Options and accessories to complete the solution, Power supply analysis function (/g4), User-defined math (/g2) – Atec Yokogawa-DLM4000 User Manual
Page 4
Auto Setup!
Hex
Symbol
SPI
I
2
C
PBDH0150(701927)
150 MHz bandwidth
±1.4kV
Input pulse
(Frequency)
Computed waveform
(F-V conversion)
F-V conversion of frequency pulse (/G2 option)
PBDH1000(701924)
1.0GHz bandwidth
1 M
Ω, approx 1.1pF
PBC100(701928) / PBC050(701929)
DC to 100 MHz / DC to 50 MHz
30 Arms
701936
Deskew correction
signal source
SCL
SDA
SCL
SDA
Device #1
Device #2
CAN_H
CAN_L
Node 1
Node n
Power supply analysis function (/G4)
Real-time Low-Pass Filter, Add, Subtract, & Multiply Waveforms,
Integral, Pulse Count, Rotary-Count of Encoder A/B Signal,
XY Display, Power Spectrum
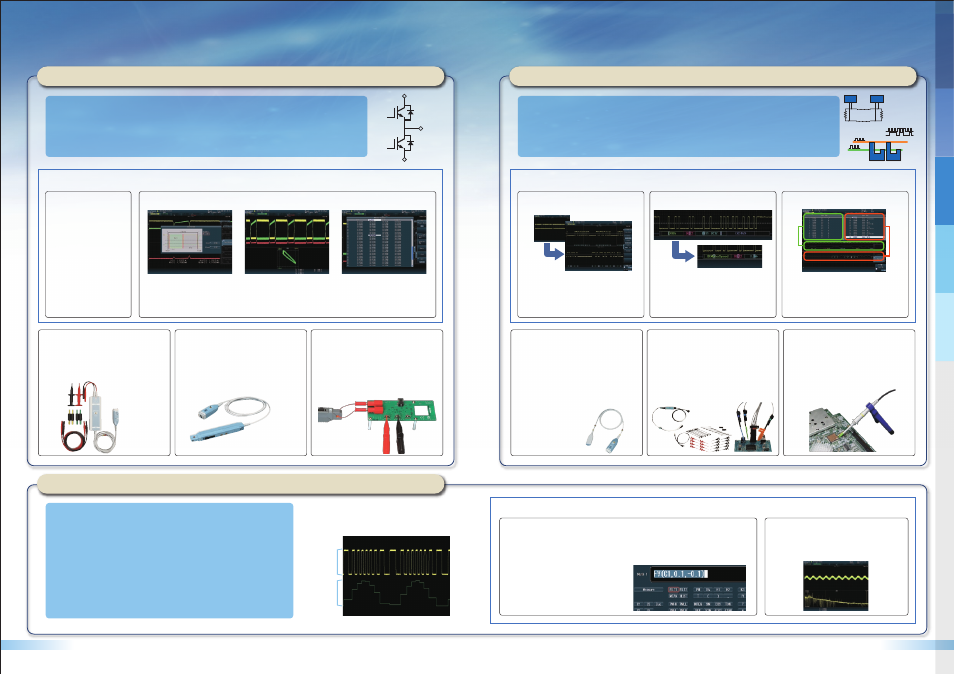
The PBDH1000 differential probe features high
input-resistance, wide bandwidth, and a wide
input-voltage range. The PBDH1000 is perfect for
measuring the noise or surge voltage of in-vehicle
high-speed serial bus waveforms, including CAN
and FlexRay.
A generous assortment of probe tip accessories
assures flexible probing options.
Analyzing High-speed Differential Signals
−PBDH1000 Differential Probe−
Logic signals are not always fast. In some cases,
high input resistance is important. Yokogawa
offers two types of logic probes, PBL100 (100
MHz, 1 M
Ω), which has mimimal loading, and
the PBL250 (250 MHz, 100 k
Ω), ideal for probing
high-speed logic waveforms.
Probing Fast & Slow Logic Signals
−PBL100 & PBL250 Logic Probe−
The 701946 is an ultra-compact passive probe for
measuring high-speed waveforms on ICs and in
high-density circuitry.
Various accessories maximise safety and
performance.
