General information, Why vibrate concrete, Consolidation – Multiquip 900HD~2600HD User Manual
Page 11: Vibration time, Vibration range
FLeXSHaFTS/VIBRaTOR HeaDS • OpeRaTIOn anD paRTS manuaL — ReV. #0 (07/16/10) — page 11
general infOrMatiOn
Multiquip's flex-shafts vibrator heads are designed to work
in medimum to high slump concrete. Typical applications
include small pours, slabs driveways, stem walls and
footings.
Typical shaft lengths range from 2 to 21 feet (0.6 to 6.4
meters). See Tables 1, 2 and 3 for the various recommended
shaft lengths.
Vibrating steel heads are attached to one end of the flex-
shaft. These heads generate a vibration via an eccentric
rotator that consoldates the concrete by removing air
pockets. The round head design allows for the transmisssion
of vibration in all directions.
There are 7 different steel head sizes that range from
7
/
8
to 2
5
/
8
inches in diameter. Typical vibration frequency for
these vibrating heads range from 9,200 to 12,150 VPM
with 1-inch slump when using electric motors.
When working with epoxy coated rebar, 4 different types of
rubber heads are available to prevent chipping of the rebar
coating. These rubber heads range in diameter from 1
7
/
8
~2
3
/
4
inches (48~69 mm).
WHy VIBRaTe COnCReTe
To ensure optimum strength and durability, vibration of
fresh concrete is an important requirement. Vibration or
compaction is the principal method for consolidation of
concrete.
COnSOLIDaTIOn
Consolidation elimates pockets of aggregate and air
bubbles maximizing strength, eliminating surface voids.
Vibrators consolidate concrete by transmitting shock waves
which allow the aggregate to float freely while pushing
lighter trapped air up and out of the concrete mix.
A properly consoldated concrete pour will display a thin line
of mortar appearing along the form near the vibrator and the
coarse aggregate has been dispersed evenly throughout
the pour and is not visible.
VIBRaTIOn TIme
Vibration time depends on frequency. The higher the
frequency, the less vibration time is required for the job.
VIBRaTIOn Range
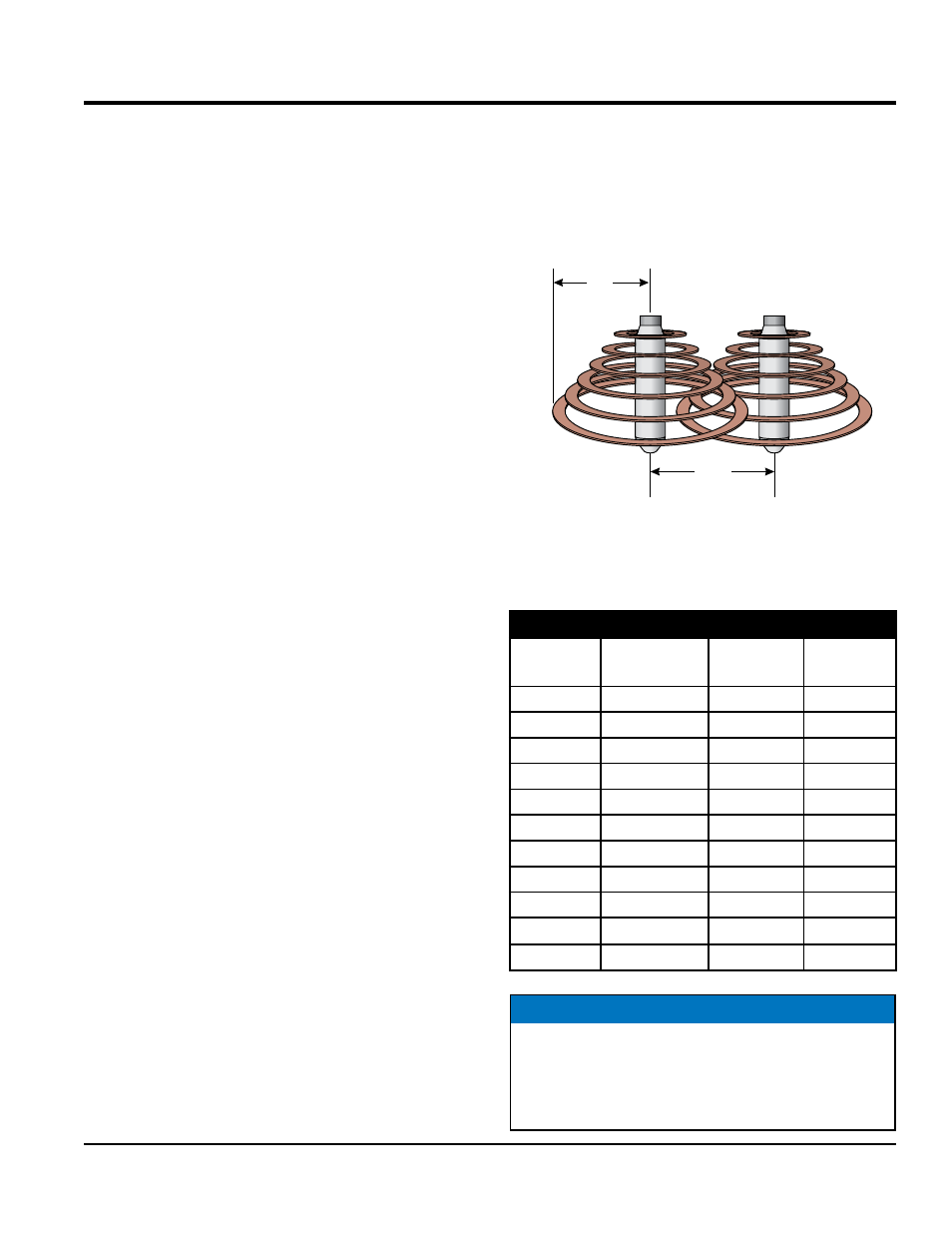
Vibration range (Figure 1) can be defined as "Area of
Influence". This area of influence (vibrating radius) is the
distance from the center of the vibrator to the outer most
edge.
Figure 1. Vibrator Radius/Spacing
Table 5 shows the vibration radius and spacing for a given
vibrator head diameter.
R
AREA OF INFLUENCE
(VIBRATING RADIUS)
VIBRATOR HEAD
INSERTION SPACING
D
Table 5. Vibrating Radius/Insertion Spacing
Vibrating
HD. model
Vibrator HD.
Dia. in. (mm)#
Vibration
Radius (R)
Vibrator
Spacing (D)
900HD
7
/
8
(22)
4 (102)
6 (152)
1000HD
1
1
/
16
(27)
5.5 (140)
8.25 (210)
1300HD
1
3
/
8
(35)
8 (203)
12 (305)
1400HD
1
3
/
8
(35)
8 (203)
12 (305)
1700HD
1
11
/
16
(43)
12 (305)
18 (457)
2100HD
2
1
/
8
(54)
14 (356)
21 (533)
2600HD
2
5
/
8
(67)
18 (457)
27 (686)
RVH188
1
7
/
8
(48)
11 (279)
16.5 (419)
RVH250
2
1
/
2
(63)
14 (356)
21 (533)
RVH275S
2
3
/
4
(69)
18 (457)
27 (686)
RVH275
2
3
/
4
(69)
15 (381)
22.5 (572)
NOTICE
Radius (area of influence
R) and vibrator head spacing
(
D) are expressed in inches/millimeters. Radius and
distance values expressed in Table 5 are only to be
used as a general guide. Values are subject to change.
