5 description of rtu codes – TOHO ELECTRONICS TRM-006A User Manual
Page 23
23
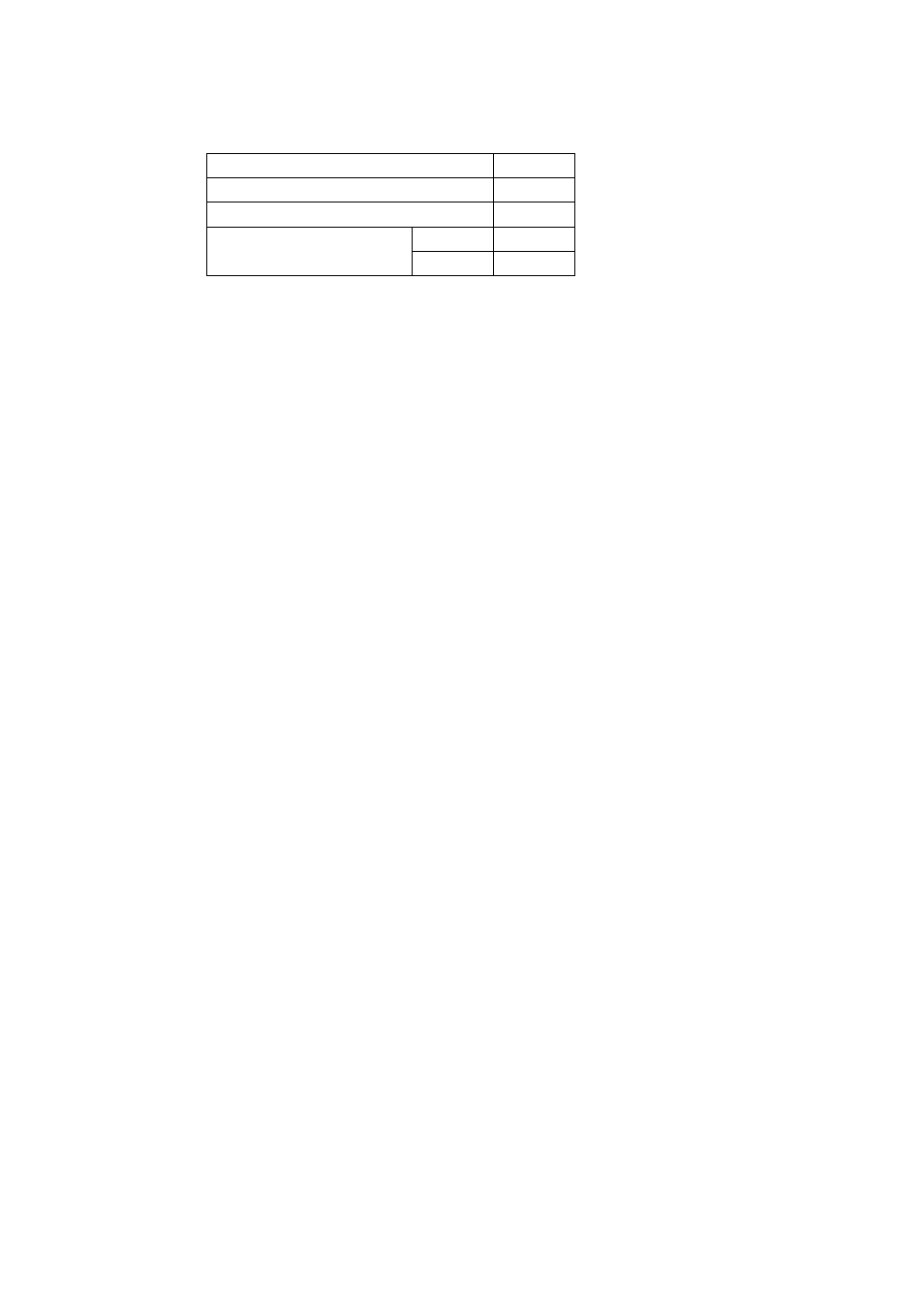
6.4.3 Response message in the case of an error
a) Slave address
1BH
b) Function code
83H
h) Error code
02H
High level
E1H
e) CRC-16
Low level
36H
←
In the case of an error, the function
code for the request message +
80H is entered.
6.5 Description of RTU codes
n The codes from a) slave address to b) function code to h) error code shown below are expressed
in 8-bit binary numbers.
a) Slave address
This is the address of the party (this product) with which the high-level computer
communicates. The address in the response message from this product represents the source
of the response message. Note that, when CH2 is used, 2 addresses are occupied. (When the
ADR is set to 1, addresses 1 and 2 are occupied.)
b) Function code
Enter a code 03H or 10H.
03H: To read data from this product
10H: To write or store data in this product
c) Register address
The locations of the data to be read or that to be written are specified in 2 bytes.
For the addresses of the commands, see "9. Table of identifiers (codes)."
The data is written in the holding register.
d) Number of registers
This specifies the number of registers to be written in. Since this product has a fixed number
of registers (which is 2), specify 0002H.
e) CRC-16
This error check code is for detecting message errors. This transmits a CRC-16 (tour
redundancy code).
The multinomial for generating a CRC-16 used in this product is X
16
+X
15
+X
2
+1.
To learn how to calculate the CRC-16, see "6.7 Example of CRC-16 calculations."
To affix an error code at the end of the message, affix the low-level byte first, then the
high-level byte of the CRC.
f)
Number of data
This specifies the number of registers to be read and written x 2. Since the number of
registers in this product is fixed at 2, specify 04H here.
