Zeroing sensor, Function descriptions – Bird Technologies 5012 User Manual
Page 3
Zeroing Sensor
Over time, the sensor’s “zero value” (reading with no applied RF
power) can drift, making all readings inaccurate by this value. For
example, if the zero value is –0.02 W, measuring a 50 W signal will
give a reading of 49.98 W, a 0.04% error. Measuring a 1 W signal will
give a reading of 0.98 W, a 2% error. If the drift would be a significant
error, rezero the sensor:
y
Make sure the sensor has reached a stable operating temperature.
y
Make sure no RF power is applied to the sensor.
y
Press “Zero”. Calibration will begin.
y
Calibration will take about 30 seconds. Do not interrupt the
calibration! A bar on the screen will display calibration progress.
y
After successful calibration, “Cal Pass” or “Calibration Complete”
will be displayed. Press any key to return to normal operation.
y
If calibration fails, “Cal Fail” will be displayed. Press a key to
return to normal operation, then check that the WPS is properly
connected, and that the RF is off. Rezero.
Function Descriptions
Average Power
Average power is a measure of the equivalent “heating” power of a
signal, as measured with a calorimeter. It measures the total RF
power in the system, and does not depend on number of carriers or
modulation scheme. The WPS is a broadband sensor that measures
power across its entire frequency range. Its diodes operate in their
‘square law’ region so that the detector output is directly proportional
to the average power, without any additional error correction.
Average power is the most important measurement of any
transmission system since the average power is normally specified on
the operating license. It is also valuable as a maintenance tool,
showing overall system health, and for calibration.
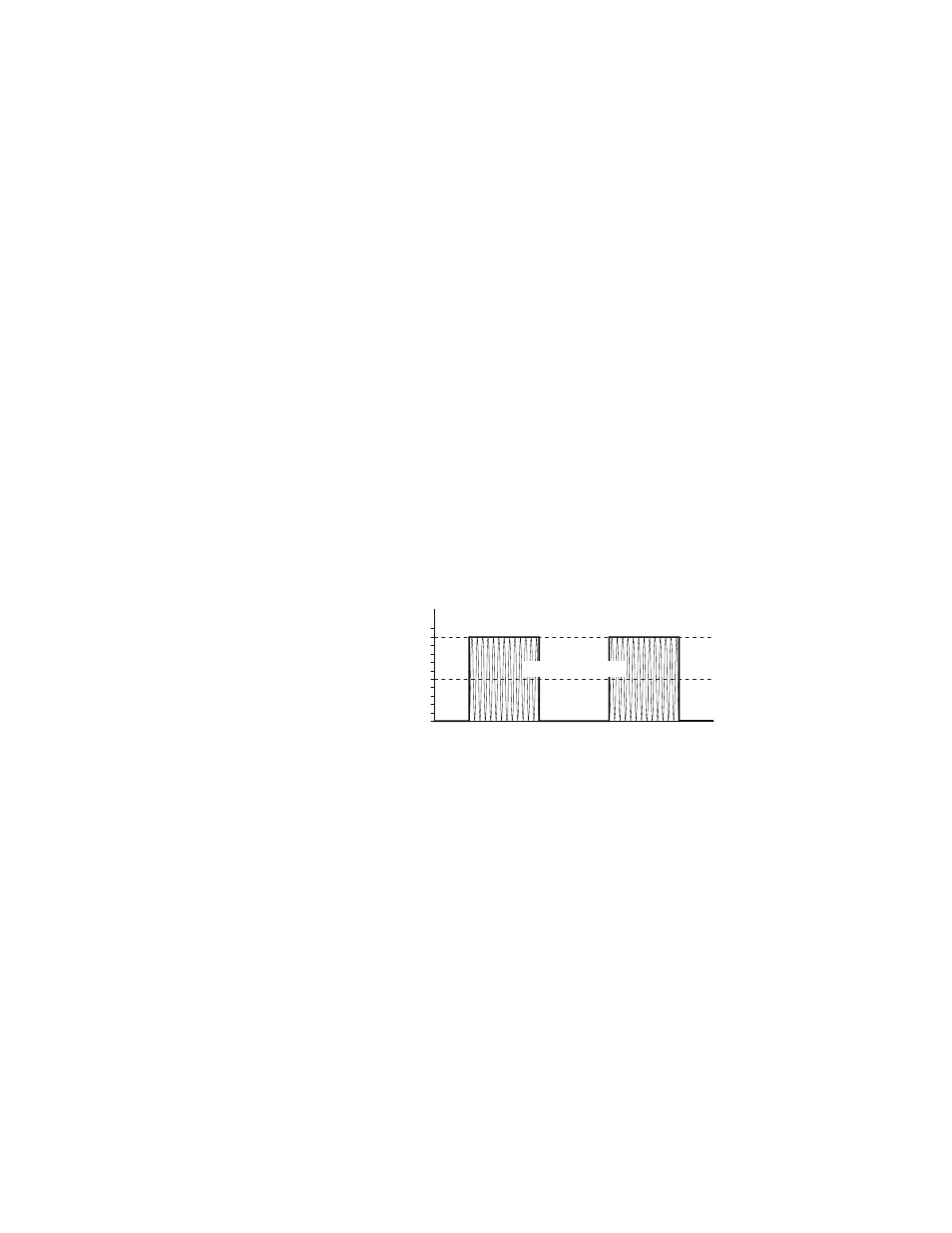
Figure 1
Average and Peak
Envelope Power
Square Wave Signal
Average Power
Peak Envelope Power
0 W
50 W
100 W
