3B Scientific Air Cushion Plate User Manual
Page 17
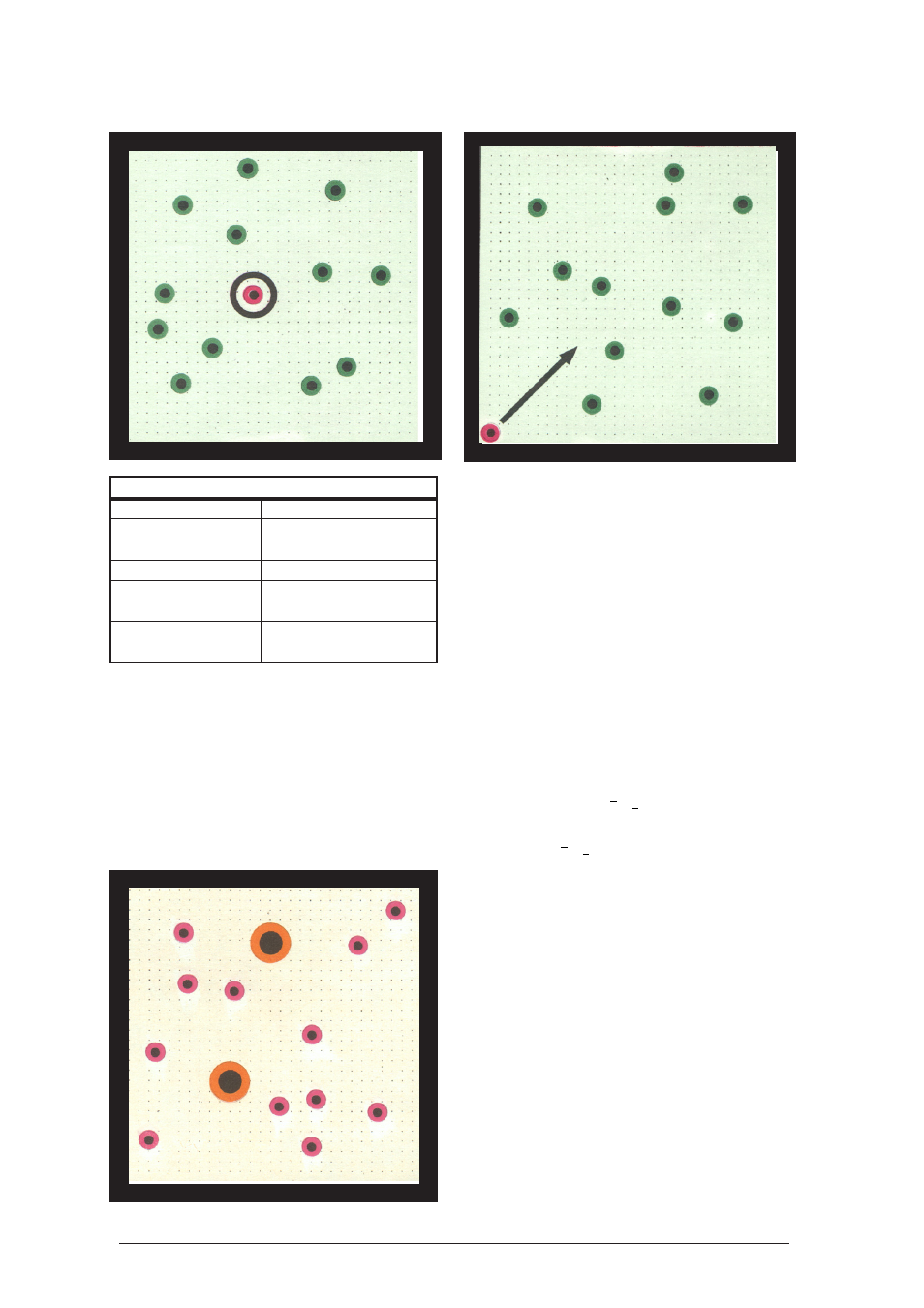
Physical Experiments on the Air-Cushion Table
18
Model simulation
Real Object
Model
Vessel containing
Experiment surface of
the gas
the air-cushion table
Walls of the vessel
Magnetic barriers
Gas molecules
Red hover disc
with small mass
Gas molecules
Orange Hover discs
with large mass
How to proceed:
Align the air-cushion table horizontally and attach
the magnetic barriers. Place the hover discs anywhere
onto the experiment surface, so that the spaces
between them are not much more than 1 cm.
Turn the fan up to a setting at which all hover discs
are sure to lift off. Observe the motions of both
types of hover discs with regard to their velocity.
Result:
The mean velocity of the orange hover disc is
much lower than the mean velocity of the red
ones.
Interpretation:
In a compound of two gases whose molecules
have different masses, the molecules have differ-
ent mean velocities. The molecules with the less-
er mass move much faster than those with the
greater mass.
Since the temperature of the gas compound cor-
responds to the mean kinetic energy of all mole-
cules, the mean kinetic energy of the molecules
with the lesser mass
E
m v
k
k
k
=
−
1
2
2
has to be equal to
the mean kinetic energy of the molecules with the
greater mass
E
m v
g
g
g
=
−
1
2
2
This leads to the conclu-
sion that in a gas compound of a given tempera-
ture the molecules of different masses have dif-
ferent mean velocities.
2.1.8
Mixing Temperature of Gases
Components:
Air-cushion table with fan
Overhead projector
Magnetic barrier, long
2 Pieces
Magnetic barrier, short
2 Pieces
Magnetic piston
l Piece
Guide piece for the
l Piece
magnetic piston
Hover disc, orange
4 Pieces
