Hanna Instruments HI 83200-01 User Manual
Page 33
64
65
Hydrazine
HYDRAZINE
SPECIFICATIONS
Range
0 to 400 µg/L
Resolution
1 µg/L
Accuracy
±4% of full scale
Typical EMC
±2 µg/L
Deviation
Light Source
Tungsten lamp with narrow band interference filter @ 420 nm
Method
Adaptation of the
ASTM Manual of Water and Environmental Technology, method
D1385-88, p-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde method. The reaction between hydrazine
and the liquid reagent causes a yellow tint in the sample.
REQUIRED REAGENT
Code
Description
Quantity
HI 93704-0
Liquid Reagent
24 drops
REAGENT SETS
HI 93704-01 Reagents for 100 tests
HI 93704-03 Reagents for 300 tests
For other accessories see page 128.
MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE
• Select the
Hydrazine method using the procedure described
in the
Method Selection section (see page 12).
• Fill one cuvette up to the mark with 10 mL of distilled water.
• Place the cap, insert the cuvette # 1 into the holder and
close the lid.
• Press the Blank function key to start adjusting the light level.
The display will show “Blank Done” when the meter is ready
to take a zero measurement.
• Fill a second cuvette with 10 mL of unreacted sample (up to the
mark) and replace the cap.
10 mL
# 1
10 mL
# 2
# 1
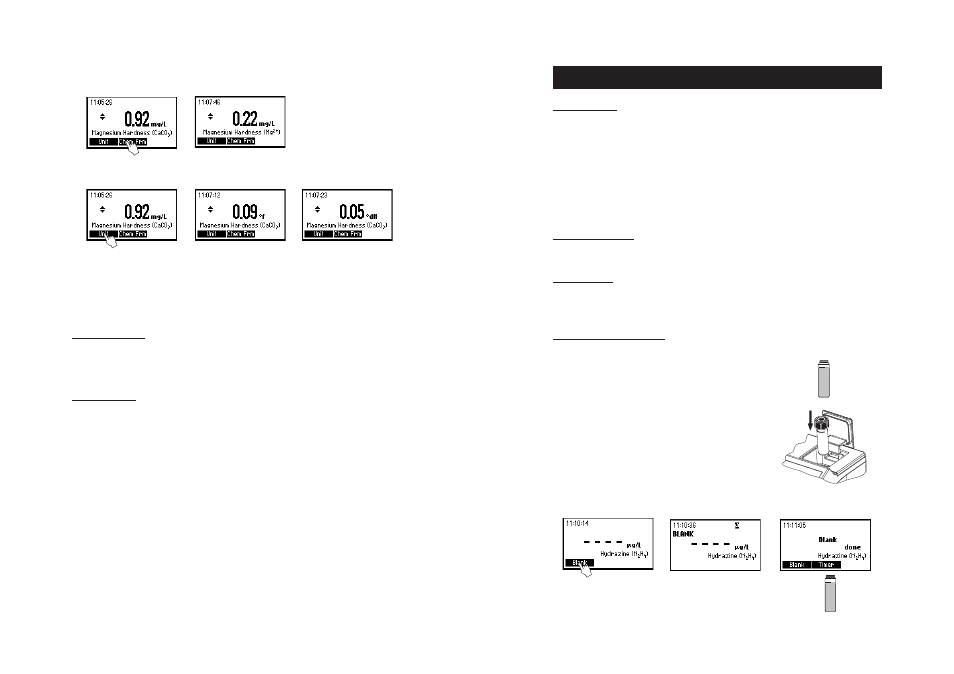
Hardness Mg
• Press the or to access the second level of functions.
• Press the Chem Frm functional key to convert the result in mg/L of Magnesium (Mg).
• Press the Unit functional key to change the current measurement unit. The results can be converted to
French degrees (°f), German degrees (°dH) and English degrees (°E).
• Press the or to go back to the measurement screen.
Note: This test will detect any magnesium contamination in the beakers, measuring syringes or sample
cells. To test cleanliness, repeat the test multiple times until you obtain consistent results.
SAMPLE DILUTION
This meter is designed to determine hardness typically found in water purification systems. In order to
measure samples with high hardness, follow dilution procedure explained on page 61 (Ca Hardness).
INTERFERENCES
Interference may be caused by excessive amounts of heavy metals.
