Table 1, Intel architecture comparison – Dell PowerEdge R820 User Manual
Page 7
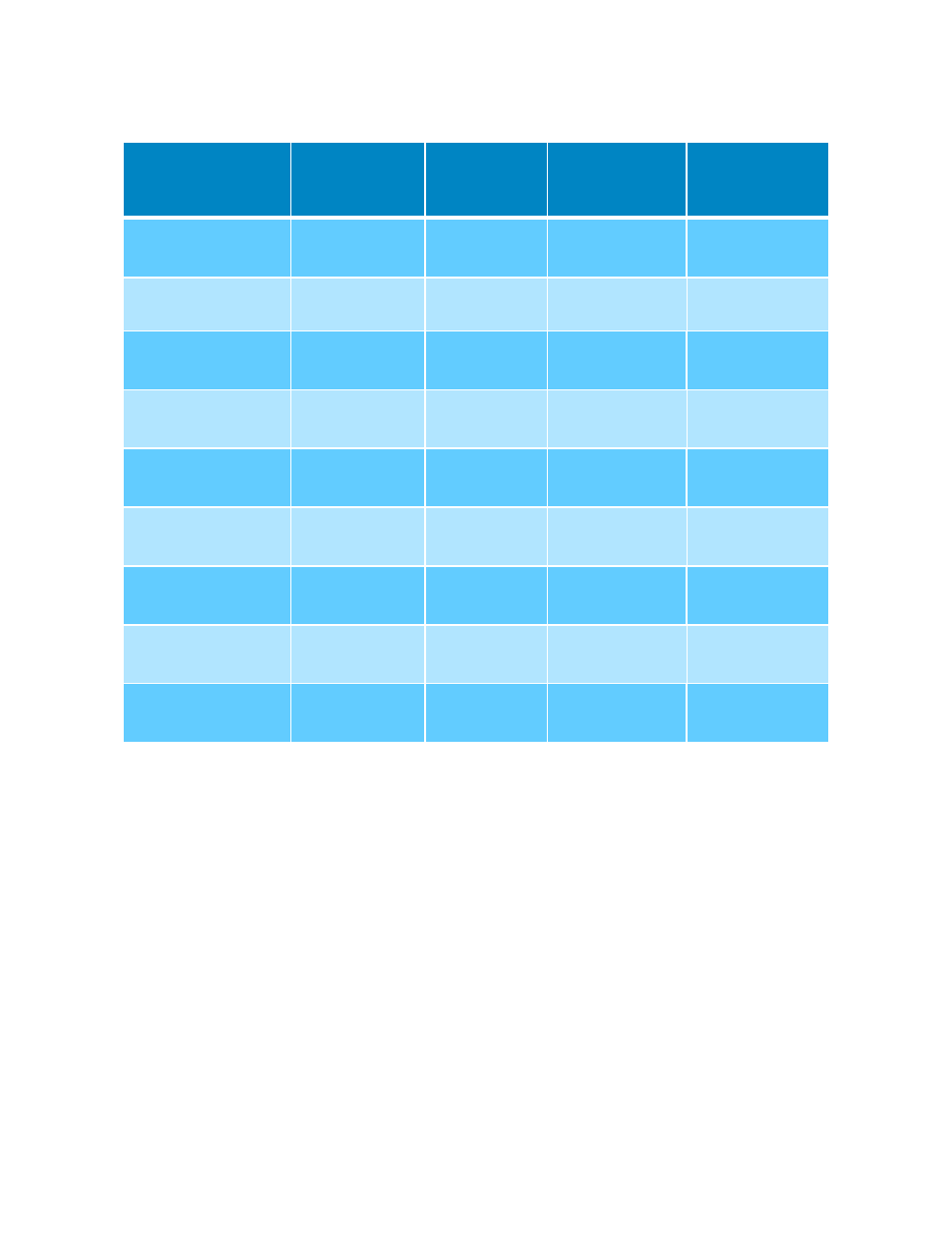
Performance Analysis of HPC Applications on Several Dell PowerEdge 12
th
Generation Servers
7
Intel architecture comparison
Table 1.
Intel Xeon
Processor 5600
Series
Intel Xeon
Processor E5-
2400 Product
Family
Intel Xeon
Processor E5-
2600 Product
Family
Intel Xeon
Processor E5-
4600 Product
Family
Architecture
Codename
Westmere–EP
Sandy Bridge-
EN
Sandy Bridge-EP
Sandy Bridge-EP
4S
Max Sockets / Cores
per socket
2/6
2/8
2/8
4/8
Memory channels
3 per socket
3 per socket
4 per socket
4 per socket
Max Memory speed
1333 MHz
1600 MHz
1600 MHz
1600 MHz
QPI links per CPU
2
1
2
2
Max QPI Speed
6.4 GT/s
8 GT/s
8 GT/s
8 GT/s
Max Processor TDP
130 W
95W
135W
130W
Max DIMMs Per
Channel (DPC)
3DPC
2 DPC
3 DPC
3 DPC
Dell PowerEdge
servers models
R610, R710,
M610
R420, R520,
M420
R620, R720,
M620
R820, M820
Figure 2 outlines the block diagram of the Sandy Bridge-EN platform architecture. Compared to the
Sandy Bridge-EP platform, the differences lie in the number of QPI links, the number of memory
channels and the number of DIMMs per channel. The EN based processors operate at a lower maximum
wattage compared to the EP based processors. InfiniBand FDR is not supported on the EN based
processers. In its place, InfiniBand FDR10 [2] is used. The EN processor is a balanced configuration in
terms of bandwidth. The processors can support a theoretical maximum of 32 GB/s through the QPI link
between the sockets and the theoretical maximum memory bandwidth from a socket to its memory is
38.4 GB/s.
