Table 3, Application and benchmark details – Dell PowerEdge R820 User Manual
Page 11
Performance Analysis of HPC Applications on Several Dell PowerEdge 12
th
Generation Servers
11
The PowerEdge M620 and PowerEdge M420 are blade based servers. The PowerEdge M620 is a half-
height blade; the PowerEdge M1000e chassis can house up to 16 such blades. The PowerEdge M420 is a
denser, quarter-height blade and the same PowerEdge M1000e chassis can house up to 32 such blades.
A full chassis of servers was used in each case to allow meaningful power measurements and to
properly amortize the shared infrastructure cost of power supplies, fans, and so on. The other
differences in the size of the clusters are due to resource limitations; however the results sections
compares performance based on the number of cores to eliminate total cluster size as a factor.
The PowerEdge M420 supports only SSD drives. The operating system for the server was installed on this
drive. None of the applications were configured to write local files on each compute node; therefore,
the choice of SSD versus SAS is not relevant to the results in this study.
The BIOS on all the servers are set to Dell HPC defaults, which include the Performance per Watt
Optimized DAPC System Profile, Node Interleaving disabled and Logical Processor disabled. This System
Profile balances power saving and performance options by enabling Turbo Boost, C states and C1-E. The
Power Profile is set to DAPC (Dell Advanced Power Controller) and the Memory Frequency is set to max
performance.
StackIQ Rocks+ 6.0.1 Dell edition [5] was used to deploy and manage the cluster.
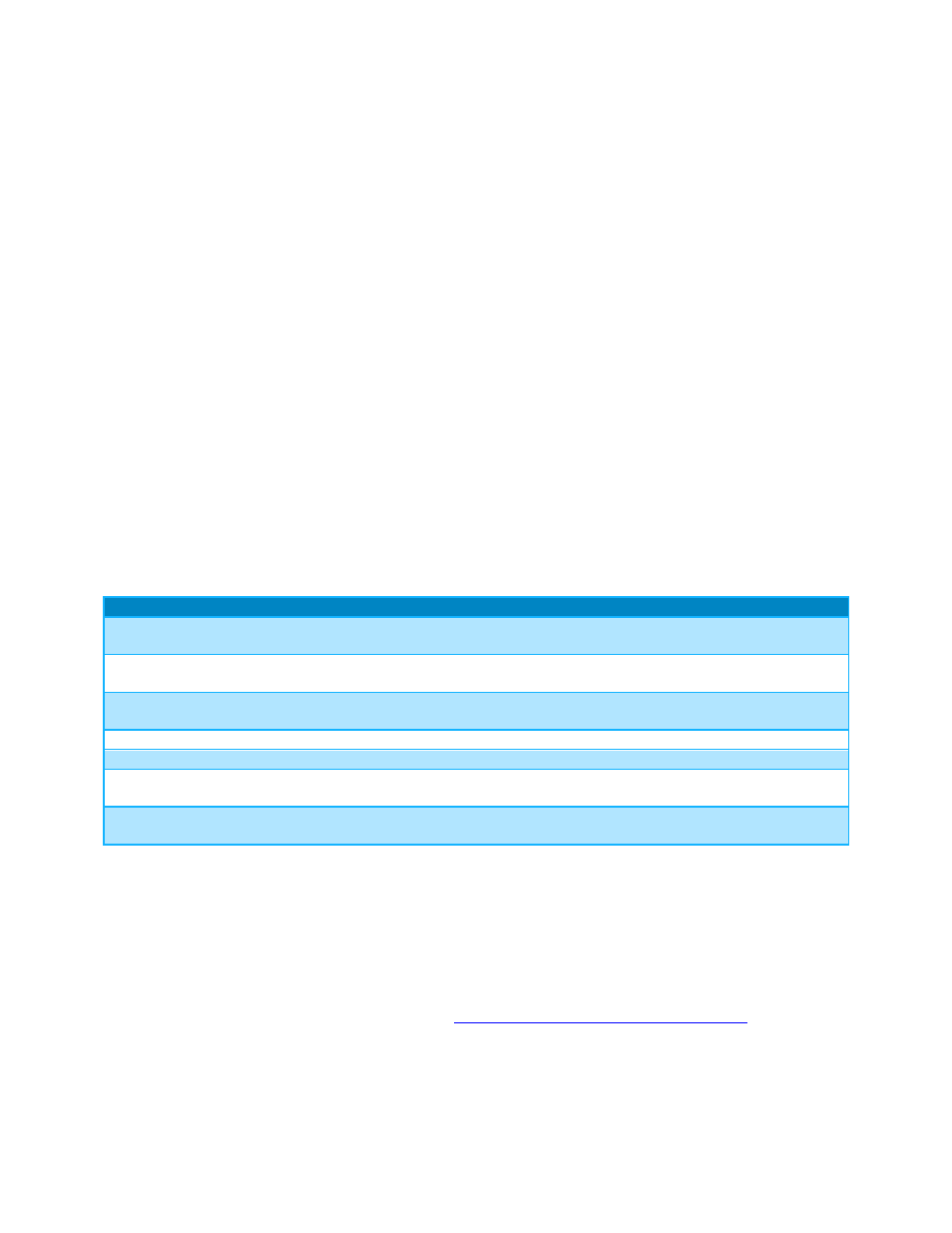
Table 3 illustrates the applications that were studied, the benchmarks used, and their characteristics.
The applications chosen are a mix of open source and commercial applications.
Application and benchmark details
Table 3.
Application
Domain
Version
Benchmark data set
High Performance
Linpack
Floating point CPU intensive
system benchmark
Intel MKL
v10.3.9.293
Problem size set to 90
percent of total memory.
Stream
Memory Bandwidth micro-
benchmark
v5.9
Array size 160000000
ANSYS Fluent
Computational Fluid Dynamics
application
v14.0.0
truck_poly_14m and
truck_111m
WRF
Weather modeling application
v3.1
Conus 12k
NAMD
Molecular Dynamics application
v2.9
STMV
MILC
Quantum Chromo-dynamics
application
v7.6.3
fnl-2009-intel.in
Based on Medium-NSFt3
LU
Lower-upper decomposition,
physical systems
NPB v3.3.1
Class D
For HPL, the performance metric used for comparison is GFLOPS and for WRF, the performance metric
used is the average time step. For NAMD, the performance metric used is days per nanosecond. For all
other applications the metric used is rating. Rating is defined as the number of times an application
can be executed in a single day. In addition to quantifying the performance on the above mentioned
server platforms, the power consumed is also measured by using a rack power distribution unit (PDU).
Because an apples to apples comparison is not possible with the test bed configuration, a cluster level
comparison of power consumption is provided in
Power Consumption and Energy Efficiency
A previous study [1] characterized the performance and energy impact of different BIOS tuning options
on the PowerEdge M620 servers. The PowerEdge M620 cluster test bed and applications used in that
