LevelOne FBR-1461 User Manual
Page 82
82
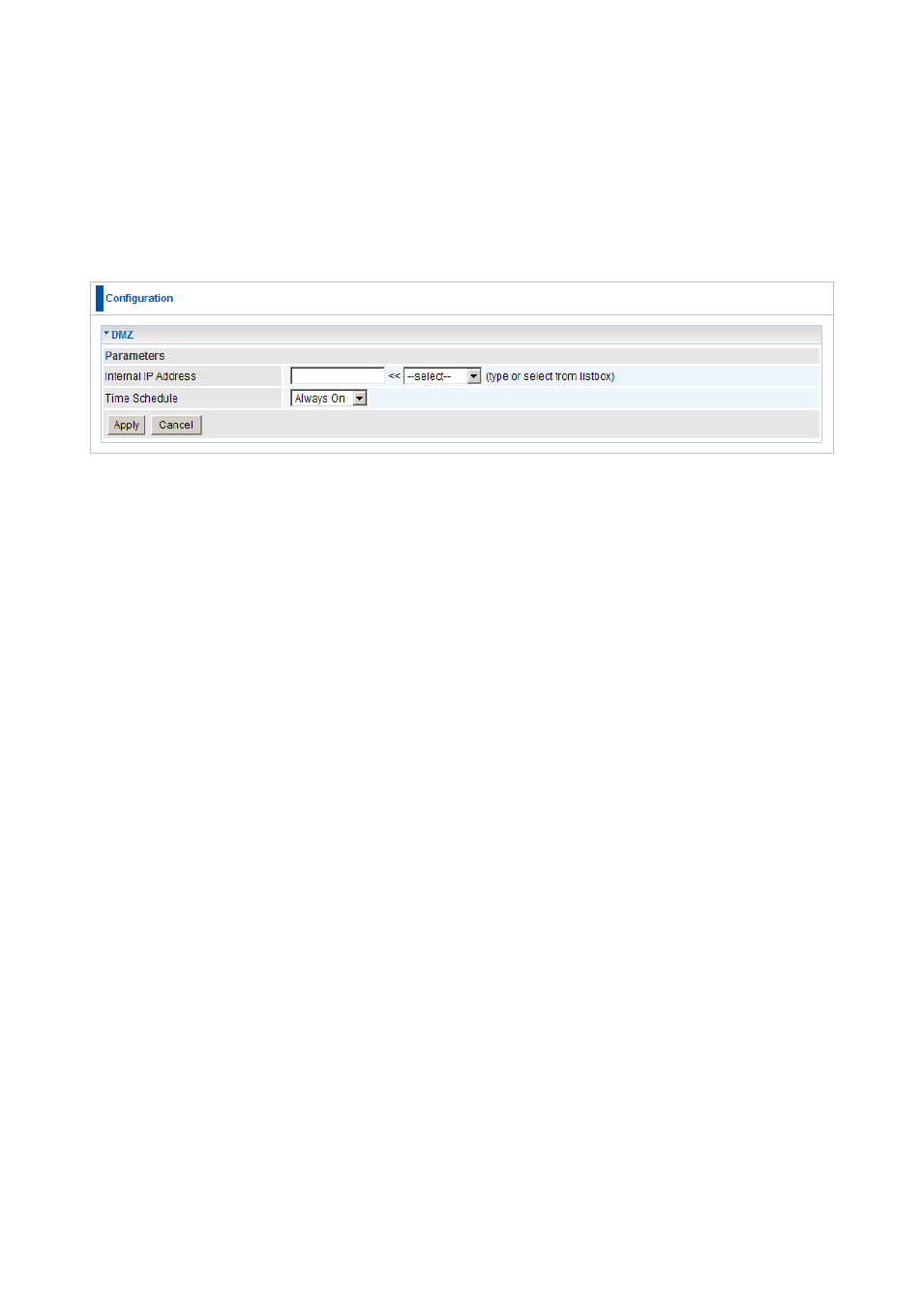
DMZ
DMZ: The DMZ Host is a local computer exposed to the Internet. When setting a
particular internal IP address as the DMZ Host, all incoming packets are checked by the
Firewall and NAT algorithms, it is then passed to the DMZ host when a packet received
does not use a port number in use by any other Virtual Server entries.
Note:
Using port mapping does have security implications, since outside users are able to
connect to PCs on your network. For this reason you are advised to use specific Virtual
Server entries just for the ports your application requires instead of simply using DMZ or
creating a Virtual Server entry for “All” protocols, as doing so results in all connection
attempts to your public IP address accessing the specified PC.
Attention
:
1. If you disable the NAT option in the WAN-ISP section, the Virtual Server function
becomes invalid.
2. If the DHCP server option is enabled, you have to be very careful in assigning the IP
addresses of the virtual servers in order to avoid conflicts. The easiest way of
configuring Virtual Servers is to manually assign a static IP address to each virtual
server PC, with an address that does not fall into the range of IP addresses that are
issued by the DHCP server. You can configure the virtual server IP address manually,
but it must still be in the same subnet as the router.
