode in HI 70300
Storage Solution for at least one hour.
Not present in gel electrodes.
Typical Electrode Life
Ambient Temperature
1 – 3 years
90 °C
Less than 4 months
120 °C
Less than 1 month
Alkaline Error
High concentrations of sodium ions interfere with readings in alkaline
solutions. The pH at which the interference starts to be significant
depends upon the composition of the glass. This interference is called
alkaline error and causes the pH to be underestimated. Hanna’s glass
formulations have the indicated characteristics.
1.0 Mol L
-1
Na
+
0.1 Mol L
-1
Na
+
Sodium Ion Correction for Glass at 20
-25 °C
Concentration
pH
Error
13.00
13.50
14.00
12.50
13.00
13.50
14.00
0.10
0.14
0.20
0.10
0.18
0.29
0.40
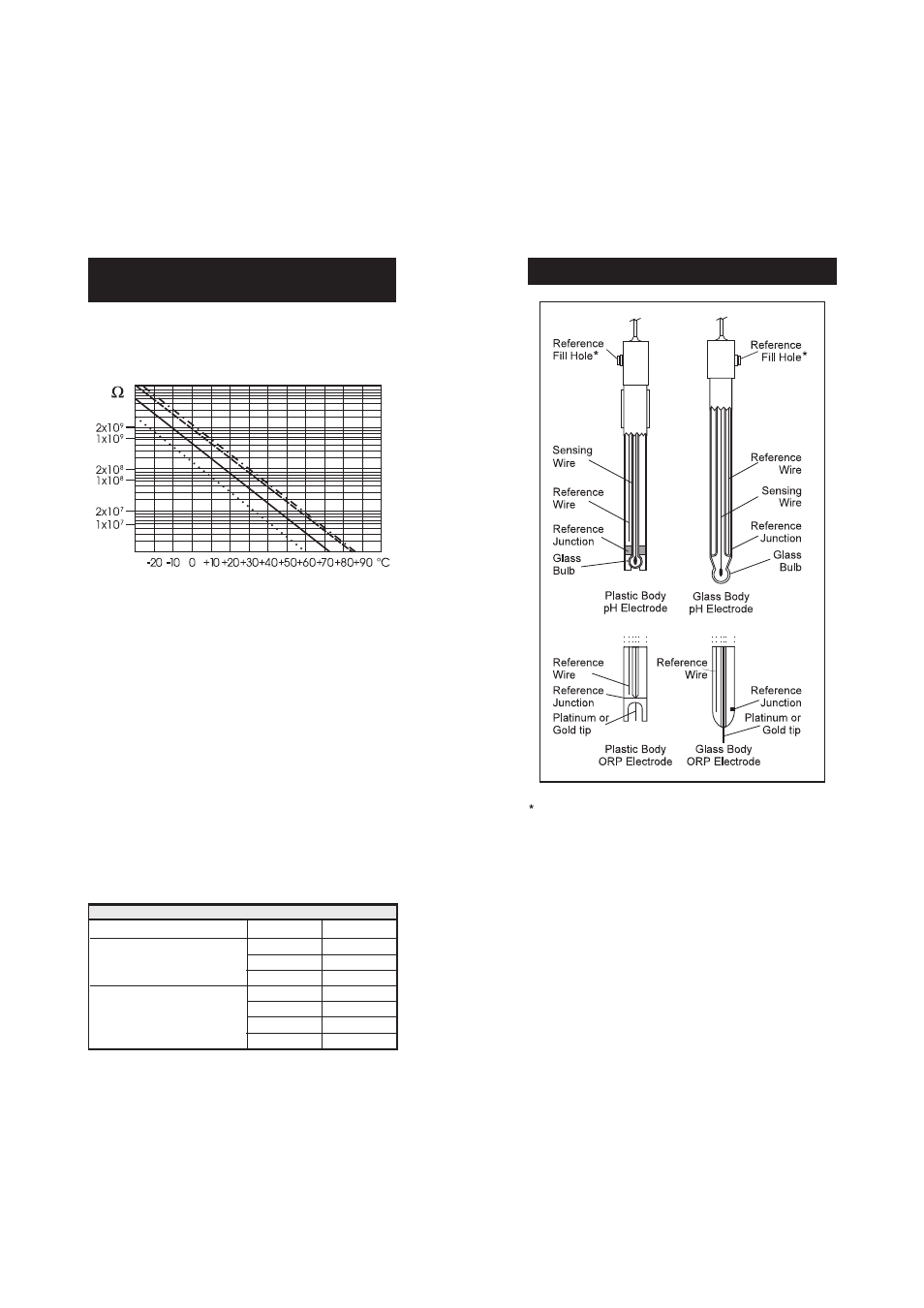
The resistance of glass electrodes partially depends on the temperature.
The lower the temperature, the higher the resistance. It takes more time
for the reading to stabilize if the resistance is higher. In addition, the
response time will suffer to a greater degree at temperatures below 25 °C.
Since the resistance of the pH electrode is in the range of 50 – 200
Mohms, the current across the membrane is in the pico Ampere range.
Large currents can disturb the calibration of the electrode for many
hours.
For these reasons high humidity environments, short circuits and static
discharges can be detrimental to a stable pH reading.
The pH electrode’s life also depends on the temperature. If constantly
used at high temperatures, the electrode life is drastically reduced.
T E M P E R A T U R E C O R R E L A T I O N
T E M P E R A T U R E C O R R E L A T I O N
T E M P E R A T U R E C O R R E L A T I O N
T E M P E R A T U R E C O R R E L A T I O N
T E M P E R A T U R E C O R R E L A T I O N
FOR
FOR
FOR
FOR
FOR p
pp
pp H SENSITIVE GLASS
H SENSITIVE GLASS
H SENSITIVE GLASS
H SENSITIVE GLASS
H SENSITIVE GLASS
