Application information – Diodes AP2141D/ AP2151D User Manual
Page 10
AP2141D/ AP2151D
Document number: DS32242 Rev. 4 - 2
10 of 18
May 2013
© Diodes Incorporated
AP2141D/ AP2151D
Application Information
The AP2141D and AP2151D are integrated high-side power switches optimized for Universal Serial Bus (USB) that require protection functions. The
power switches are equipped with a driver that controls the gate voltage and incorporates slew-rate limitation. This, along with the various protection
features and special functions, makes these power switches ideal for hot-swap or hot-plug applications.
Protection Features:
Under-Voltage Lockout (UVLO)
Under-voltage lockout function (UVLO) guarantees that the internal power switch is initially off during start-up. The UVLO functions only when the
switch is enabled. Even if the switch is enabled, the switch is not turned ON until the power supply has reached at least 1.9V. Whenever the input
voltage falls below approximately 1.9V, the power switch is turned off. This facilitates the design of hot-insertion systems where it is not possible to
turn off the power switch before input power is removed.
Over-Current and Short Circuit Protection
An internal sensing FET is employed to check for over-current conditions. Unlike current-sense resistors, sense FETs do not increase the series
resistance of the current path. When an overcurrent condition is detected, the device maintains a constant output current and reduces the output
voltage accordingly. Complete shutdown occurs only if the fault stays long enough to activate thermal limiting.
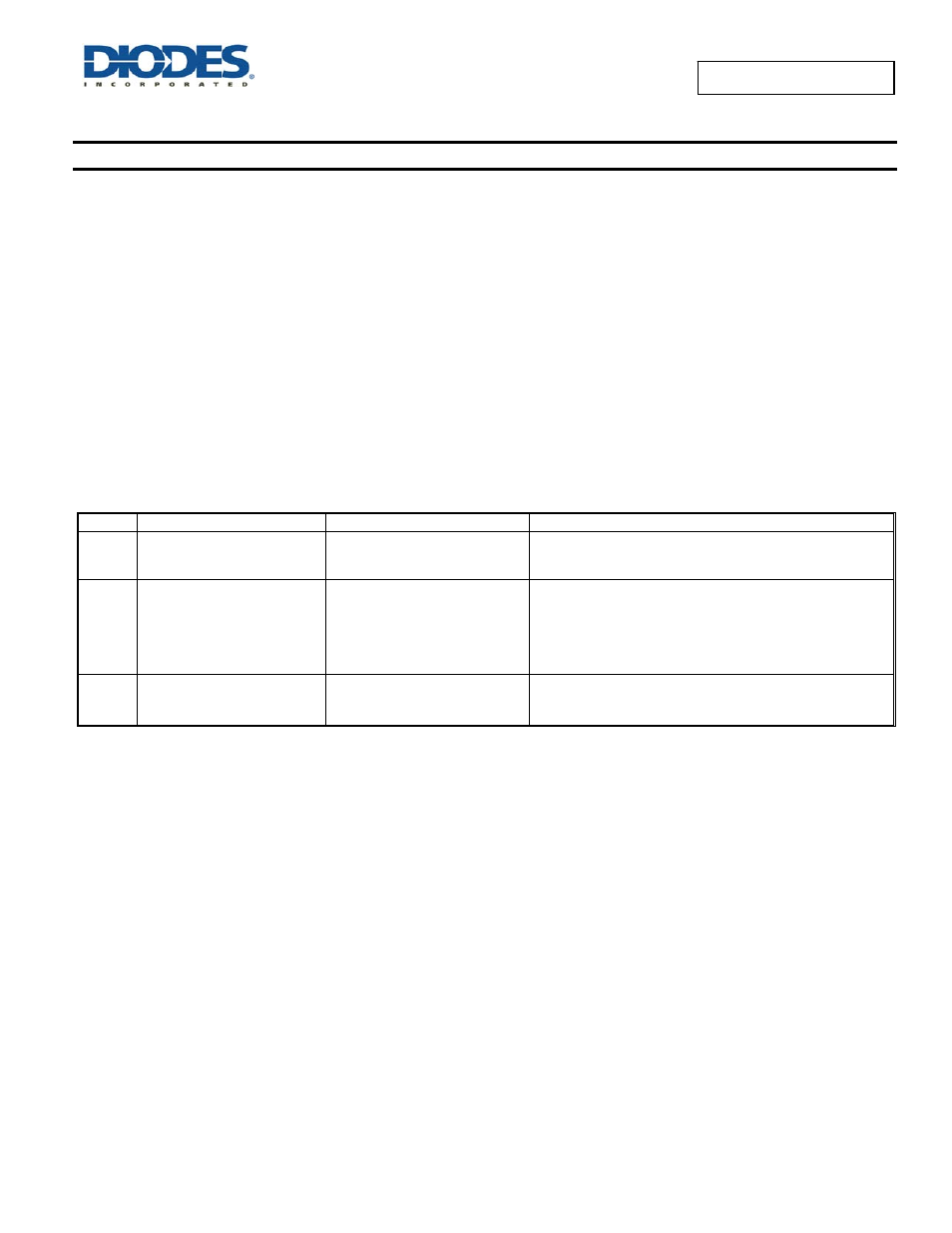
The different overload conditions and the corresponding response of the AP2141D/2151D are outlined below:
S.NO
Conditions
Explanation
Behavior of the AP2141D/2151D
1
Short circuit condition at start-up
Output is shorted before input
voltage is applied or before the
part is enabled
The IC senses the short circuit and immediately clamps output
current to a certain safe level namely I
LIMIT.
2
Short-circuit or Overcurrent
condition
Short-Circuit or Overload condition
that occurs when the part is
enabled.
At the instance the overload occurs, higher current may flow for
a very short period of time before the current limit function can
react.
After the current limit function has tripped (reached the over-
current trip threshold), the device switches into current limiting
mode and the current is clamped at I
