Leslie Controls NYC Heat Exchanger User Manual
Page 12
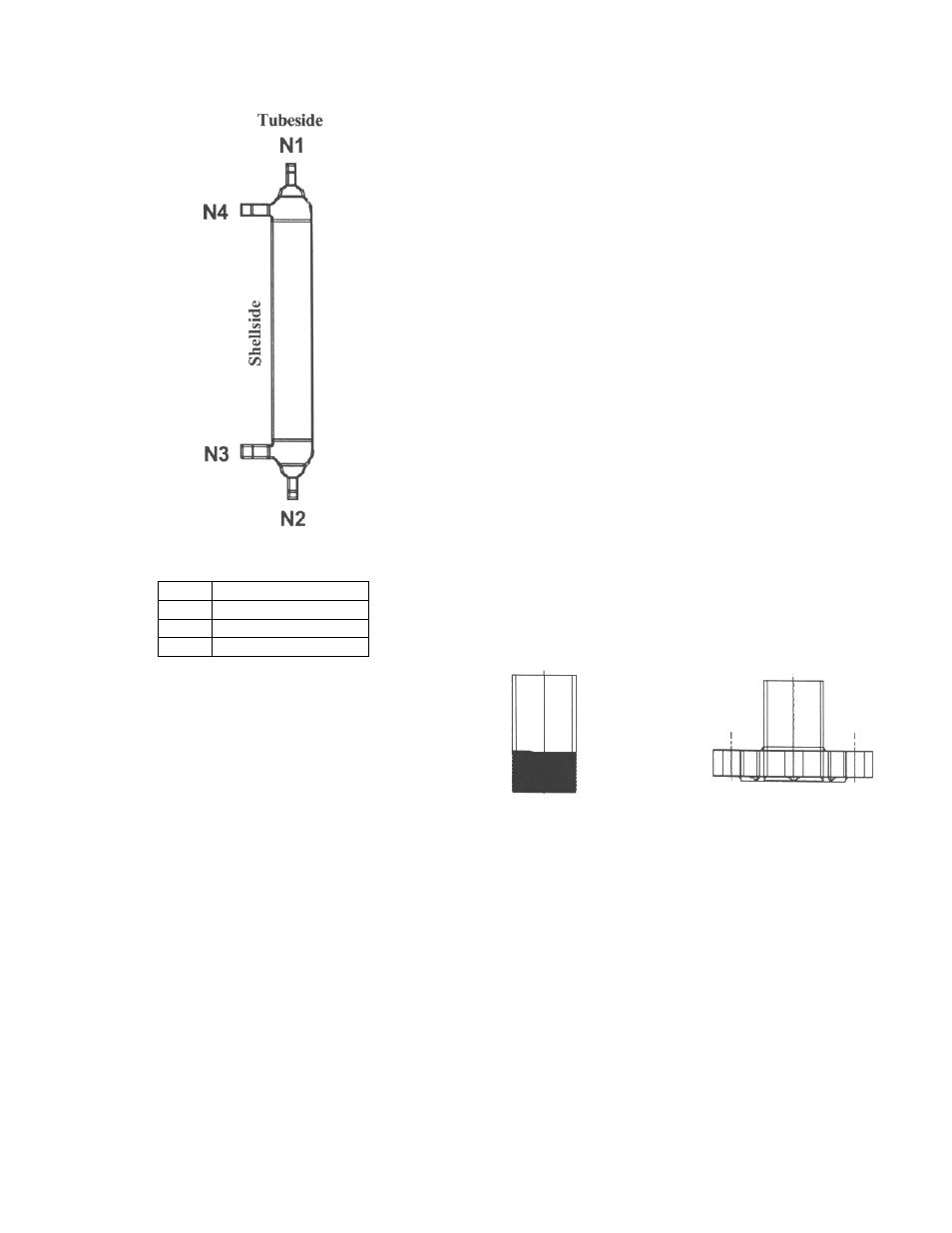
Page 12 of 25
Figure 9 - Flow Distribution in Heat Exchangers
N 1
Heating Fluid In
N 2
Heating Fluid Out
N 3
Cold Fluid In
N 4
Cold Fluid Out
MATERIALS
Heat exchangers are manufactured according to following
table.
Standard Materials
Shell
ASTM 316L
Tubes
ASTM 316L
Nozzle
ASTM 316L
Connection flanges
Stainless Steel/ Carbon Steel
with Stainless Steel Lining
OPERATING PARAMETERS OF HEAT
EXCHANGERS
Standard
maximum
working
parameters
of
heat
exchangers are as follows:
Design Pressure
Shell
300 psig (2.0 Mpa)
Tube
300 psig (2.0 Mpa)
Design temperature
Shell
422°F (217°C)
Tube
422°F (217°C)
OPERATING PRECAUTIONS
In order to achieve maximum performance from heat
exchanger, following must be strictly followed:
Heat
exchangers
should
be
used
according
to
specification given.
Pressures and temperatures should not exceed limits set
forth in Operating Parameters and Selection of Heat
Exchangers Section.
Initial start up should be done according to Start up
Section.
Heat exchangers should be free of any debris existing in
fluid.
In central heating applications, hot water should not
exceed 140 °F (60 °C). Over this limit, lime will form on
tube walls.
Prevent evaporation of fluid on shell side. Steam or vapor
should only flow through tubes.
Clean heat exchangers according to Cleaning Section.
System should be designed to prevent heat exchanger
from encountering pressure shocks.
Prevent rapid temperature increases in heat exchangers.
This would include installation of expansion tanks and
safety valves into system.
Prevent any fluids from dropping below freezing point.
Figure 10 - Threaded and Flanged (compatible with CL
300) connections
A name plate is placed on shell and includes following
data:
Type of heat exchanger
Serial number
Production year
Maximum working pressure and temperature
ASME stamp of approval
CRN registration number
Manufacturer logo
STORAGE AND TRANSPORTATION
Heat exchangers should be stored in a clean place away
from corrosive environments or weather elements (e.g.
