Online spare memory configuration – HP ProLiant DL380 G5 Server User Manual
Page 45
Hardware options installation 45
correctable errors exceeds a pre-defined threshold rate. The server does not fail because of correctable
memory errors. Advanced ECC provides additional protection over Standard ECC because it is possible
to correct certain memory errors that would otherwise be uncorrectable and result in a server failure.
Whereas standard ECC can correct single-bit memory errors, Advanced ECC can correct single-bit
memory errors and multi-bit memory errors if all failed bits are on the same DRAM device on the
FBDIMM.
In addition to general configuration requirements, Advanced ECC memory also has the following
configuration requirements:
•
FBDIMMs must be installed in pairs.
•
FBDIMMs must be installed in sequential order, beginning with bank A.
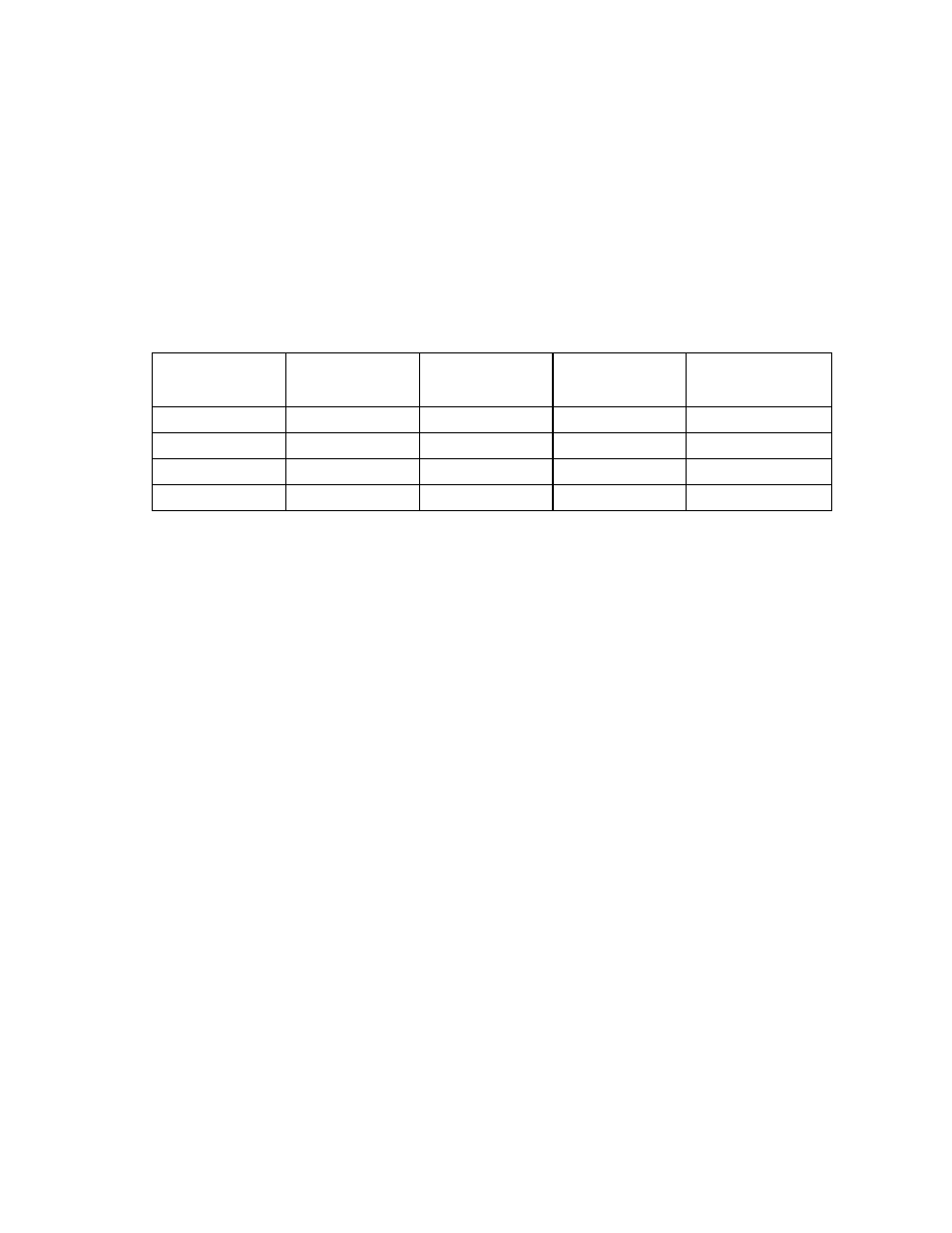
In Advanced ECC mode, FBDIMMs must be populated as specified in the following table:
Configuration Bank
A
1A and 3A
Bank B
5B and 7B
Bank C
2C and 4C
Bank D
6D and 8D
1 X — — —
2 X X — —
3 X X X —
4 X X X X
Online spare memory configuration
Online spare memory provides protection against degrading FBDIMMs by reducing the likelihood of
uncorrectable memory errors. This protection is available without any operating system support.
An understanding of single-rank and dual-rank FBDIMMs is required to understand memory usage in
online spare mode. FBDIMMs can either be single-rank or dual-rank. Certain FBDIMM configuration
requirements are based on these classifications. A dual-rank FBDIMM is similar to having two single-rank
FBDIMMs on the same module. Although only a single FBDIMM module, a dual-rank FBDIMM acts as two
separate FBDIMMs. The purpose of dual-rank FBDIMMs is to provide the largest capacity FBDIMM for the
current DRAM technology. If the current DRAM technology allows for 2-GB single-rank FBDIMMs, a dual-
rank FBDIMM using the same technology would be 4-GB.
In online spare mode, a single rank of memory acts as the spare memory. For single-rank FBDIMMs, the
entire FBDIMM acts as the spare memory. For a dual-rank FBDIMM, only half of the FBDIMM acts as the
spare memory while the other half is available for operating system and application usage.
If one of the non-spare FBDIMMs receives correctable memory errors at a higher rate than a specific
threshold, the server automatically copies the memory contents of the degraded rank to the online spare
rank. The server then deactivates the failing rank and automatically switches over to the online spare.
Because FBDIMMs that experience a high rate of correctable memory errors also have a higher
probability of receiving an uncorrectable memory error, this configuration reduces the likelihood of
uncorrectable memory errors that would result in server downtime.
Online spare is performed per branch of the memory controller. For a server with both branches
populated, two ranks are used for online spare memory. One branch can fail over to the associated
online spare while the other branch is still protected.
Each branch is made up of two banks:
•
Branch 0 contains banks A and C
