Tilton Standard Oil Cooler Pump (98-1901) User Manual
Installation instructions, Transmission / differential oil cooler pump
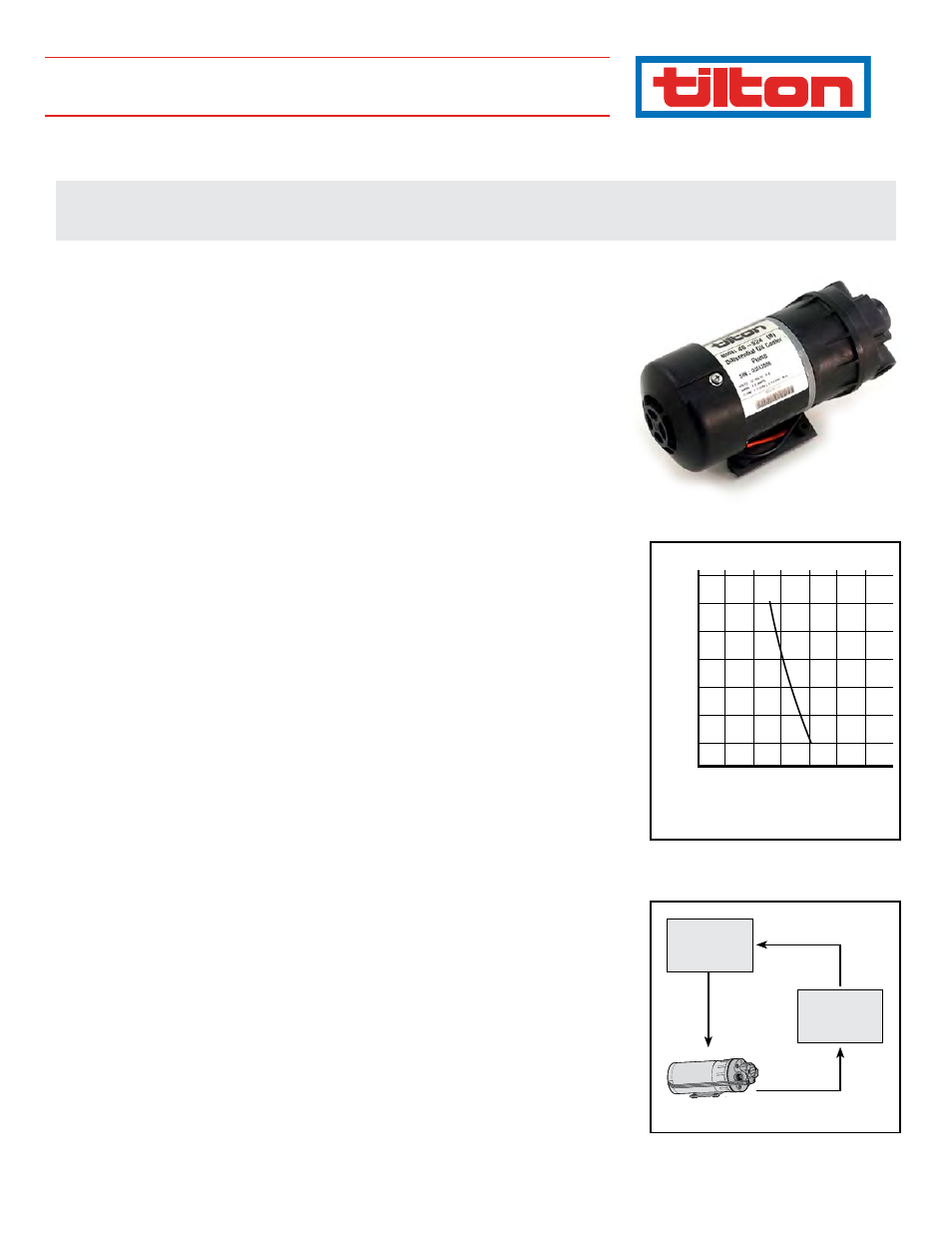
How It works
The Tilton Differential Pump is a positive displacement type of pump, so its output is directly proportional
to the motor speed. If a lighter load increases the motor speed by 25%, then the flow rate increases by
25%. The flow rate vs. pressure is shown in Graph 1 with a maximum available pressure of 60 PSI. A fluid
system will only flow as much as the smallest restriction will allow. Larger diameter lines and fittings allow
more flow and place less load on the pump. This pump is self-priming and can be placed up to 8 ft above
the source from which it draws. The typical application for the pump is in a differential or transmission
cooling system. However, the pump can be used for other applications such as emptying fuel tanks. A 12-
volt DC, 10-amp power supply is required. The current draw is 6.6 amps under a maximum load condition
with a more typical current draw between 2 and 3 amps. This pump has a very light weight at 3.5 lbs and
has a flow rate of 1-2 gallons per minute. There are two types of diaphragms available for the differential
pumps; the BUNA type diaphragms are for standard coolants and the VITON diaphragms are for the more
corrosive coolants.
InstallatIon notes
The Tilton Differential Pump is placed inline with the cooling system as shown in Diagram 1. Placing the
pump on the outlet side of the cooler exposes it to lower temperatures significantly increasing the life
and reliability of the pump. A 40-mesh (400 micron) strainer or filter placed inline before the inlet of the
pump prevents foreign objects from damaging the pump. Heavy gear oil must be brought up to oper-
ating temperature before the pump is engaged. The cold fluid can be very thick and place an unusually
large strain on the pump. Tilton recommends the use of an on/off switch so the pump can be turned off
during warm-up periods. The pump includes an integral cooling fan to keep the pump cool during loaded
conditions. If the pump is mounted in a vertical position, mount the pump with the motor above the pump
inlet and outlet to prevent damage to the motor in the event of a fluid leak. The pump head can be rotated
in 180-degree increments, allowing a variety of hose positions. Be careful not to damage the plastic pump
housing by over tightening the fittings. If a check valve is placed inline with the pump, the check valve
must have an opening pressure of no more than 2 PSI. The electrical hook-up is simple. Connect the pump
to a 12-volt DC supply with a 10-amp fuse inline with the (red) positive lead. The black lead is the chassis
ground.
PumP removal
1. Drain any excess coolant out of the pump before continuing
2. Disconnect the electrical connections
3. Disconnect the inlet and outlet lines
4. Remove the pump from the vehicle
mountIng Hole DImensIons
• 2.25” vertical centers x 3.25” horizontal centers.
• Drill hole diameter: 3/16”, 4 places.
• Use high quality #10 bolts with lock nuts
PlumbinG
• For best results, use AN8 steel braided flexible hose.
• Use only 3/8” NPT fittings at the pump inlet and outlet.
OPeratiOn
• Allow the pump to prime with the discharge line open to prevent airlock.
• The pump will not be harmed if it is allowed to run dry. It is self-priming.
electrical
• Use a minimum of 16AWG stranded wire for power connections.
• Use a 10-amp inline fuse on the 12-volt DC (red) power connection.
Head-Flow Performance
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
.5
0
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
Flow Rate (GPM)
Pr
essur
e (PSI)
Graph 1
Flow: 1-2 GPM (4.6-9.1 LPM) | Pressure: 60 PSI (3.5 BAR) MAX | Voltage: 12 VDC | Current: 8 AMPS
| Temperature range: 40-160˚ F Continous; 265˚ F (MAX) Intermittent | Prime: Self-priming up 8 ft (2.6 meters) vertical height
(40-524 & 40-525)
Transmission / Differential Oil Cooler Pump
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
98
-19
01
Diff/trans
cooler
Differential
or
transmission
Diagram 1
