Security – GeoDesy GD-3000 Series User Manual
Page 27
27
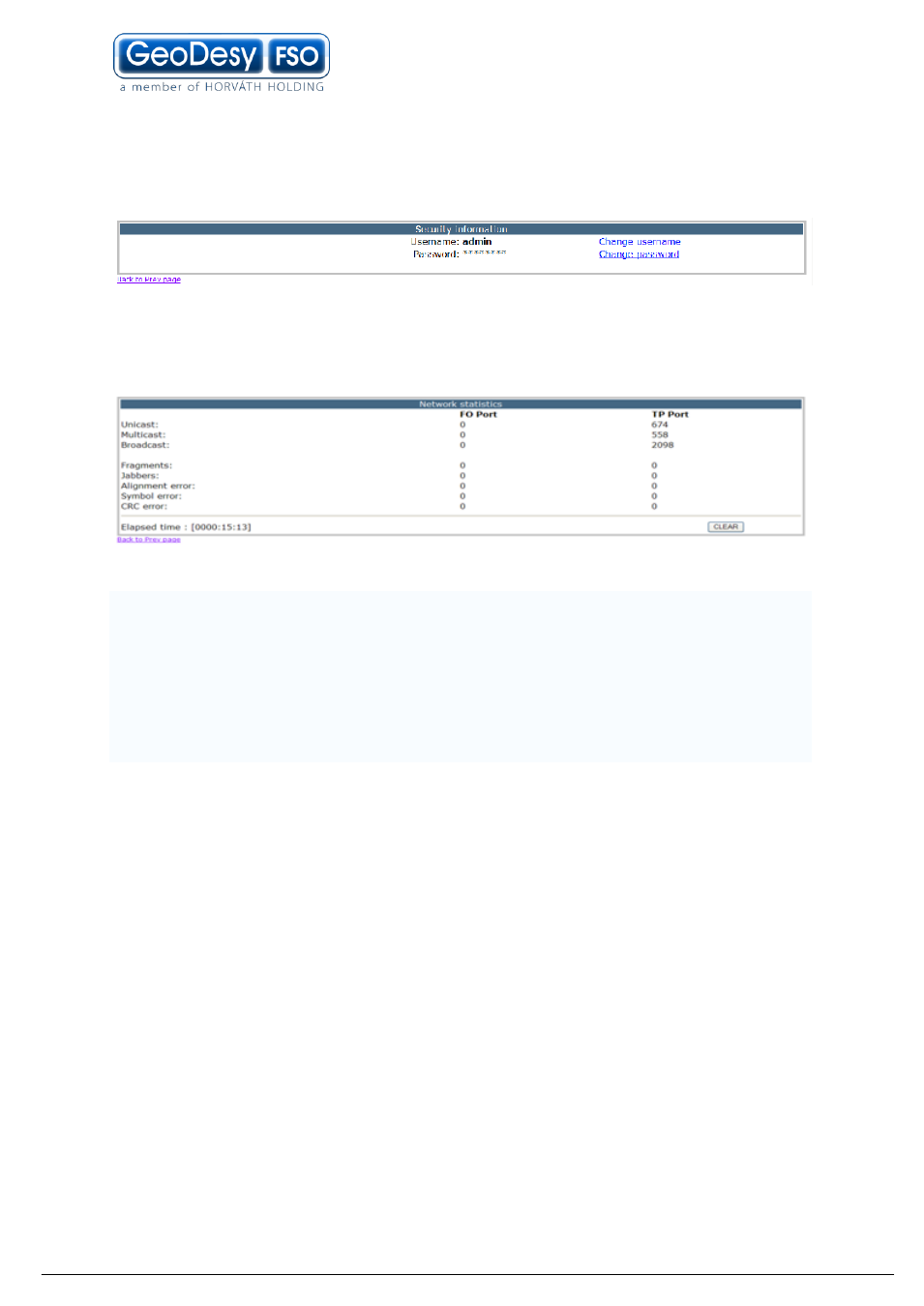
Security
On the security section you can set the username and the password for the unit. If
you have forget the usernam and/or the password please contact The technical
support.
Network statistics page
As a new feature of the Next series of products, you can monitor the live traffic flows
over the link. These figures are showing the reception on a port of FO(fibre optic
from the remote end) or TP(Twisted pair, form the local connected equipment).
Unicast: sending of information packets to a single destination
Multicast: is the delivery of information to a group of destinations simultaneously
using the most efficient strategy to deliver the messages over each link of the
network only once and only create copies when the links to the destinations split.
The word "Multicast" is typically used to refer to IP Multicast, the implementation of
the multicast concept on the IP routing level, where routers create optimal spanning
tree distribution paths for datagram sent to a multicast destination address in real-
time. But there are also other implementations of the multicast distribution strategy
listed below.
Broadcast: refers to transmitting a packet that will be received (conceptionally) by
every device on the network. In practice, the scope of the broadcast is limited to a
broadcast domain. Not all computer networks support broadcasting; for example,
neither X.25 nor frame relay supply a broadcast capability, nor is there any form of
Internet-wide broadcast. Broadcasting is largely confined to local area network
(LAN) technologies, most notably Ethernet and Token Ring, where the performance
impact of broadcasting is not as large as it would be in a wide area network. Both
Ethernet and IPv4 use an all-ones broadcast address to indicate a broadcast packet.
Fragments: datagram can be fragmented into pieces small enough to pass over a
link with a smaller MTU than the original datagram size.
Jabber: transmission of a packet on a computer network that is larger than the
network's MTU. Such transmissions hog bandwidth and congest the network. Many
network switches have a built-in capability to detect when a device is jabbering and
block it until it resumes proper operation.
Alignment error:Decoded package alignment is faulty.
Symbol error: Coding symbol is missing or faulty.
CRC error: cyclic redundancy check is a type of hash function used to produce a
checksum
– a small, fixed number of bits – against a block of data, such as a packet
