2description of the experiments – 3B Scientific Air Cushion Plate User Manual
Page 13
Physical Experiments on the Air-Cushion Table
14
2
Description of the Experiments
2.1.2
Motion of the Molecules in a Gas
Components:
Air-cushion table with fan
Overhead projector
Magnetic barrier, long
2 Pieces
Magnetic barrier, short
2 Pieces
Hover disc, red
16 Pieces
Model simulation
Real Object
Model
Vessel containing
Experiment surface of
the gas
the air-cushion table
Walls of the vessel
Magnetic barriers
Gas molecules
Hover discs
How to proceed:
Align the air-cushion table horizontally and attach
the magnetic barriers.
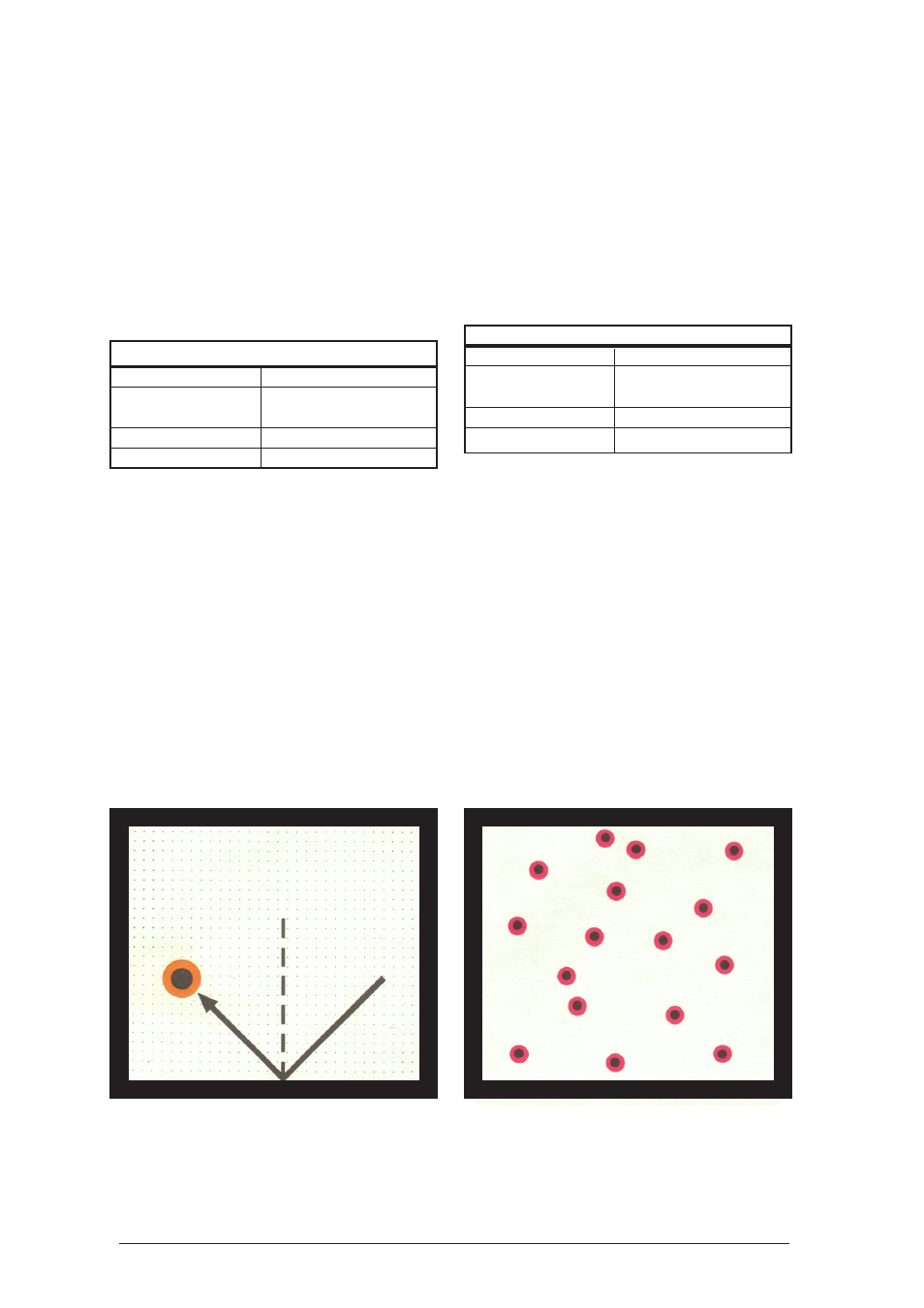
Place the 16 red hover discs anywhere on the
experiment surface so that the spaces between them
are approximately 1 cm. Then turn the fan to a
setting in which all hover discs are sure to lift off.
Result:
Each hover disc moves in a straight and uniform
way as long as it does not hit any other hover disc
or a magnetic barrier. When two hover discs
collide, their speed and direction of velocity usually
changes. These collisions cause a transmission of
kinetic energy. When hitting the magnetic barrier,
only the direction of velocity changes.
Interpretation:
Elastic collisions occur between the molecules
of a gas and when molecules hit the vessel wall.
Along the distance covered between two colli-
sions, the “free length of path”, the motion of the
molecules is straight and uniform.
2.1
Structure and Properties of Gases
2.1.1 Motion of a Molecule in High Vacuum
Components:
Air-cushion table with fan
Overhead projector
Magnetic barrier, long
2 Pieces
Magnetic barrier, short
2 Pieces
Hover discs
l Piece
Model simulation
Real Object
Model
Vessel containing
Experiment surface of
the gas
the air-cushion table
Walls of the vessel
Magnetic barriers
Gas melecules
Hover discs
How to proceed:
Align the air-cushion table horizontally and attach
the magnetic barriers.
Turn the fan to a medium setting. Place the hover
disc onto the experiment surface and give it an
impact so that it hits a magnetic barrier in the
middle at an angle of 45°.
Result:
The motion of the hover disc is straight and uni-
form. When it hits a barrier, the direction of its
motion changes. The speed is unchanged. The
hover disc rebounds at the same angle at which it
hits the barrier. The law of reflection applies.
Interpretation:
The gas molecule moves in accordance with the
laws of classical mechanics.
