KROHNE CORIMASS MFC 85 EN User Manual
Page 14
14
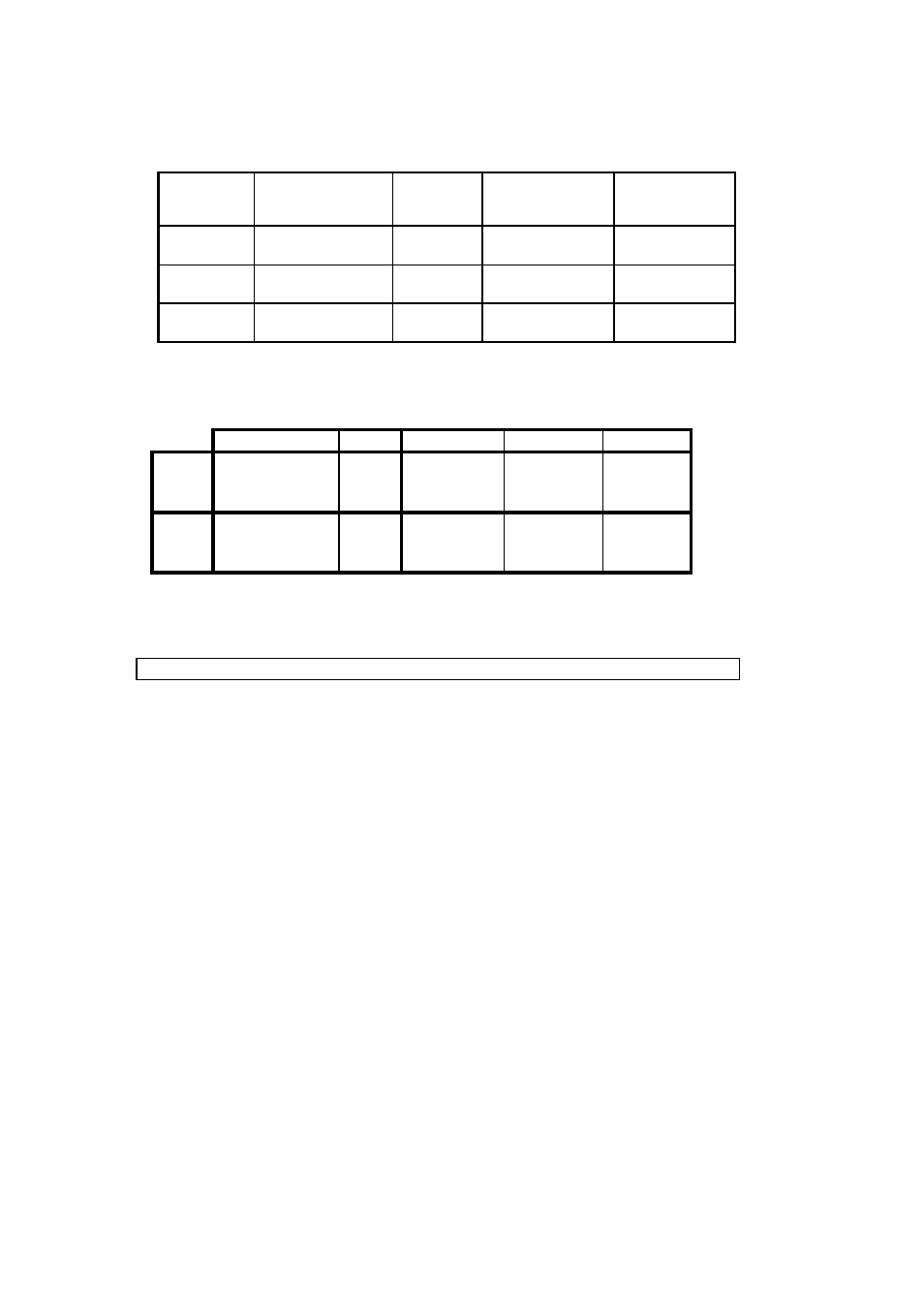
Enter the raw data (bold) into the table below then for each temperature calculate
ρ
c
and
ρ
s
using the above equations.
Temp. /°C
Conc. by Mass /%
Density
/g/cm
3
ρ
c
ρ
s
10
5.52
1.040473
1.002565
2.9473856
14.9
1.112023
20
5.52
1.037835
1.0006212
2.8540898
14.9
1.107953
30
5.52
1.034454
0.9977574
2.7906384
14.9
1.103516
Transfer the
ρ
c
and
ρ
s
into the table below and calculate the
ρ
20
, K1 and K2 values for each
using the equations of Case 2:
Density
Temp.
K
2
K
1
ρ
20
Liquid
ρ
1
= 1.002565
10
-0.0000046
-0.0002404
1.000621
ρ
2
= 1.0006212
20
ρ
3
= 0.9977574
30
Solid
ρ
1
= 2.9473856
10
+0.0001492
-0.0078374
2.85409
ρ
2
= 2.8540898
20
ρ
3
= 2.7906384
30
Program these values into the converter. For this example the fit of the concentration
algorithm, over the range 3 to 17%, is accurate to better than
±
0.1
4.4
Entering the data into the converter
Having calculated the necessary parameters they must now be entered into the converter. In
performing the
ρ
20
, K
1
, K
2
calculations it does not matter which density units are used, (g/cm
3
,
kg/m
3
, lb/US Gallon etc), provided all data is then entered in those units.
For an example consider an oil / water emulsion where the oil has densities of 650.0, 648.5,
and 647.3 kg/m
3
at temperatures 10, 20 and 30°C respectively. From this data:
ρ
20
=
648.5 kg/m
3
K
1
=
-0.135 kg/m
3
/°C
K
2
=
0.0015 kg/m
3
/°C
2
