Theory of operation, 1 comparator status, 2 controlling the comparator – CTI Products IIB Console Interface User Manual
Page 9: 3 associating an iib with a comparator i/o module, 4 system example
IIB Hardware Reference
Theory of Operation
CTI Products, Inc.
68-10844-115
4
3.
Theory of Operation
This section describes the operation of the IIB module in an MCN comparator
display system.
3.1
Comparator Status
The Comparator I/O Module (such as an AIB or CIB) accepts the VOTE,
RECEIVE, DISABLE, and FAIL receiver status indicators from the comparator.
It sends status messages to the IIB module. The IIB module controls the VOTE,
RECEIVE, DISABLE, and FAIL parallel lines of the operator interface (such as a
console).
3.2
Controlling the Comparator
The IIB module monitors the VOTE and DISABLE lines from the console. When
the console activates a VOTE or DISABLE line, the IIB module will send a
FORCE VOTE or DISABLE command to the comparator. The Comparator I/O
Module will then generate the proper FORCE VOTE or DISABLE/ENABLE
signal to control the comparator.
3.3
Associating an IIB with a Comparator I/O Module
When an IIB is installed into a system, you need to configure the IIB with the
address of the Comparator I/O Module it will be operating with. Section 6.1
describes how to enter this extra address. By having the address of the
Comparator I/O Module, the IIB knows how to route its control messages for
FORCE VOTE and DISABLE over the MCN network.
3.4
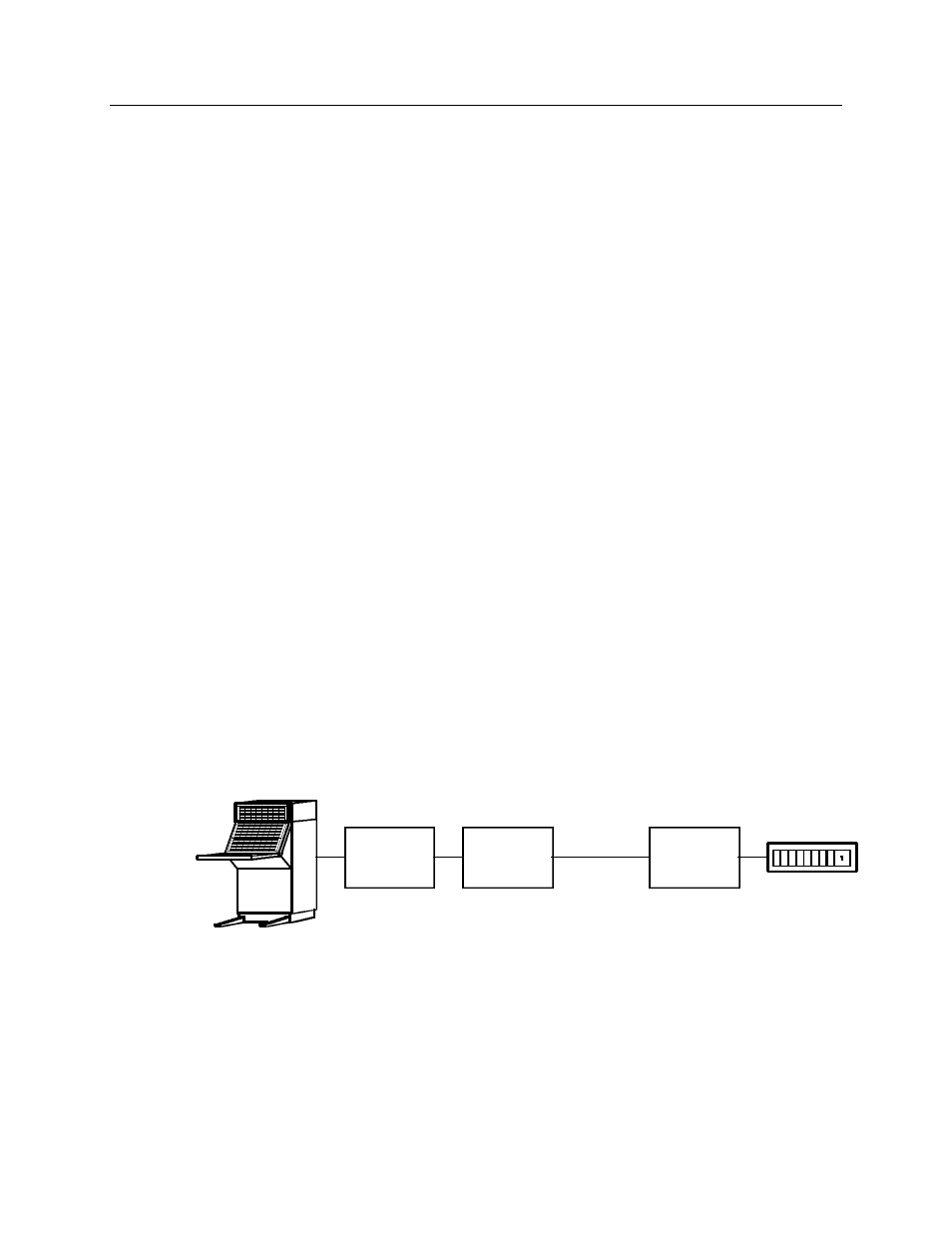
System Example
Figure 3 shows an example comparator display system using the IIB module with a
console for the operator station.
CA-80034-100
CA-80034-100
MODULE
IIB
COMPARATOR
I/O
CONSOLE
ELECTRONICS
COMPARATOR
MCN NETWORK
CONSOLE
Figure 3 - IIB System Example
When the comparator detects that a receiver is active, it sends a RECEIVE
command followed by a VOTE command (if that receiver becomes voted). The
Comparator I/O Module processes these commands and sends them to the IIB.
The IIB then activates the VOTE and RX outputs for that receiver.
