Carrier 012 User Manual
Page 11
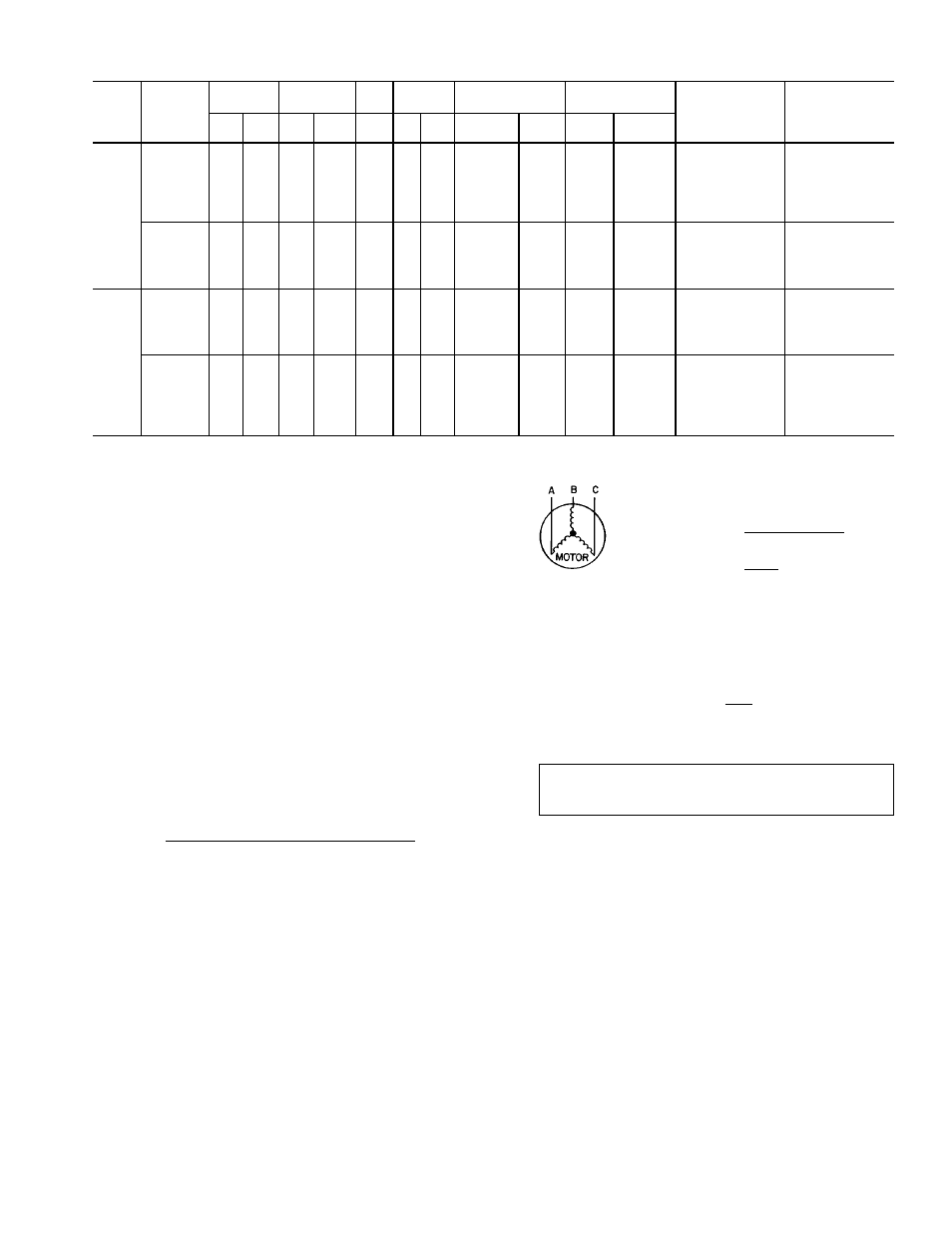
Table 2 — Electrical Data
UNIT
50LJQ
NOMINAL
V-PH-HZ
VOLTAGE
RANGE
COMPR
(each)
OFM
IFM
ELECTRIC HEAT POWER SUPPLY ELECTRIC HEAT
POWER WIRING
FIG. NO.
ELECTRIC HEAT
PART NO.
50DJ901—
Min
Max RLA
LRA
FLA
Hp FLA
Nominal
kW*
FLA
MCA
MOCP†
008
220-3-50
198
242
15.3
82.0
1.5
1.5
5.8
—
—
41.7
50
—
—
9.5
24.7
70.3
80
10
711
14.6
38.0
85.7
90
10
601
22.7
59.0
130.0
150
11
611
29.3
76.2
158.5
175
11
621
38.8
100.9
179.5
200
12
711, 621**
400-3-50
360
440
7.7
41.0
1.5
1.5
2.6
10.5
15.2
21.4
25
7
681
12.5
18.0
44.0
45
7
631
21.0
30.3
59.3
60
8
641
25.0
36.1
66.5
70
8
651
31.5
45.5
78.3
80
9
681, 641**
012
220-3-50
198
242
19.6 105.0
1.5
2.0
7.5
—
—
53.1
60
—
—
9.5
24.7
81.6
90
10
711
14.6
38.0
97.1
100
10
601
29.3
76.2
141.3
150
11
621
43.9
114.1
190.9
200
13
601, 621**
400-3-50
360
440
10.4
55.0
1.5
2.0
3.5
10.5
15.2
28.4
35
7
681
12.5
18.0
51.0
60
7
631
21.0
30.3
66.3
70
8
641
25.0
36.1
73.5
80
8
651
31.5
45.5
85.2
90
9
681, 641**
37.5
54.2
96.6
100
9
631, 651**
LEGEND
COMPR — Compressor
FLA
— Full Load Amps
HACR
— Heating, Air Conditioning and Refrigeration
IFM
— Indoor-Fan Motor
LRA
— Locked Rotor Amps
MCA
— Minimum Circuit Amps
MOCP
— Maximum Overcurrent Protection
OFM
— Outdoor-Fan Motor
RLA
— Rated Load Amps
*Heaters are field-installed only. Heater capacity (kW) is based on
heater voltage of 230 v or 400 v. If power distribution voltage to unit
varies
from
rated
heater
voltage,
heater
kW
will
vary
accordingly.
†Fuse or HACR circuit breaker.
**Requires 2 heater packages.
NOTES:
1. MCA and MOCP values are calculated in accordance with NEC
(National Electric Code) (U.S.A. Standard), Article 440.
2. Motor RLA and FLA values are established in accordance with UL
(Underwriters’ Laboratories) Standard 465 (U.S.A. Standard).
3. Unbalanced 3-Phase Supply Voltage
Never operate a motor where a phase imbalance in supply volt-
age is greater than 2%. Use the following formula to determine
the % voltage imbalance.
% Voltage Imbalance
max voltage deviation from average voltage
= 100 x
average voltage
Example: Supply voltage is 400-3-50.
AB = 393 v
BC = 403 v
AC = 396 v
393 + 403 + 396
Average Voltage =
3
1192
=
= 397
3
Determine maximum deviation from average voltage.
(AB) 397 − 393 = 4 v
(BC) 403 − 397 = 6 v
(AC) 397 − 396 = 1 v
Maximum deviation is 6 v.
Determine % voltage imbalance.
6
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x
= 1.5%
397
This amount of phase imbalance is satisfactory as it is below the
maximum allowable 2%.
IMPORTANT: If the supply voltage phase imbalance is
more than 2%, contact your local electric utility company
immediately.
11
