3B Scientific Air Cushion Plate User Manual
Page 40
41
Physical Experiments on the Air-Cushion Table
hover disc in such way that the mean drift veloc-
ity is constant. The hover disc is slowed down by
the interactions with the oscillating magnets. It
transfers part of its energy to the magnets so that
the amplitude of their oscillations increases. Both
the velocity of the hover disc and the amplitude
of the lattice oscillations increase as the degree
of inclination of the air-cushion table is increased
Interpretation:
The electrons in a metallic conductor move at a
constant mean velocity under the influence of an
electric field. In the course of interacting with
the lattice elements they transfer part of their
energy onto these, causing an increase in the lat-
tice oscillations and therefore also a rise in the
temperature of the conductor.
2.4.7
Motion of the Free Electrons in a Metal
Components:
Air-cushion table with fan
Overhead projector
Magnetic barrier, long
2 Pieces
Magnetic barrier, short
2 Pieces
Holding device
1 Piece
Lattice model
1 Piece
Hover disc, red
25 Pieces
Model simulation
Real Object
Model
Part of a metallic
Experiment surface of
conductor
the air-cushion table
Metal lattice
Lattice model
Electrons
Hover discs
How to proceed:
Align the air-cushion table horizontally and ar-
range the magnetic barriers around the experi-
ment surface. Attach the holding device to the
air-cushion table and insert the lattice model. Set
it to its highest position. Place the hover discs
onto the experiment surface.
Turn up the fan so that all hover discs move freely
on the air-cushion table. Observe their motions and
interactions with the magnets of the lattice model.
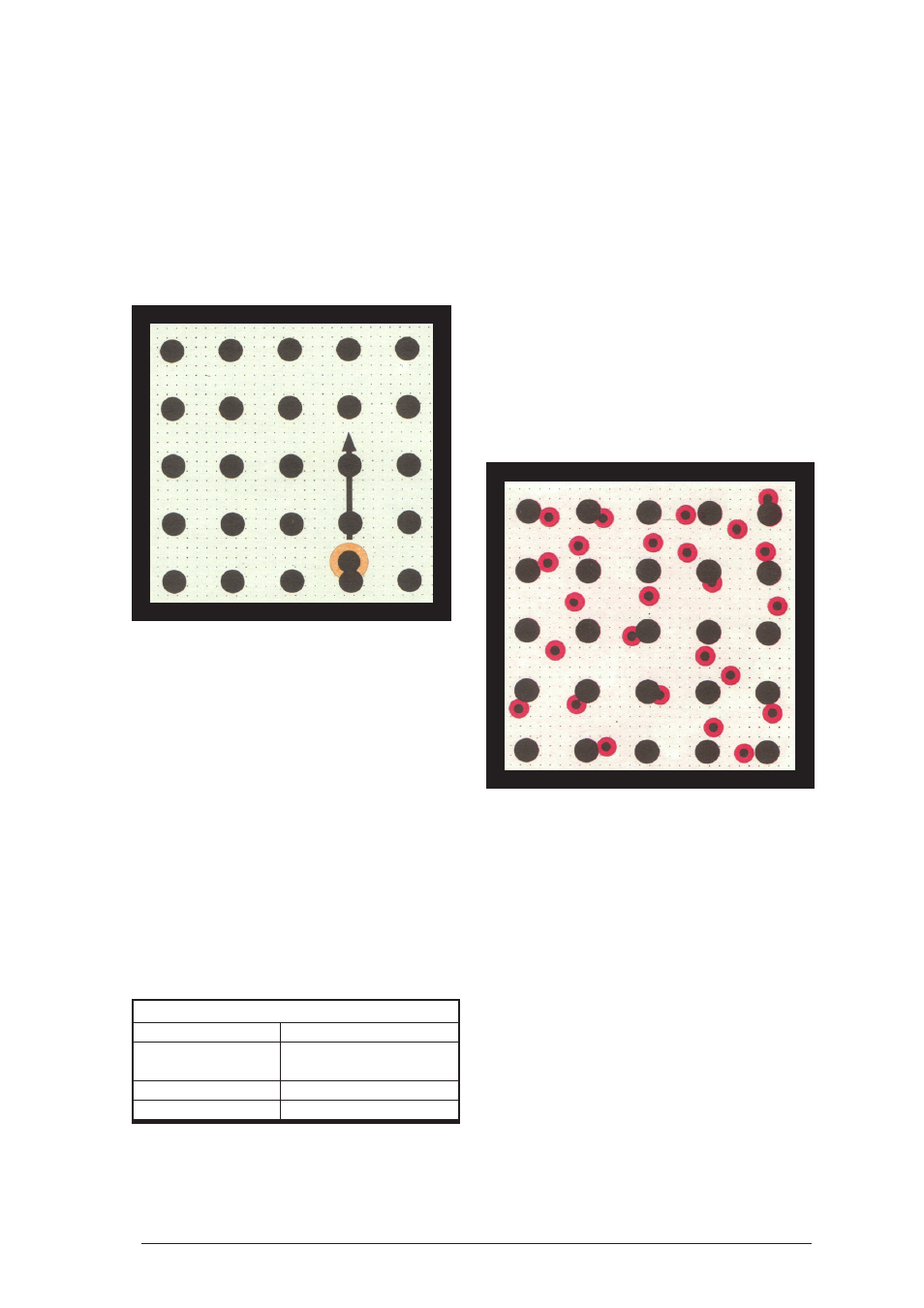
Result:
The motions of the hover discs are similar to those
of the molecules of a gas. Interactions occur when
they approach a magnet of the lattice model. A
hover disc with a high velocity can make a hang-
ing magnet oscillate at a higher amplitude. A
hanging magnet with higher oscillations can cause
the velocity of a hover disc to rise.
Interpretation:
The motions of conduction electrons in a metal
are similar to the motions of the molecules in a
gas. They interact with the lattice elements. A rise
in the temperature of the metal causes an increase
in the mean velocity of the electrons. An increased
velocity of the electrons causes a rise in the tem-
perature of the metal.
2.4.8
Thermal Emission
Components:
Air-cushion table with fan
Overhead projector
Magnetic barrier, long
2 Pieces
Magnetic barrier, short
2 Pieces
Holding device
1 Piece
Lattice model
1 Piece
Hover disc, red
15 Pieces
Hover disc, green
11 Pieces
