Figure 5, Hpl performance – Dell PowerEdge R820 User Manual
Page 14
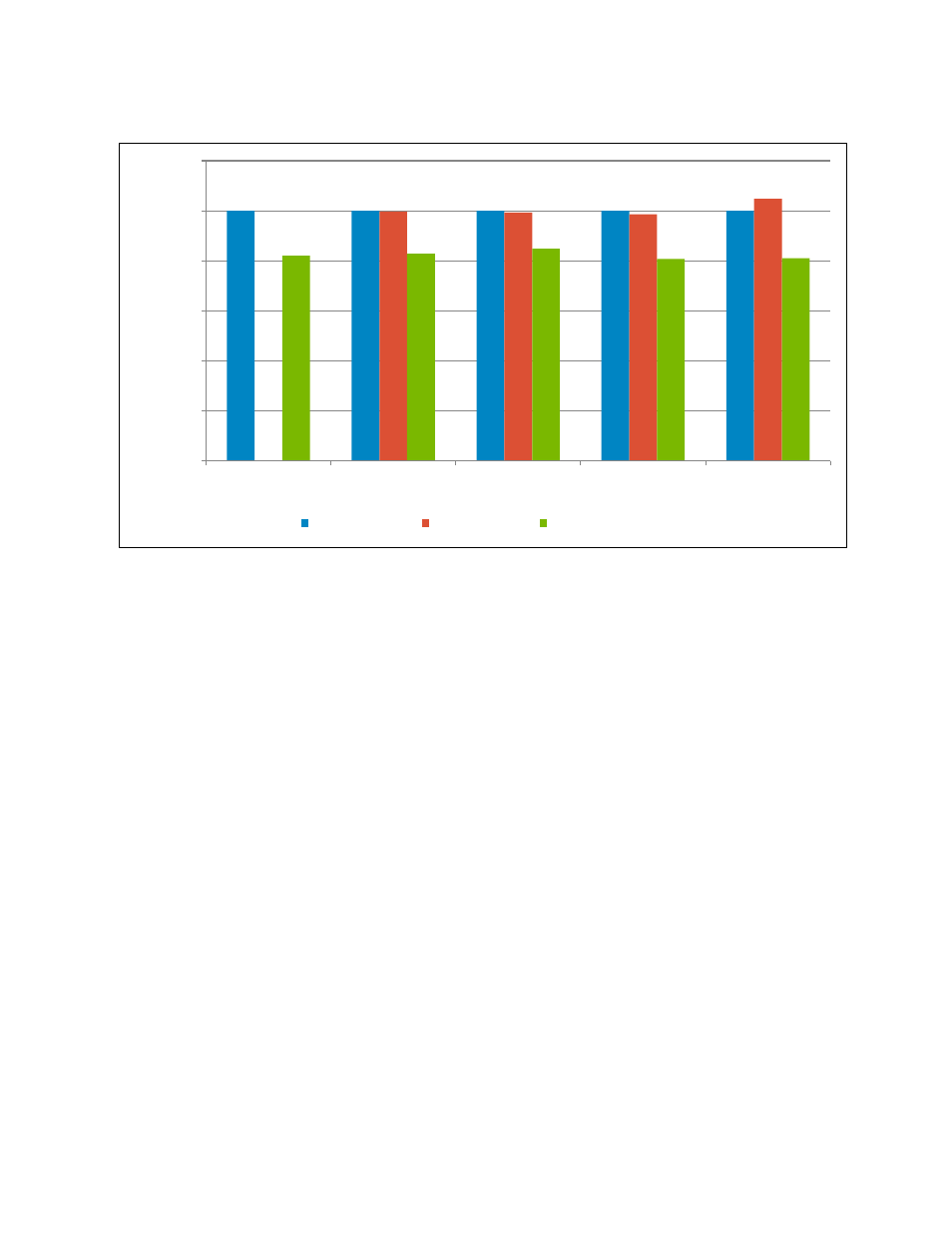
Performance Analysis of HPC Applications on Several Dell PowerEdge 12
th
Generation Servers
14
HPL performance
Figure 5.
4.3. LU
Figure 6 presents the performance of the LU benchmark from the NAS Parallel Benchmarks (NPB) suite
on the three clusters. When the servers are fully subscribed, the Dell PowerEdge M620 performs ~8
percent better than the PowerEdge R820 and ~6 to ~12 percent better when compared to the
PowerEdge M420. From a previous study analyzing the various memory configurations on Dell
PowerEdge 11
th
generation servers [8], a 16 percent drop in measured memory bandwidth led to a 2
percent drop in LU performance. This indicates that LU is not a memory intensive application. The
PowerEdge R820 has a single QPI link connecting the sockets whereas the PowerEdge M620 has two QPI
links. The extent of intra-node communication is higher on the PowerEdge R820 because of the higher
core count. Recall that there are no crosslinks between sockets zero and two on the PowerEdge R820
and thus the messages need to traverse two QPI links for any communication as described in Figure 3.
The difference in this QPI bandwidth can be associated with the lower performance on the PowerEdge
R820. However, the value of the PowerEdge R820 is that a fewer number of servers are needed to
achieve a certain performance or core count because this is a quad-socket system.
The performance drop on the PowerEdge M420 when compared to the PowerEdge M620 can be
attributed to the 15 percent lower clock speed, single QPI link, and lower memory configuration.
0.82
0.83
0.85
0.81
0.81
0.00
0.20
0.40
0.60
0.80
1.00
1.20
256
128
64
32
16
Per
fo
rmance
R
el
at
ive
to
Power
Ed
ge
M620
(H
ig
her
is
B
et
ter
)
Number of Cores
M620-2.7GHz
R820-2.7GHz
M420-2.3GHz
