Printer and paper storage environment, Paper specifications, Paper output capacity – Dell 1110 Laser Mono Printer User Manual
Page 37
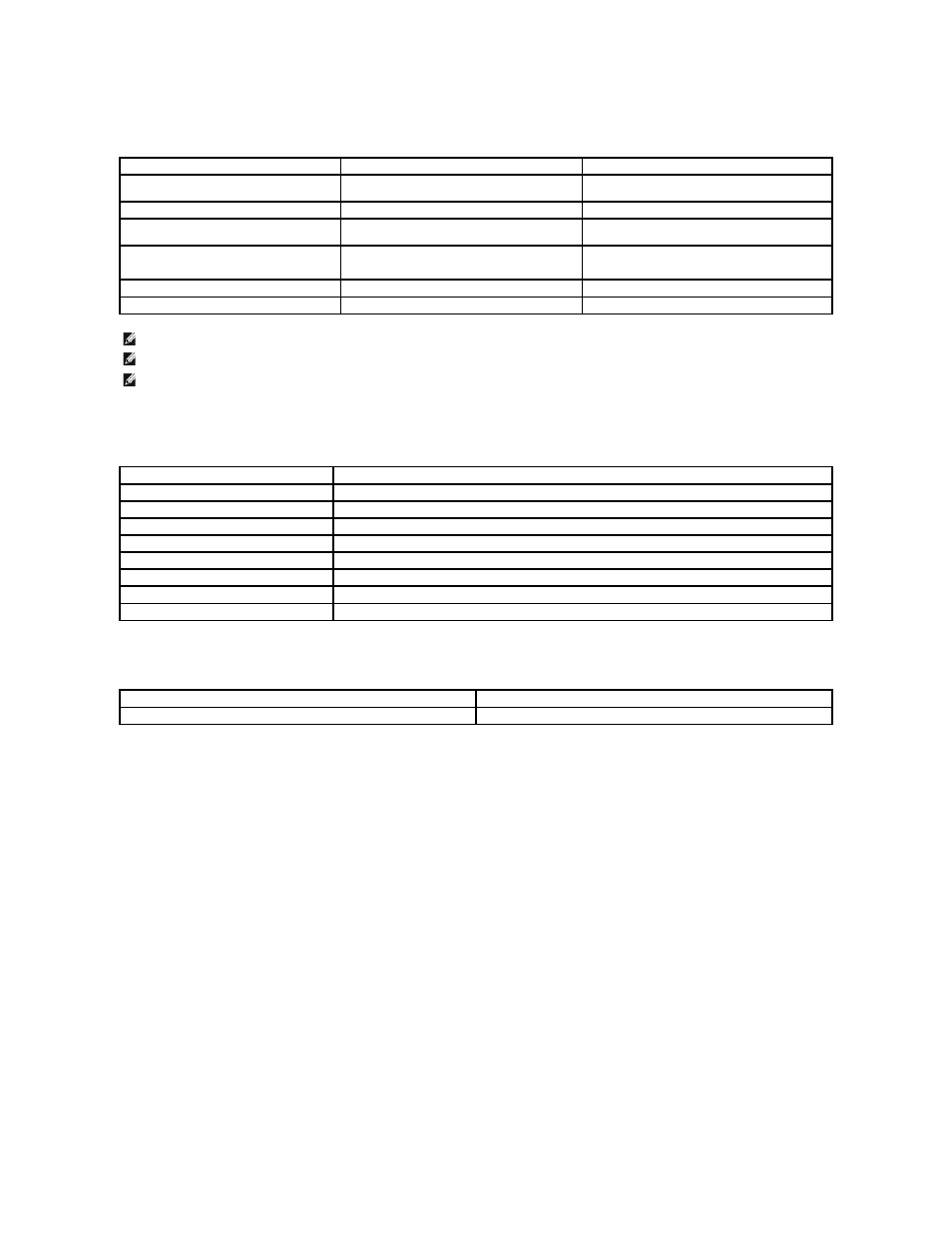
The following problems may cause print quality deviations, jamming, or even damage to the printer:
Paper Specifications
Paper Output Capacity
Printer and Paper Storage Environment
Paper storage conditions directly affect the feed operation.
Ideally, the printer and paper storage environment should be at or near room temperature, and not too dry or humid. Remember that paper is hygroscopic: it
absorbs and loses moisture rapidly.
Heat works with humidity to damage paper. Heat causes the moisture in paper to evaporate, while cold causes it to condense on the sheets. Heating
systems and air conditioners remove most of the humidity from a room. As paper is opened and used, it loses moisture, causing streaks and smudging. Humid
weather or water coolers can cause the humidity to increase in a room. As paper is opened and used it absorbs any excess moisture, causing light print and
dropouts. Also, as paper loses and gains moisture it can become distorted. This can cause paper jams.
Care should be taken not to purchase more paper than can be used in a short time (about 3 months). Paper stored for long periods may experience heat and
moisture extremes, which can cause damage. Planning is important to prevent damage to large supplies of paper.
Unopened paper in sealed reams can remain stable for several months before use. Opened packages of paper have more potential for environment damage,
especially if they are not wrapped with a moisture-proof barrier.
The paper storage environment should be properly maintained to ensure optimum performance. The required condition is 20°C to 24°C (68°F to 75°F), with a
relative humidity of 4 percent to 55 percent. The following guidelines should be considered when evaluating the paper's storage environment:
l
Paper should be stored at or near room temperature.
l
The air should not be too dry or too humid.
Symptom
Problem with Paper
Solution
Poor print quality or toner adhesion, problems
with feeding
Too moist, too rough, too smooth, or embossed;
faulty paper lot
Try another kind of paper, between 100-400
Sheffield, 4%~5% moisture content.
Dropout, jamming, curl
Stored improperly
Store paper flat in its moisture-proof wrapping.
Increased gray background shading/printer
wear
Too heavy
Use lighter paper; use the rear output slot.
Excessive curl problems with feeding
Too moist, wrong grain direction, or short-grain
construction
•
Use the rear output slot.
•
Use long-grain paper.
Jamming, damage to printer
Cutouts or perforations
Do not use paper with cutouts or perforations.
Problems with feeding
Ragged edges
Use good quality paper.
NOTE:
Do not use letterhead paper printed with low-temperature inks, such as those used in some types of thermography.
NOTE:
Do not use raised or embossed letterhead.
NOTE:
The printer uses heat and pressure to fuse toner to the paper. Insure that any colored paper or preprinted forms use inks that are compatible
with this fusing temperature (200°C or 392°F for 0.1 second).
Category
Specifications
Acid Content
5.5~8.0 pH
Caliper
0.094~0.18 mm (3.0~7.0 mils)
Curl in Ream
Flat within 0.02 in (5 mm)
Cut Edge Conditions
Cut with sharp blades with no visible fray.
Fusing Compatibility
Must not scorch, melt, offset, or release hazardous emissions when heated to 200°C (392°F) for 0.1 second.
Grain
Long Grain
Moisture Content
4%~6% by weight
Smoothness
100~250 Sheffield
Output Location
Capacity
Paper Output Tray (Face Down)
100 sheets of 75 g/m² bond (20 lb) paper
