Goulds Pumps 3311 - IOM User Manual
Page 9
9
Determining the strainer pressure loss
Example:
Feed line = DN 125
Flow rate 80 m³/h
ζ = 4
v = 1.81 m/s in the feed line
Hv =
66
.
0
62
.
19
276
.
3
4
81
.
9
2
81
.
1
4
2
=
•
=
•
•
m
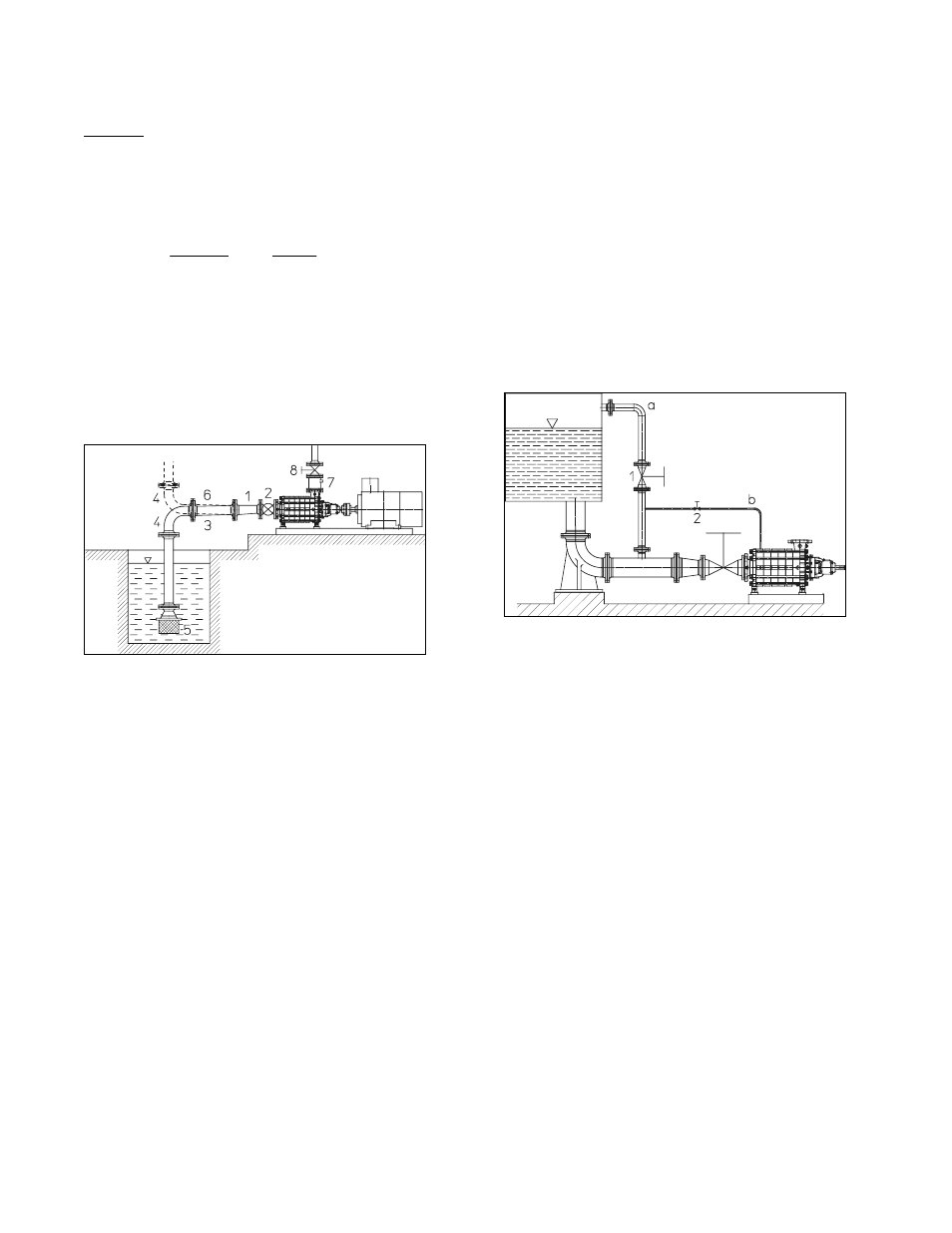
The suction line must be leak-proof and it must be
possible to release all air. The suction opening of the
suction line should be well below the liquid level, and a
foot valve with a strainer should be used. The foot valve
must be far enough from the bottom to avoid excessive
inlet losses which could impair performance.
1 Eccentric reducer (suction operation) or
concentric reducer (feed operation)
2 Shut-off valve
3 Suction line
4 Bend
5 Foot valve
6 Feed line
7 Non-return valve
8 Control valve
Pump installation
A shut-off valve should be installed in the feed line; it is
to be closed for maintenance work.
It should be installed such that air pockets cannot form in
the spindle cap, i.e. with the spindle in a horizontal
position or pointing vertically downward.
3.1.3 Vacuum equalizing pipe
If the pump draws from a system or tank under vacuum,
an equalizing pipe must be installed connecting the vent
connection at the suction casing or the highest point of the
suction line to a point above the maximum liquid level in
the suction tank.
- The line should be fitted with a shut-off valve which
should only be closed for maintenance work on the
pump.
To assist in starting the pump, we also recommend that a
pipeline, which can be shut off, be installed between the
first stage and the equalizing line.
a Equalizing line
b Additional line
1 Shut-off valve
2 Shut-off valve (vacuum-tight)
Vacuum operation
3.1.4 Discharge line
For flow control, install a shut-off valve as close to the
pump nozzle as possible. It is recommended that a non-
return valve be installed between pump nozzle and shut-
off valve, thus protecting the pump against reverse
rotation and also the pump and the foot valve against
water hammer that may occur in the event of sudden shut-
down.
