Limitations, Distributed crawling overview – Google Search Appliance Configuring Distributed Crawling and Serving version 7.2 User Manual
Page 5
Google Search Appliance: Configuring Distributed Crawling and Serving
5
You can use GSA mirroring with a distributed crawling and serving configuration. If a master or
nonmaster primary node in the distributed crawling configuration fails, you can promote the mirror
node to function as a primary node in the distributed crawling and serving configuration.
Limitations
For information about distributed crawling and serving limitations, see
.
Distributed Crawling Overview
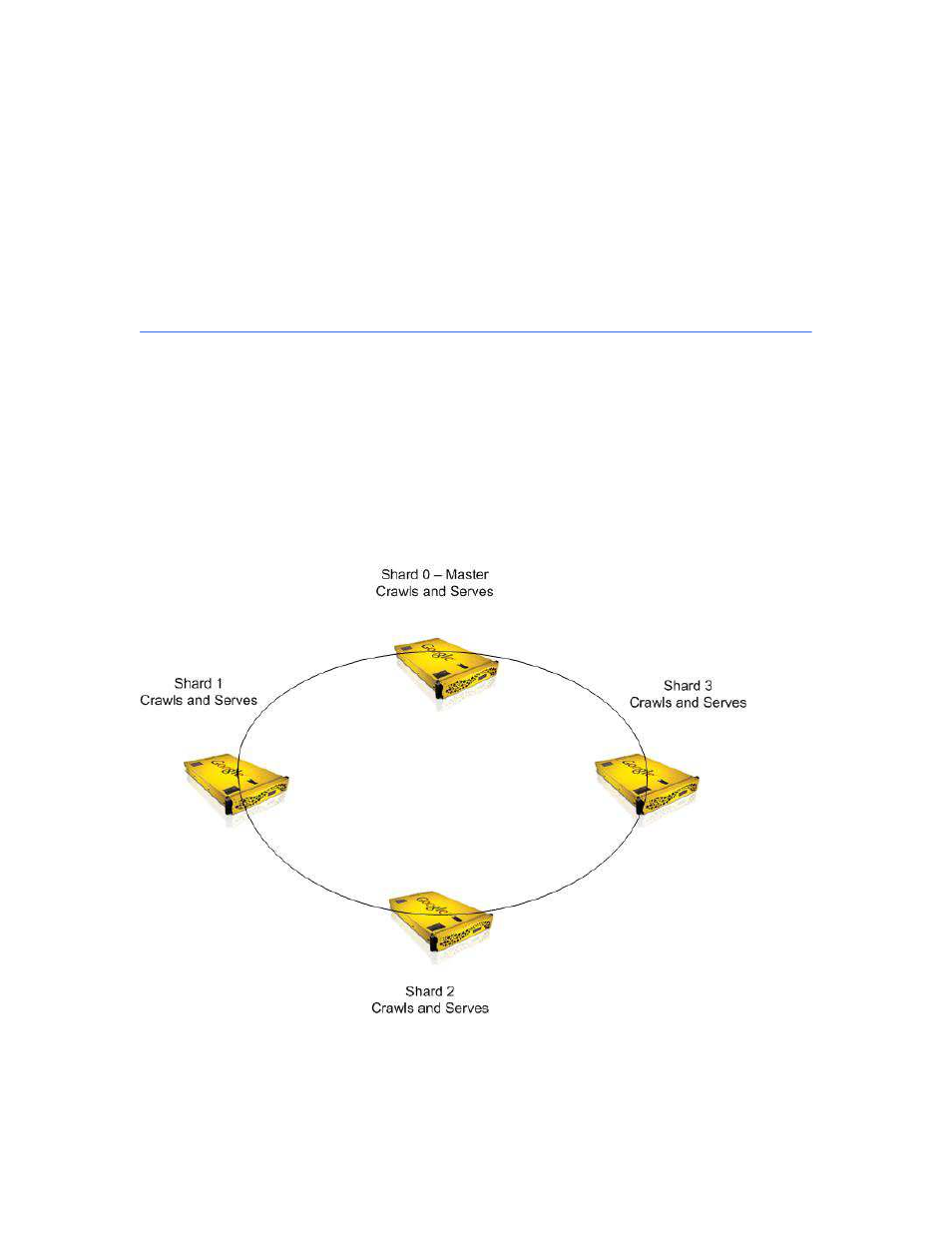
In the following diagram, four search appliances are configured with distributed crawling. Each search
appliance is designated as a particular shard in the distributed crawling configuration. Shard 0 is the
master search appliance. The shard number is incremented by 1 for each additional search appliance in
the configuration. The distributed crawling configuration is created on the master and the settings are
exported in a configuration file. The configuration file is uploaded to Shard 1, Shard 2, and Shard 3. After
the configuration file is uploaded, all search appliance features are configured on the master. The
indexes on all of the nodes are synchronized when the master node takes control of the non-master
nodes. The crawl is distributed among the search appliances and a single index is created. Each search
appliance is considered a primary (non-replica) search appliance. All of the search appliances can serve
results. The results for a search query will be identical regardless of which search appliance serves the
results.