High-density IC and PCB Probing
−701946 Miniature passive probe−
Intelligent serial-bus auto-setup feature enables
quick and easy setup. The bit-rate and voltage
thresholds are set automatically.
Serial-Bus Auto-Setup Saves Time
Serial-bus waveforms are processed in realtime
by a dedicated processor. Decoded serial-bus
data is displayed alongside the bus waveform in
a user-selected format (Binary, HEX, or ASCII).
Symbol display based on a user-defined symbol
library is also easily setup.
Hardware-based Decoding
Many systems contain multiple serial buses. The
DLM4000 analyzes four different serial-bus types
simultaneously. A combination trigger of two
different serial buses is also possible.
Dual Bus Analysis
Serial bus analysis function (/F1, /F2, /F3, /F4, /F5, /F6)
Triggering and real-time Decoding
Customizable User-Defined Equations
Example of the functions in /G2 option, User Define Math:
Expansion of FFT Calculation
User-defined math performs computation on
input-waveforms and math-channel results;
user-defined math can also use parametric
measurement results within a computation
expression.
In addition to power spectrum, advanced FFT functions
such as coherence and transfer function calculations
are available for detailed frequency-domain analysis.
User-Defined Math (/G2)
Power Analysis
Power Measurement
The built-in algorithm fine tunes
Power Loss calculations.
User-specified parameters include
device such as IGBTs and MOSFETs.
Automated measurement of
power parameters such as
active power, apparent
power, power factor etc.
(Calculation of three-phase
power is also possible)
By dividing the long memory into segments,
the SOA (safe operating area) can be
analysed and, peak voltages between
switching cycles can be compared by
overlaying or one-by-one replay.
It is also possible to display a list of
the switching loss of each cycle and
save the results. By clicking a value
in the list, the corresponding
waveform will be directly displayed.
Example: Switching Loss Analysis
The High Voltage Differential Probe range includes
models such as the compact PBDH0150
(1400Vpeak) as well as the 701926 (7kVpeak).
Easy Probing for Floating Signals
−High-Voltage Differential Probe−
The PBC100 and PBC050 high-bandwidth current
probes measure DC to 100MHz and 50MHz at up
to 30Arms. The 701931 is available for higher
currents up to 500Arms. The current probe range
covers a wide range of applications.
Wide Range of Current Measurement
−Current probe−
When measuring very fast switching devices,
probe delay time correction (de-skew) is crucial.
The 701936 signal source and auto de-skew
feature makes de-skewing quick and and simple.
Enables Precise Power Measurement
−Deskew correction signal source−
Examples of Standard Computations:
The DLM4000 features advanced, powerful, and flexible
waveform computation abilities.
An increasing number of mechatronics applications require
measurements on the computational-result of a waveform,
and not on the input waveform itself.
Examples include PWM control signals, pulse-signals from
rotating-shaft applications, vibration-sensor data, and
accelerometer waveforms.
Duty cycle analysis for PWM waveform, F-V conversion, High-pass/Low-pass/Band-pass filtering,
moving average, differential-integral, trigonometric, exponential-logarithm, arithmetic calculation of
multiple channels, DA conversion of logic signals
The DLM4000 offers advanced serial-bus analysis – saving precious development
time of ECUs and Embedded Systems. Eight analog input channels means that
multiple analog, serial-bus, and logic waveforms can be easily and simultaneously
observed whilst preserving their relative timing.
Up to four serial-buses can be analysed at the same time.
Eight analog input channels enables four pairs of voltage and current
measurements, thereby supporting today’s high-speed and sophisticated power
electronics circuit development. Optional analysis functions and accessories
support the comprehensive measurement of power electronic devices.
-Switching Loss
-Safe Operating
Area
-Harmonic Analysis
-Joule Integral
For power device circuit voltage/current measurement
CAN, LIN, I
2
C, SPI, & UART(RS232) … Protocol Analysis
PWM, F-V, FFT, Diff/Integ … For an Increasingly Mechatronic World
Options and Accessories to Complete the Solution
Product Introduction
Functions & Featur
es
Options &
Accessories
Oper
ability & Softw
ar
e
Specifications
07
06