LIMIT
.
3
Gradual increase from nominal
operating current to I
LIMIT
Load increases gradually until the
current-limit threshold.(I
TRIG
)
The current rises until I
TRIG
or thermal limit. Once the threshold
has been reached, the device switches into its current limiting
mode and is set at I
LIMIT
.
Note that when the output has been shorted to GND at extremely low temperature (< -20
o
C), a minimum 120
μF electrolytic capacitor on the output
pin is recommended. A correct capacitor type with capacitor voltage rating and temperature characteristics must be properly chosen so that
capacitance value does not drop too low at the extremely low temperature operation. A recommended capacitor should have temperature
characteristics of less than 10% variation of capacitance change when operated at extremely low temp. Our recommended aluminum electrolytic
capacitor type is Panasonic FC series.
Thermal Protection
Thermal protection prevents the IC from damage when the die temperature exceeds safe margins. This mainly occurs when heavy-overload or short-
circuit faults are present for extended periods of time. The AP2141D/AP2151D implements thermal sensing to monitor the operating junction
temperature of the power distribution switch. Once the die temperature rises to approximately 140°C, the Thermal protection feature gets activated
as follows: The internal thermal sense circuitry turns the power switch off and the FLG output is asserted thus preventing the power switch from
damage. Hysteresis in the thermal sense circuit allows the device to cool down to approximately 25°C before the output is turned back on. The built-
in thermal hysteresis feature avoids undesirable oscillations of the thermal protection circuit. The switch continues to cycle in this manner until the
load fault is removed, resulting in a pulsed output. The FLG open-drain output is asserted when an over-current occurs with 7-ms deglitch.
Reverse Current Protection
In a normal MOSFET switch, current can flow in reverse direction (from the output side to the input side) when the output side voltage is higher than
the input side, even when the switch is turned off. A reverse-current blocking feature is implemented in the AP21x1 series to prevent such back
currents. This circuit is activated by the difference between the output voltage and the input voltage. When the switch is disabled, this feature blocks
reverse current flow from the output back to the input.
