Thermal Transfer Systems M6-MW User Manual
Page 4
EPM00058EN 0407
How to contact Alfa Laval
Contact details for all countries
are continually updated on our website.
Please visit www.alfalaval.com to
access the information directly.
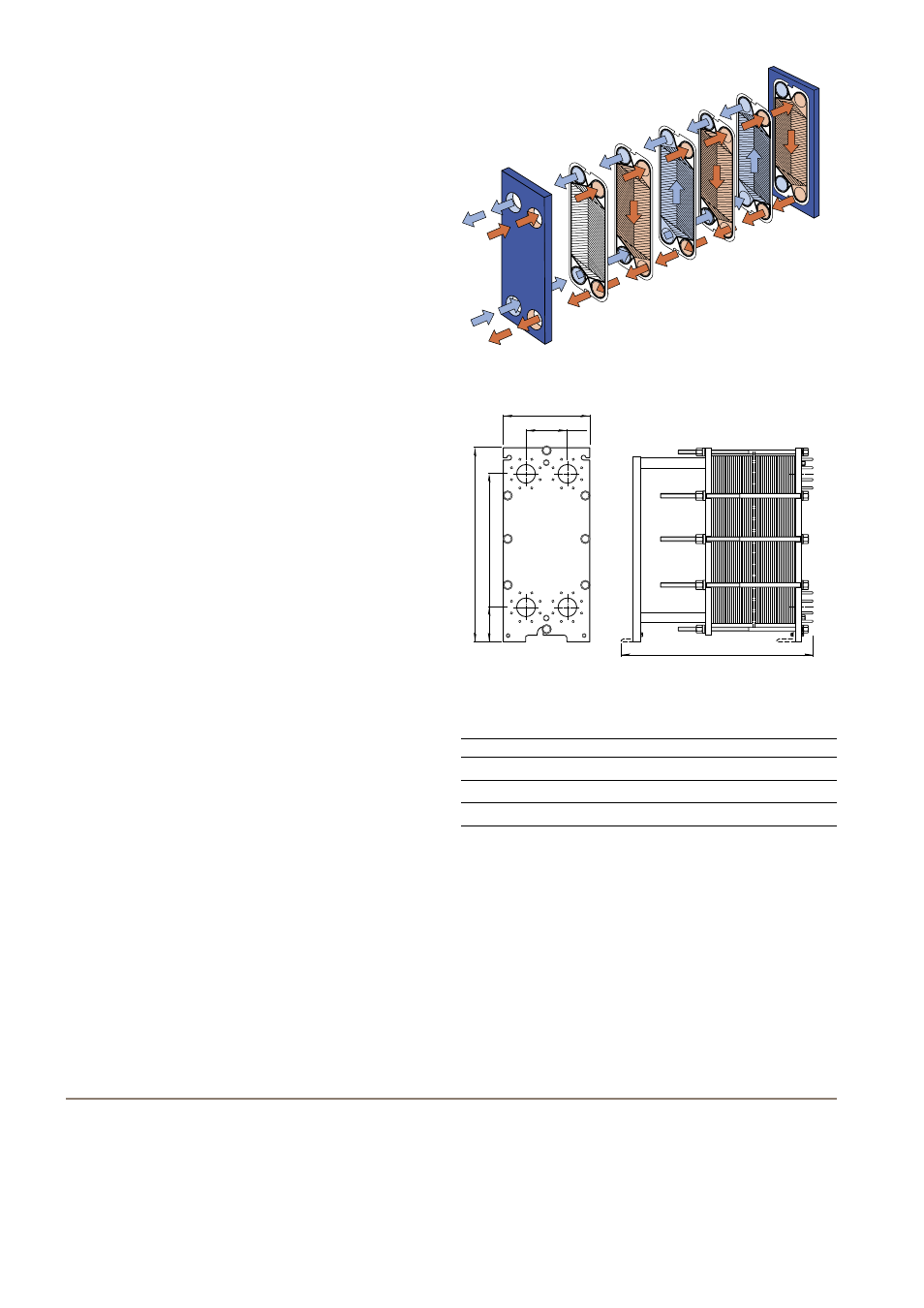
Working principle
Channels are formed between the plates and the corner ports
are arranged so that the two media flow through alternate
channels. The heat is transferred through the plate between
the channels, and complete counter-current flow is created
for highest possible efficiency. The corrugation of the plates
provides the passage between the plates, supports each
plate against the adjacent one and enhances the turbulence,
resulting in efficient heat transfer.
Standard materials
Frame plate
Mild steel, Epoxy painted
Nozzles
Carbon steel
Metal lined; Stainless steel, Titanium
Plates
Stainless steel AISI 316 or Titanium
Gaskets
Field gaskets
Nitrile, EPDM
Ring gaskets
Chloroprene, EPDM
Connections
FG PED
Size 100 mm DIN PN16
FG ASME Size 4"
ANSI 150
FD PED
Size 100 mm DIN PN25
FD ASME Size 4"
ANSI 300
REF PED
Size 100 mm Pipe
Technical data
Mechanical design pressure (g) / temperature
FG PED
1.6 MPa / 180°C
FG ASME 150 psig / 350°F
FD PED
2.5 MPa / -50 to 180°C
FD ASME 300 psig / -40 to 350°F
REF PED
2.5 MPa / -50 to 150°C
Maximum heat transfer surface
75 m² (825 sq. ft)
Flow principle of a plate heat exchanger
All rights reserved for changes in specifications
�����������
�
���
�
����������
�
Dimensions
Measurements (mm)
Type
H
W
h
M10-FG
1084
470 215
M10-FD
981
470 131
M10-FD ASME
1084
470 215
M10-BW REF
1110
470 163
The number of tightening bolts may vary depending on pressure rating.
Particulars required for quotation
– Flow rates or heat load
– Temperature program
– Physical properties of liquids in question (if not water)
– Desired working pressure
– Maximum permitted pressure drop
– Available steam pressure
THERMAL TRANSFER SYSTEMS, INC.
[email protected]
PH: 800-527-0131 FAX: 972-242-7568
