Bird Technologies 5012 User Manual
Page 6
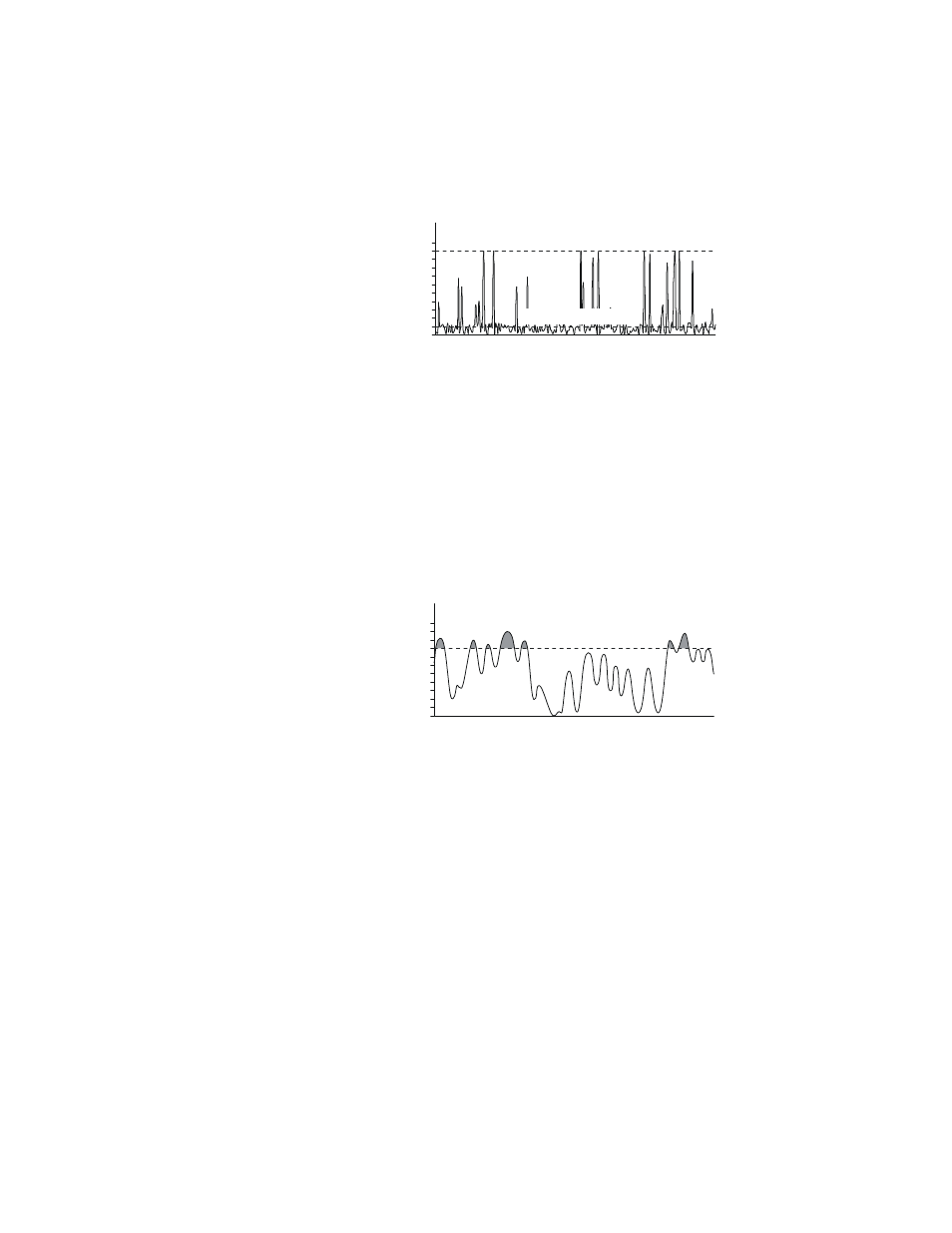
Crest Factor
Crest factor (CF) is the ratio of the peak and average powers, in dB.
The WPS calculates the Crest Factor from the Forward Peak and
Average Power measurements.
Crest factor is becoming one of the most important measurements as
communication systems move into the digital age. For CDMA and
similar modulation types the CF may reach 10 dB. If the crest factor is
too large, the transmitter will not be able to handle the peak powers
and amplitude distortion will occur. Crest factor can also detect
overdrive and overshoot problems. Knowing the CF allows end-users
to more accurately set base station power and lower operating costs.
Complementary Cumulative Distribution Function (CCDF)
CCDF measures the amount of time the power is above a threshold.
Equivalently, it is the probability that any single measurement will be
above the threshold. The WPS samples the power over a 300 ms
window and compares it to a user-specified threshold, in Watts. The
time above the threshold relative to the total time is the CCDF.
CCDF measurements are most useful for pseudo-random signals, such
as WCDMA, where a high CCDF means that the transmitter is being
overdriven. CCDF can also detect amplitude distortion within an
envelope caused by unwanted modulating signals. In TDMA systems,
CCDF indicates the health of power amplifier stages and their ability
to sustain rated power over an appropriate timeframe. As a trouble-
shooting aid, CCDF allows tracking of trends such as amplifier
overdrive (which can cause dropped calls and high bit error rates).
Figure 4
Crest Factor
10 dB CDMA Signal
100 W Peak
10 W Ave
Figure 5
CCDF
100 W Signal
80 W Threshold
20% CCDF
Average Power
Peak Envelope Power
0 W
100 W
50 W
80 W
0 W
50 W
100 W
