Materials used in klein harnesses – Klein Tools Harnesses User Manual
Page 8
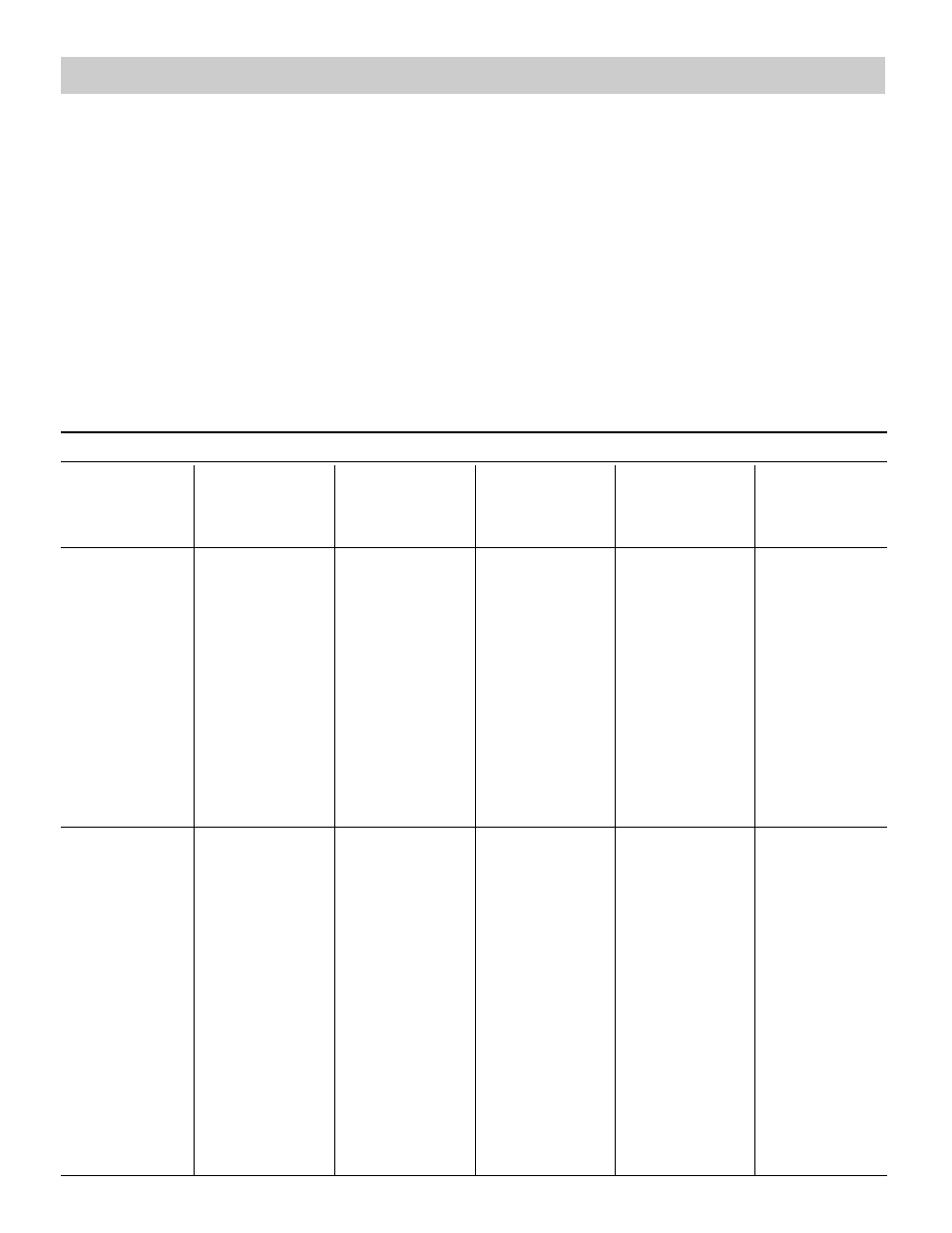
Type of
Material
Nylon
Exposure to
Excessive Heat
Poor resistance.
Becomes brittle,
has a shriveled
brown appear-
ance. Fibers will
break when
flexed.Weakens
at 300°F
(149°C).
Exposure to
Chemicals
Generally good
resistance,
except around
strong acids and
phenolic com-
pounds, which
cause it to
become brittle.
Exposure to
Molten Metal
or Flame
Poor resistance.
Strands fuse
together and
form hard shiny
spots. Has hard
and brittle feel.
Will not support
combustion.
Exposure to
Paints
or Solvents
Generally offers
good resistance.
However, paint
can penetrate
into the weave
and dry. This can
cause webbing to
become hard
and brittle and
can eventually
break the fibers.
Some solvents
may affect fibers
(see “Exposure
to Chemicals”).
Exposure
Near Live
Electrical Lines
& Equipment
Poor protection
(no dielectric
strength).
Provides no
protection against
exposure to live
electrical lines
or equipment.
Polyester
Poor resistance.
Fibers become
brittle and will
shrivel and turn
brown in color
and break when
flexed. Should
not be used
above 180°F
(82°C).
Good resistance
to most chemi-
cals, including
hydrochloric acid,
aqueous alkalies,
and many sol-
vents. Exposure
to incompatible
chemicals may
cause fibers to
change color and
texture, similar
to a brownish
smudge or smear.
Also will become
less elastic, with
transverse cracks
resulting from
bending.
Poor resistance.
Fiber strands
fuse together
and become
hard, brittle,
and shiny.
Generally offers
good resistance.
However, paint
can penetrate
into the weave
and dry. This can
cause webbing to
become hard
and brittle and
can eventually
break the fibers.
Some solvents
may affect fibers
(see “Exposure
to Chemicals”).
Poor protection
(no dielectric
strength).
Provides no
protection against
exposure to live
electrical lines
or equipment.
Nylon Webblng. Klein uses high-quality, commer-
cial-grade nylon. The web is impregnated with latex or
resin for extra durability.
Polyester Webbing. Used in certain Klein light-
weight harnesses. Polyester resists a wider variety of
chemicals than nylon does.
Softee™ Pads. These pads, which are stitched onto
many Klein belt components, are made of soft, non-
abrasive nylon with rounded edges for comfort.
Ultra-Hyde™. This highly durable, leather-like material
with high density and a “tight” surface is used primarily
for belt linings and pads. It is well suited for severe-
service environments. Klein does not use Ultra-Hyde
as the load-bearing material in OPE harnesses.
Drop-Forged Steel. Klein D-rings and snap hooks
are manufactured from drop-forged steel with a
corrosion-resistant finish and are tested to meet or
exceed applicable OSHA regulations.
Buckles. Klein Harnesses have single-tongue buckles,
friction-style buckles and/or easy-connect buckles. All
buckles are made of steel that is tested to meet or
exceed applicable OSHA regulations. Adjustments to
single-tongue buckles are made through holes that are
reinforced with solid brass grommets. Friction-style
buckles provide a continuous range of adjustment.
Easy-connect buckles also have friction slide adjusters
which hold straps in place, so the user does not
need to readjust for each use.
Physical Properties
Materials Used in Klein Harnesses
8
