Memory allocations – Dell Precision 610 User Manual
Page 99
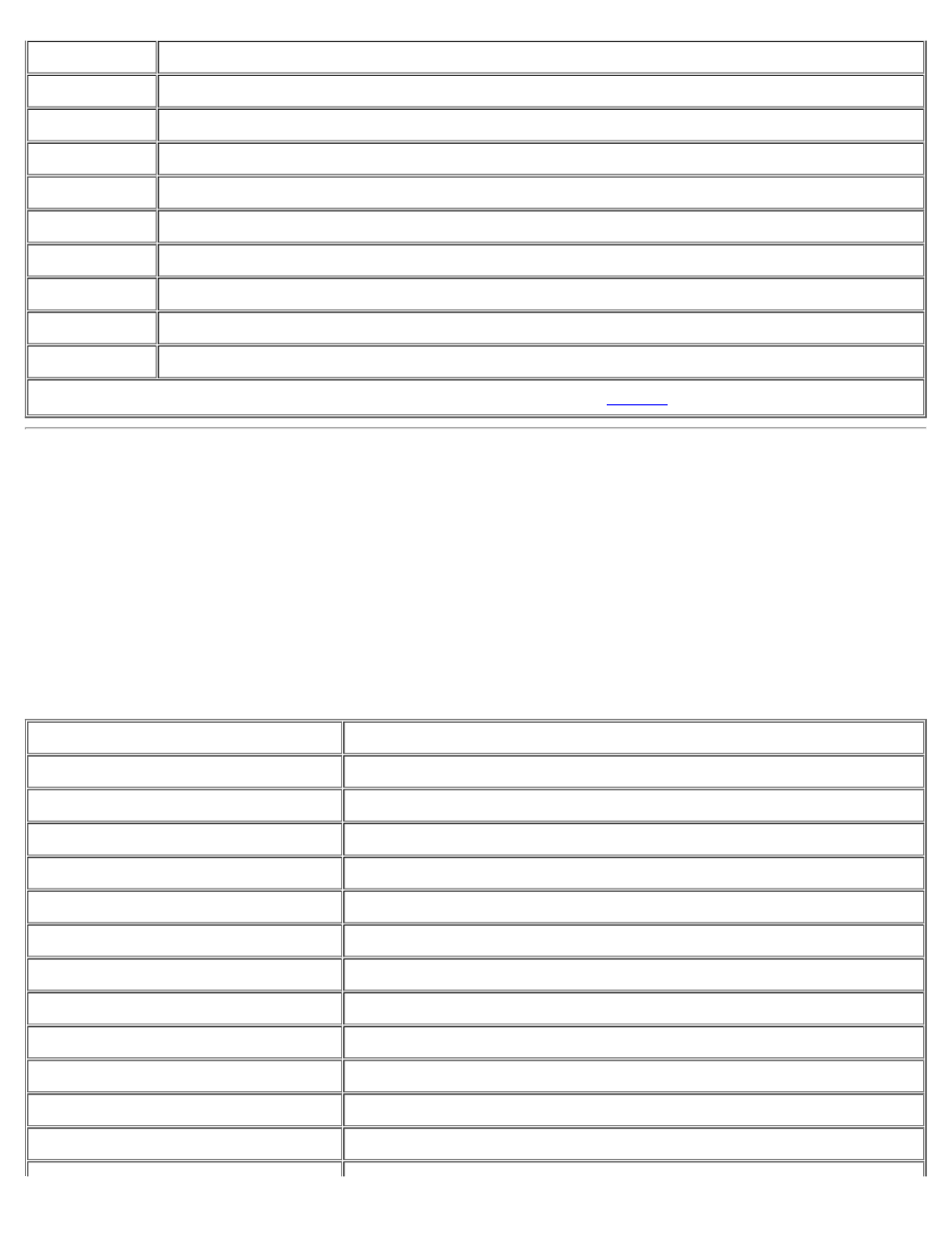
IRQ6
Diskette drive interface
IRQ7
Parallel port
IRQ8
RTC
IRQ9
Available if ACPI is set to Off in System Setup program
IRQ10
Available
IRQ11
Available
IRQ12
Mouse controller
IRQ13
Math coprocessor
IRQ14
Primary EIDE interface (if Enabled in System Setup program)
IRQ15
Secondary EIDE interface (if Enabled in System Setup program)
NOTE:
For the full name of an abbreviation or acronym used in this table, see the "
".
Memory Allocations
A processor and programs operating under MS-DOS (real-mode operation) can address only 1 megabyte (MB) (1024 kilobytes
[KB]) of system memory. This area is divided into conventional memory (sometimes called base memory) and upper memory. All
system memory above this 1 MB is called extended memory and cannot be directly addressed by MS-DOS-based programs
without the aid of some special memory-managing software.
Table B-10 provides a map of the conventional memory area. When the processor or a program addresses a location within the
conventional memory range, it is physically addressing a location in main memory, which is the only main memory it can address
under MS-DOS.
Table B-10. Conventional Memory Map
Address Range
Use
00000h-003FFh
Interrupt vector table
00400h-004FFh
BIOS data area
00500h-005FFh
MS-DOS and BASIC work area
00600h-0FFFFh
User memory
10000h-1FFFFh
User memory
20000h-2FFFFh
User memory
30000h-3FFFFh
User memory
40000h-4FFFFh
User memory
50000h-5FFFFh
User memory
60000h-6FFFFh
User memory
70000h-7FFFFh
User memory
80000h-8FFFFh
User memory
