3 example programs, 1 cr1000 example program for measuring a cmp6, Example programs – Campbell Scientific CMP6-L, CMP11-L, and CMP21-L Pyranometers User Manual
Page 25: Cr1000 example program for measuring a cmp6, 6. cr1000 wiring for cmp6 example program
CMP6-L, CMP11-L, and CMP21-L Pyranometers
Where,
Vx = the value provided by the half bridge instruction
In CRBasic, the conversion to resistance is entered as a mathematical
expression. In Edlog, Instruction P59 (Bridge Transform) does the conversion.
The Steinhart-Hart equation is used to convert resistance to temperature. The
Steinhart-Hart equation for converting resistance to degree Celsius is as
follows:
Temperature = 1/[A + B*LN(resistance) + C*(LN(resistance))^3] - 273.15
Where A, B, and C are coefficients for the Steinhart-Hart equation.
The coefficients for the Steinhart-Hart equation are specific to the thermistor
contained in your CMP21. A calibration certificate that lists these coefficients
is shipped with each CMP21 pyranometer.
In CRBasic, the Steinhart-Hart equation is entered as a mathematical
expression. Edlog dataloggers can use Instruction P200 (requires a newer
datalogger operating system).
7.3.3 Example Programs
7.3.3.1 CR1000 Example Program for Measuring a CMP6
Although this example is for the CR1000, other CRBasic dataloggers are
programmed similarly. The following program measures the CMP6 every
second and converts the millivolt output to W•m
–2
. A sensor calibration of
14.33 µV / W•m
–2
is used for the example program. Every 10 minutes, the
program outputs the average and standard deviation of the flux (W•m
–2
)
measurements.
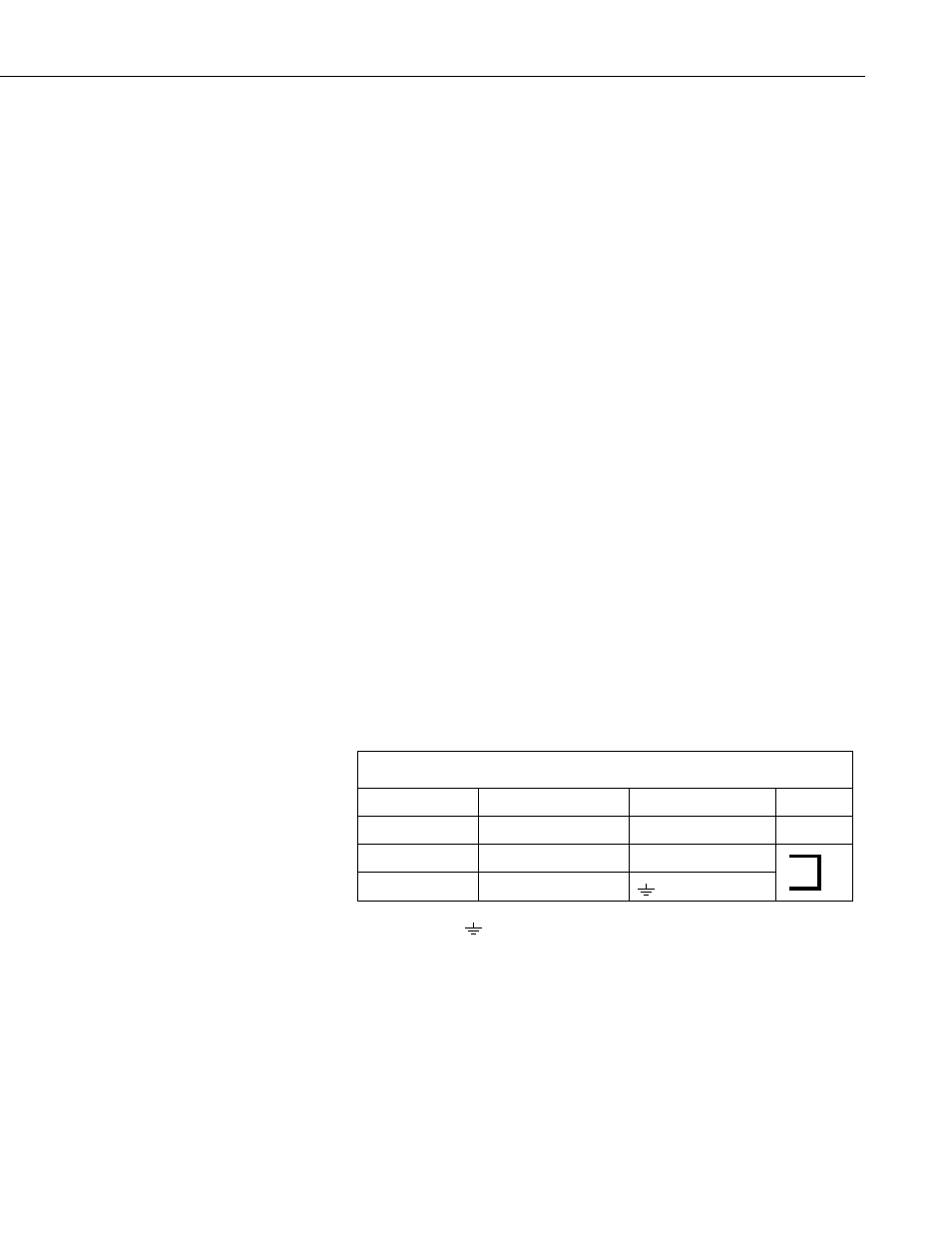
Wiring for this example is given in TABLE 7-6.
TABLE 7-6. CR1000 Wiring for CMP6 Example Program
Wire Color
Description
CR1000
Jumper*
White
Solar Signal (+)
1H
Black
Solar Signal (–)
1L
Clear
Shield
* Jumper 1L to
with user-supplied 26 AWG or larger wire.
17
