Nitrogen dioxide sample analysis – SKC 500-200 UMEx 200 Passive Sampler for Nitrogen Dioxide User Manual
Page 3
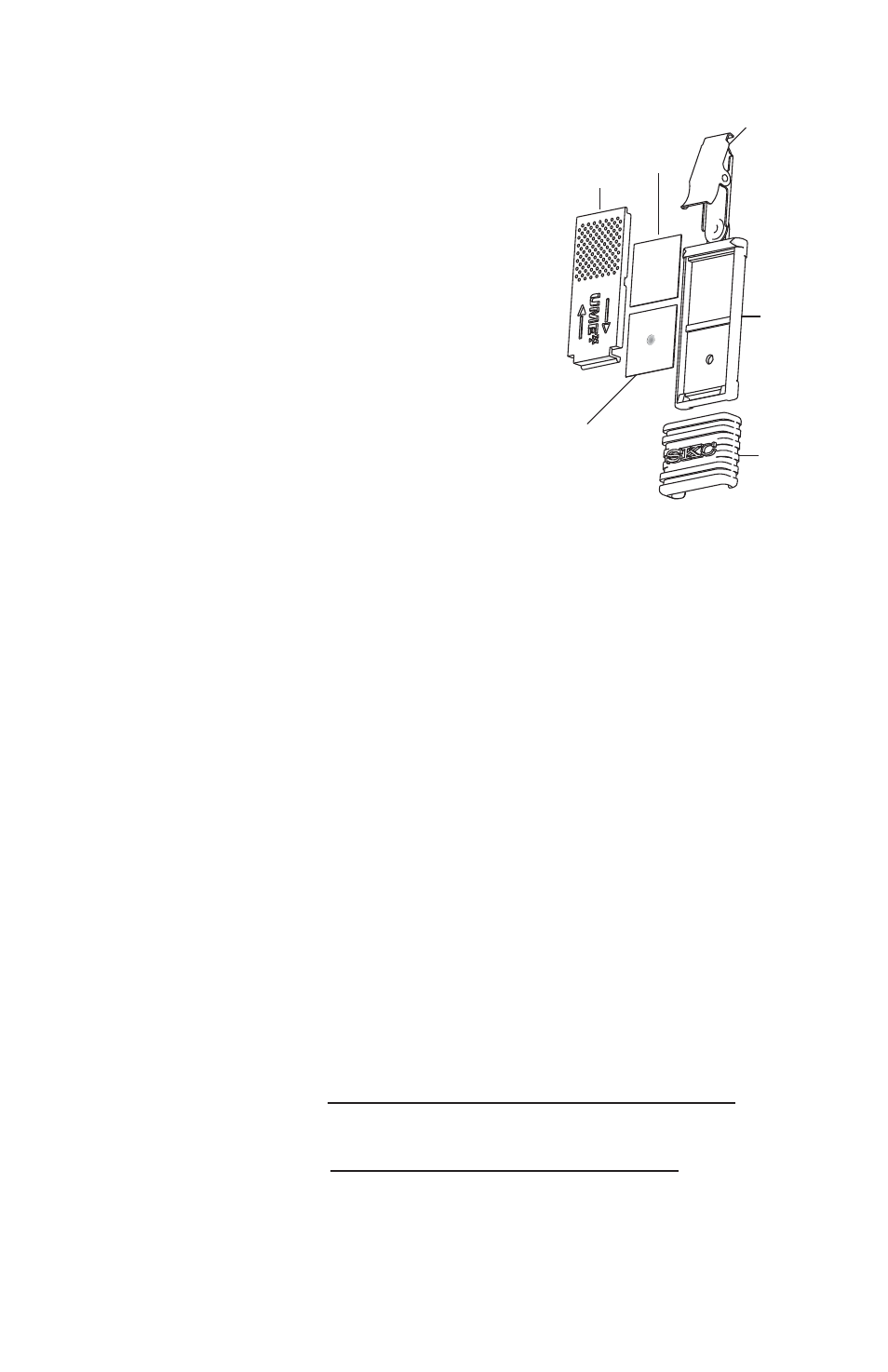
Diffusion plate
Reactive tape (sample)
Collar clip
Body
Sliding
cover
Reactive tape
(blank/correction)
4. Immediately transfer 1 ml of extract to an auto-
sampler vial for analysis of nitrogen dioxide.
5. If also analyzing for SO
2
,
§
pipett e 1 ml of
extract into a vial and dilute with 1 ml of 0.15%
hydrogen peroxide. Shake well for analysis of
sulfur dioxide.
§ Sampling rate for SO
2
is 15.2 ml/min.
Nitrogen Dioxide Sample Analysis
1. The sample extracts are analyzed for nitrite by ion chromatography with
conductivity detection.
2. A 20 microliter portion of the extract is injected onto a Dionex 4 x 250-mm
AS14A column and with an 8.0/1.0 mM sodium carbonate/sodium bicarbonate
eluent. For low levels (≤ 0.4 ppm), inject 70 μl onto the column.
3. Calculate the nitrite results by comparing against a standard calibration
curve.
4.
Convert the results from nitrite to nitrogen dioxide using the following formula:
Concentration μg/ml nitrogen dioxide = Concentration μg/ml nitrite
Where 46.01 is the molecular weight of both nitrogen dioxide and nitrite
5. Total mass of nitrogen dioxide is calculated below:
Concentration nitrogen dioxide (μg/ml) x Desorption volume (2 ml)
6. The nitrogen dioxide of the blank/correction tape must always be subtracted
from the sample tape when calculating air concentrations.
7. Calculate the air concentration in ppm using the following equations:
Volume of air (liters) = Time (minutes) x Sampling rate (17.3 ml/min)
1000
Concentration (ppm) =
Mass (mg) x 24450
Air volume (L) x Molecular weight (46.01)
