B.3 mean vapor pressure examples, B.3.1 – Campbell Scientific HMP155A Temperature and Relative Humidity Probe User Manual
Page 33
Appendix B. Example Programs
B.3 Mean Vapor Pressure Examples
These examples compute mean vapor pressure. TABLE B-3 shows the wiring
used for these examples.
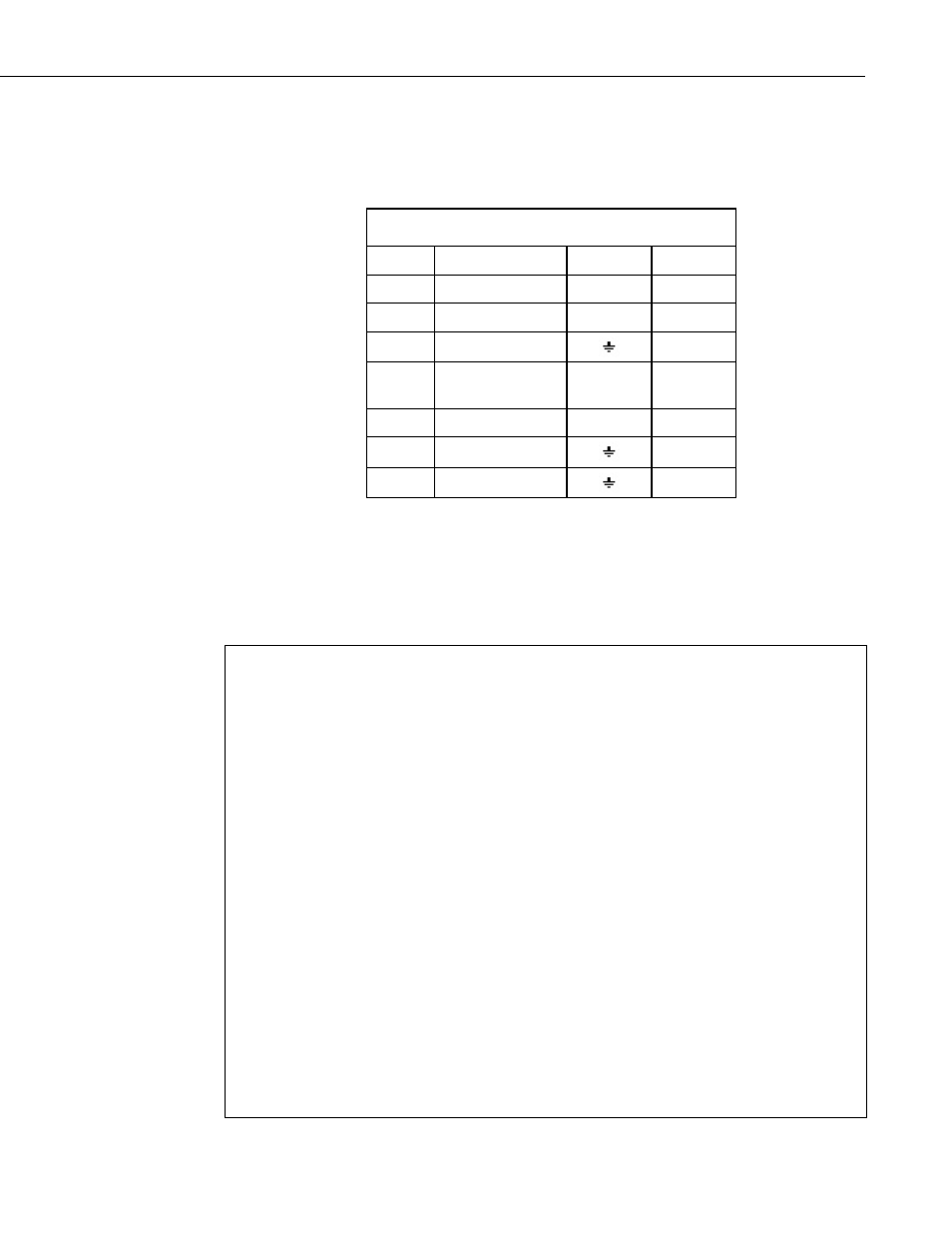
TABLE B-3. Wiring for Vapor Pressure Examples
Color
Description
CR1000
CR10(X)
Yellow
Temperature
SE 2 (1L) SE 3 (2H)
Blue
Relative Humidity SE 1 (1H) SE 4 (2L)
White
Signal Reference
AG
Jumper from
SW12V Control
C1
Red
Power
SW12V
SW12 V
Black
Power Ground
AG
Clear
Shield
G
B.3.1 CRBasic Vapor Pressure and Saturation Vapor Pressure
Program
Below is an example CR1000 program. Other CRBasic dataloggers are
programmed similarly.
'CR1000 program that calculates Vapor Pressure
Public AirTC
Public RH
Public RH_Frac, e_Sat, e_kPa
DataTable(Temp_RH,True,-1)
DataInterval(0,60,Min,0)
Average(1,AirTC,IEEE4,0)
Sample(1,RH,IEEE4)
Sample(1,e_kPa,IEEE4)
EndTable
BeginProg
Scan(5,Sec,1,0)
'HMP155A Temperature & Relative Humidity Sensor measurements AirTC and RH:
PortSet (9,1)
Delay(0,2,Sec)
VoltSE(AirTC,1,mV2500,2,0,0,_60Hz,.14,-80)
VoltSE(RH,1,mV2500,1,0,0,_60Hz,0.1,0)
PortSet (9,0)
If RH>100 And RH<108 Then RH=100
'Calculate Vapor Pressure
'Convert RH percent to RH Fraction
RH_Frac = RH * 0.01
'Calculate Saturation Vapor Pressure
SatVP(e_Sat, AirTC)
'Compute Vapor Pressure, RH must be a fraction
e_kPa = e_Sat * RH_Frac
CallTable(Temp_RH)
NextScan
EndProg
B-5
