B.3.1 wind vector calculations, Measured raw data, Calculations – Campbell Scientific Wireless Sensor Network (CWB100, CWS220, and CWS900) User Manual
Page 60
Appendix B. Measurement Names and Meanings
Default
Name
Meaning
Units
RWDSD Resultant wind direction standard
deviation. Vector mean wind
direction standard deviation
calculated over the polling interval
with the CSI wind speed weighted
algorithm (See B3.1 for details).
Degrees
B.3.1 Wind Vector Calculations
When a wind speed sample is 0, the CWS900 uses 0 to process scalar or
resultant vector wind speed and standard deviation, but the sample is not used
in the computation of wind direction.
Measured raw data:
S
i
= horizontal wind speed
Θ
i
= horizontal wind direction
Ue
i
= east-west component of wind
Un
i
= north-south component of wind
N = number of samples
Calculations:
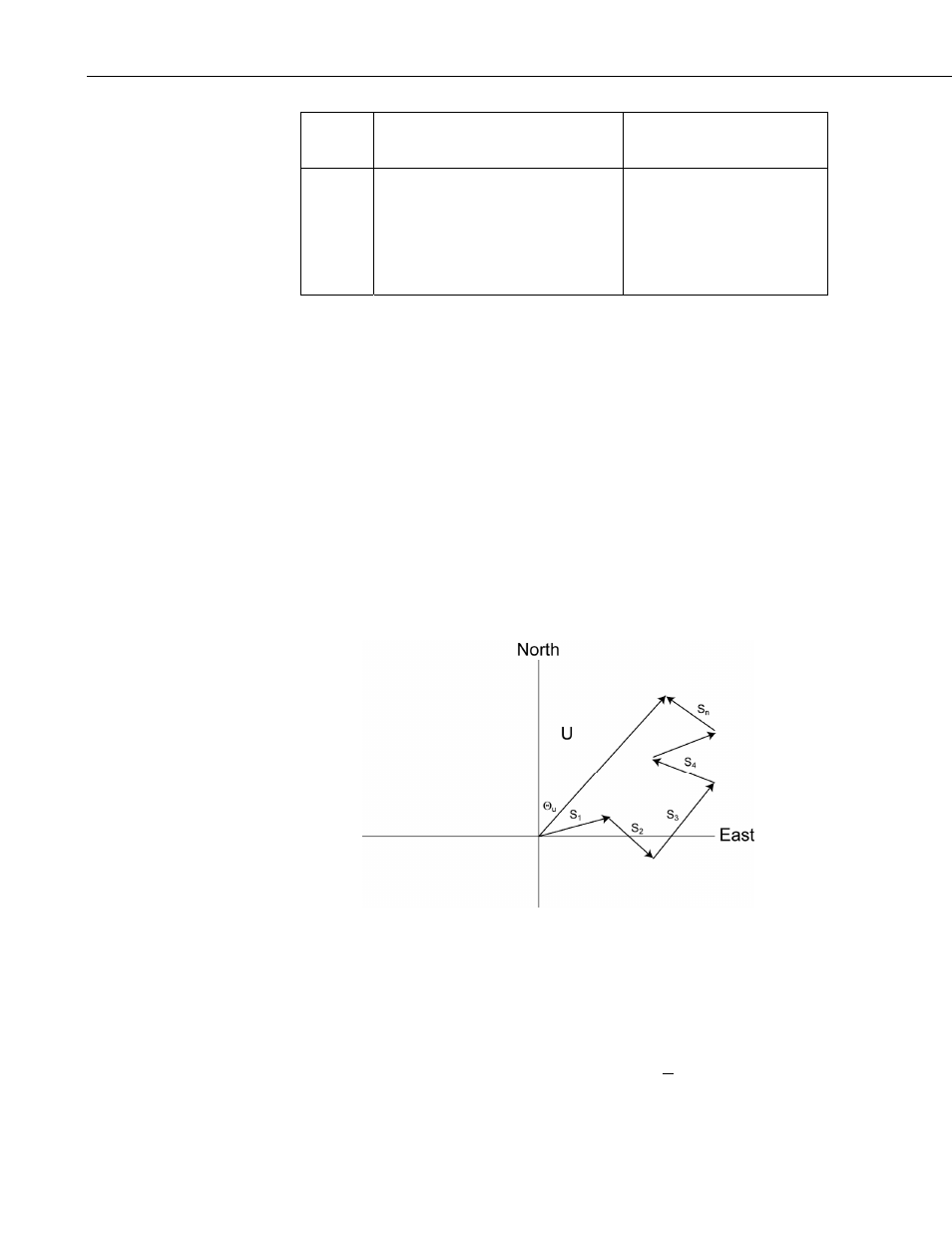
FIGURE B.3-1. Input Sample Vectors
In Figure B.3-1, the short, head-to-tail vectors are the input sample vectors
described by
s
i
and
Θ
i
, the sample speed and direction, or by Ue
i
and Un
i
, the
east and north components of the sample vector. At the end of output interval
T, the sum of the sample vectors is described by a vector of magnitude U and
direction
Θu. If the input sample interval is t, the number of samples in output
interval
T
is
N
T t
=
/
. The mean vector magnitude is
U U N
=
/
.
B-4
