3 functional principle, 1 an-ise sc probe, Functional principle – Hach-Lange NISE sc User Manual
Page 9: An-ise sc probe, Order number, General information
9
General information
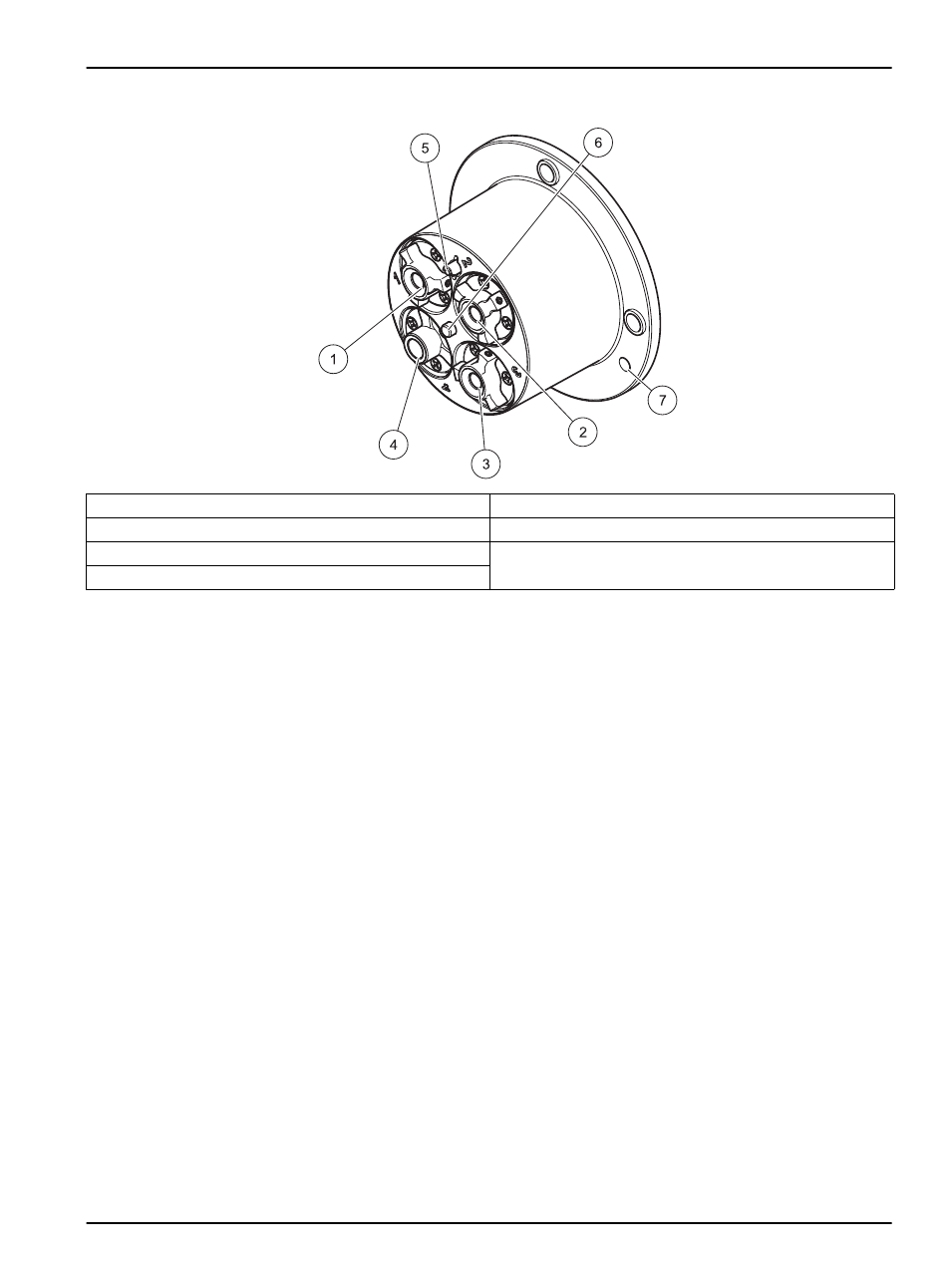
Figure 3
Sensor cartridge
2.3 Functional principle
Ion-selective electrodes have a special membrane to which only a specific type of ion can
adhere. As a result, an ion-specific potential forms on the membrane surface. To measure
a potential difference, a reference system is required that will not be affected by the
sample to be measured.
The CARTRICAL
TM
technology reduces cross-sensitivity by calibrating not only the
individual electrodes but also the measuring electrode against the compensation
electrode and the reference; this is carried out at the factory. The reference system is
designed using pH-differential technology and is therefore particularly stable in terms of
drift and contamination.
2.3.1 AN-ISE sc probe
The AN-ISE sc probe uses the ion-selective electrode technology to measure ammonium
ions (NH
4
+
) and nitrate ions (NO
3
–
) in a waste water sample.
Known interfering factors due to potassium (when measuring ammonium), chloride (when
measuring nitrate) and temperature are compensated by suitable built-in electrodes.
1
Ammonium electrode
1,2
1
Active with AN-ISE sc
2
Active with AISE sc
5
Reference system
2
Nitrate electrode
1,3
3
Active with NISE sc
6
Temperature sensor
3
Potassium electrode
1,2
7
Marker hole for assembling the probe
4
Chloride electrode
1,3
