Campbell Scientific CS110 Electric Field Meter User Manual
Page 16
CS110 Electric Field Meter
160
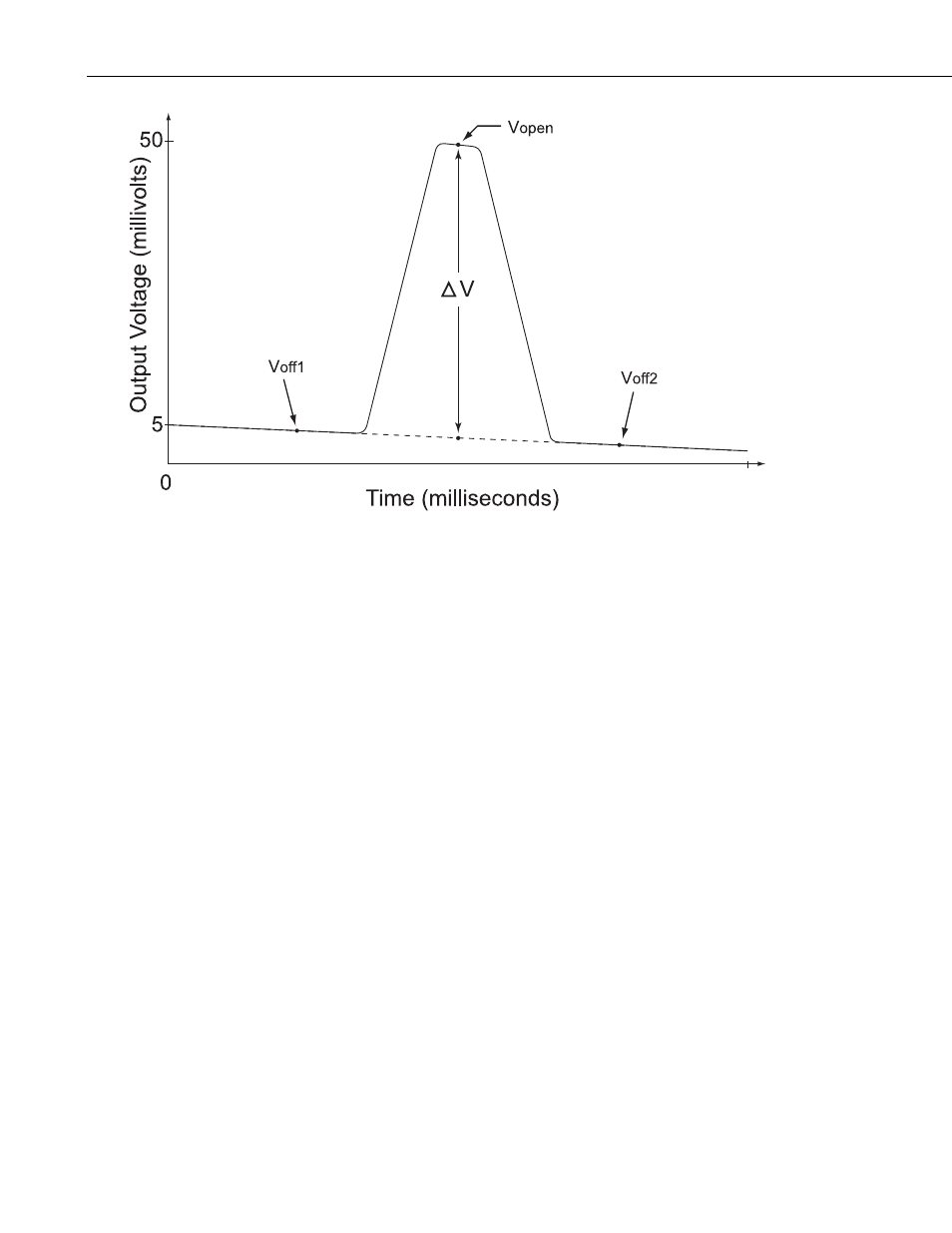
FIGURE 3. Charge amplifier output during an electric field
measurement cycle
Offset voltages Voff1 and Voff2 are zero field reference measurements made
when the shutter is closed, and utilized to accurately estimate voltage
ΔV when
the shutter is completely open. Electronic offset voltages, surface potentials
between various metallic parts and leakage currents on the charge amplifier input
result in non-zero values of Voff1 and Voff2. An electronic reset of the charge
amplifier is performed prior to the measure of Voff1 to keep the charge amplifier
output near zero volts when the shutter closed. The measured electric field E, as
determined from the charge amplifier output is as follows:
E = k
⋅ΔV = k⋅[Vopen – (Voff1 + Voff2)/2]
(eq. 1)
Where k is a constant determined by electrode geometry and electronic gain.
The resulting algorithm effectively eliminates measurement error sources that vary
slowly with respect to the time between zero field reference measurements, which
is approximately 140 ms. Measurement noise due to 50 or 60 Hz AC power can
be suppressed by utilizing the 50 Hz or 60 Hz noise rejection measurement
capability of the datalogger.
Current source Ileak in Figure 2 represents leakage currents across the Teflon
insulators supporting the sense electrode, along with the input bias current of the
operational amplifier. Deleterious effects of Ileak are compensated for in the
determination of
ΔV as given in (eq. 1). However, it is desirable to minimize the
difference between Voff1 and Voff2 in order to preserve dynamic range for large
magnitude Vopen voltages. Hence a leakage-current compensation circuit is
utilized to generate the current Icomp, illustrated in Figure 2, such that Icomp =
Ileak. The leakage-current compensation algorithm determines Icomp for the
present measurement based on Ileak from the previous measurement, which is
determined as follows:
8
