Working with raid, Raid level 0, Raid level 1 – Dell Alienware M17x (Mid 2009) User Manual
Page 26
026
026
/
CHAPTER 4: USING YOUR NOTEBOOK
Working With RAID
A redundant array of independent disks (RAID) is a disk storage configuration
that increases performance or data redundancy. There are two basic RAID levels
discussed in this section.
RAID level 0 is recommended for higher performance (faster throughput).
•
RAID level 1 is recommended for users who need a high level of data integrity.
•
NOTE: RAID requires multiple hard drives. The number of hard drives
required varies depending on the RAID configuration.
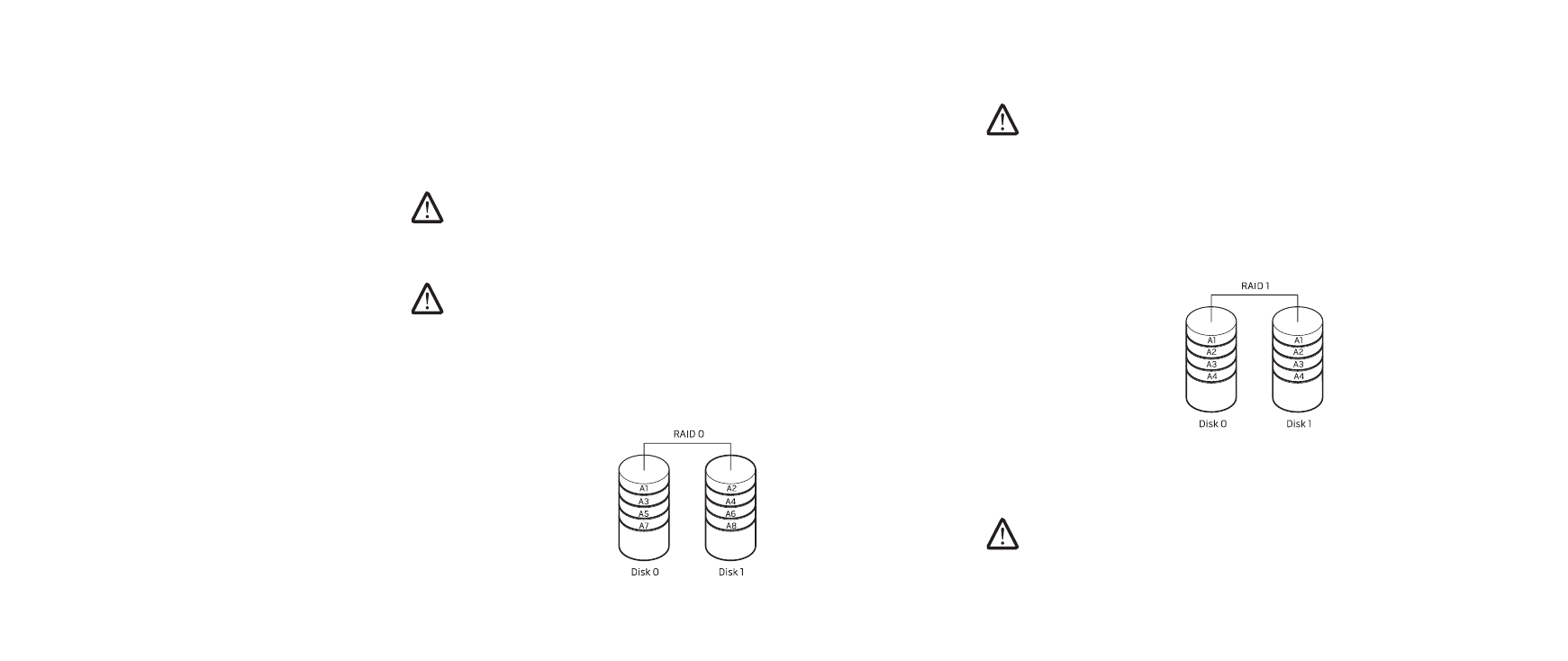
RAID Level 0
CAUTION: RAID level 0 provides no redundancy. Therefore, a failure of one
drive results in the loss of all data. Perform regular backups to protect
your data.
RAID level 0 uses data striping to provide a high data access rate. Data striping
writes consecutive segments, or stripes, of data sequentially across the physical
drive(s) to create a large virtual drive. This allows one of the drives to read data
while the other drive is searching for and reading the next block.
RAID 0 uses the full storage capacities of both drives. For example, two 2 GB hard
drives combine to provide 4 GB of hard drive space on which to store data.
NOTE: In a RAID 0 configuration, the size of the configuration is equal to the
size of the smallest drive multiplied by the number of drives in the
configuration.
RAID Level 1
RAID level 1 uses data mirroring to enhance data integrity. When data is written to
the primary drive, the data is also duplicated, or mirrored, on the secondary drive in
the configuration. RAID 1 sacrifices high data-access rates for data redundancy.
If a drive failure occurs, read and write operations are directed to the remaining
drive. A replacement drive can then be rebuilt using the data from the remaining
drive.
NOTE: In a RAID 1 configuration, the size of the configuration is equal to the
size of the smallest drive in the configuration.
