9060 cascade low voltage controller - operation – Ransburg 9060 LV Cascade Controller 80131-XXX User Manual
Page 30
9060 Cascade Low Voltage Controller - Operation
25
CP-13-07.2
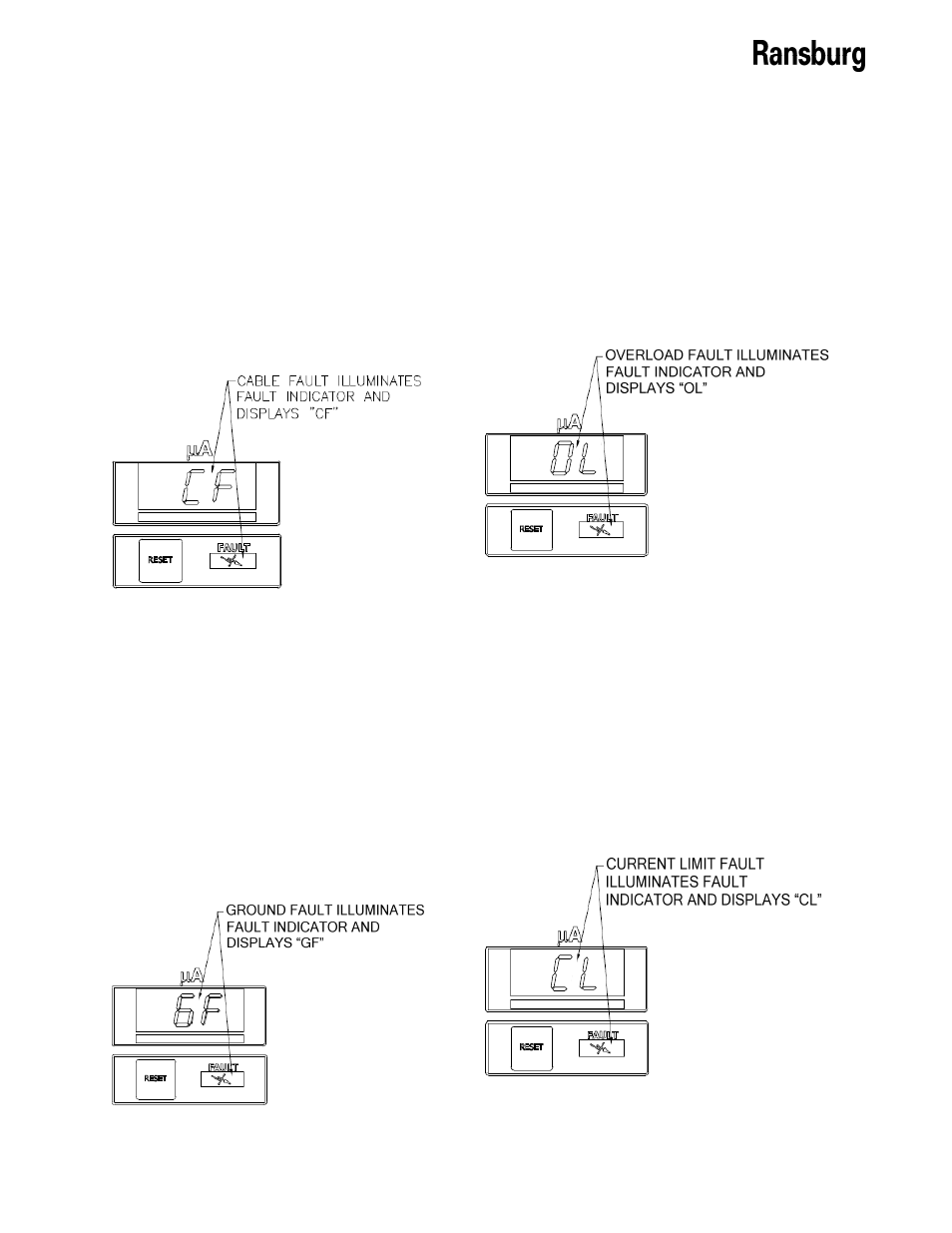
Overload Fault (OL)
This fault will occur if the overload feature is
active (see ‘Overload Activation” previously in
the “Operation” section) and the output current
exceeds the overload current value. This can
be caused by excessive overspray on the ap-
plicator or paint formulation that is too conduc-
tive. Clean the applicator, check the paint for-
mulation, or move overload jumper (JP17) to
the open position.
Figure 25: Overload Fault Display
Figure 23: Cable Fault Display
Ground Fault (GF)
If this fault occurs, the fault indicator on the
control unit will illuminate, a GF indication will
show in the uA display. This fault will occur if
the microprocessor detects a loss of ground at
the high voltage section. If this fault occurs,
reset the fault. This fault can be caused by a
broken ground path between the handgun and
the control unit and may indicate a faulty cable
or plug assembly. For more information, refer
to Fault Troubleshooting Section.
Figure 24: Ground Fault Display
Cable Fault (CF)
This fault will occur if high voltage is active and
the microprocessor detects that no current is
being supplied to the applicator. This indicates
a connection problem from the control unit to
the handgun barrel assembly. Typical causes
include a faulty low voltage cable, stuck pins on
the plug assembly, or contaminated contacts on
the applicator. This may also indicate a faulty
barrel assembly for a handgun. For additional
information, refer to the Fault Troubleshooting
Section.
Current Limit Fault (CL)
This fault occurs if the output current exceeds
the maximum current by 20µA. This fault can
be caused by excessive overspray on the ap-
plicator or a paint formulation that is too con-
ductive. It may also be caused by a failed
handgun barrel or faulty pc board. Clean the
applicator, check the paint formulation, and re-
test. See Fault Troubleshooting Section for
more information.
Figure 26: Current Limit Fault Display
