Pin description functional diagrams, Detailed description, Input stage circuitry – Rainbow Electronics MAX920 User Manual
Page 9
MAX917–MAX920
SOT23, 1.8V, Nanopower, Beyond-the-Rails
Comparators With/Without Reference
_______________________________________________________________________________________
9
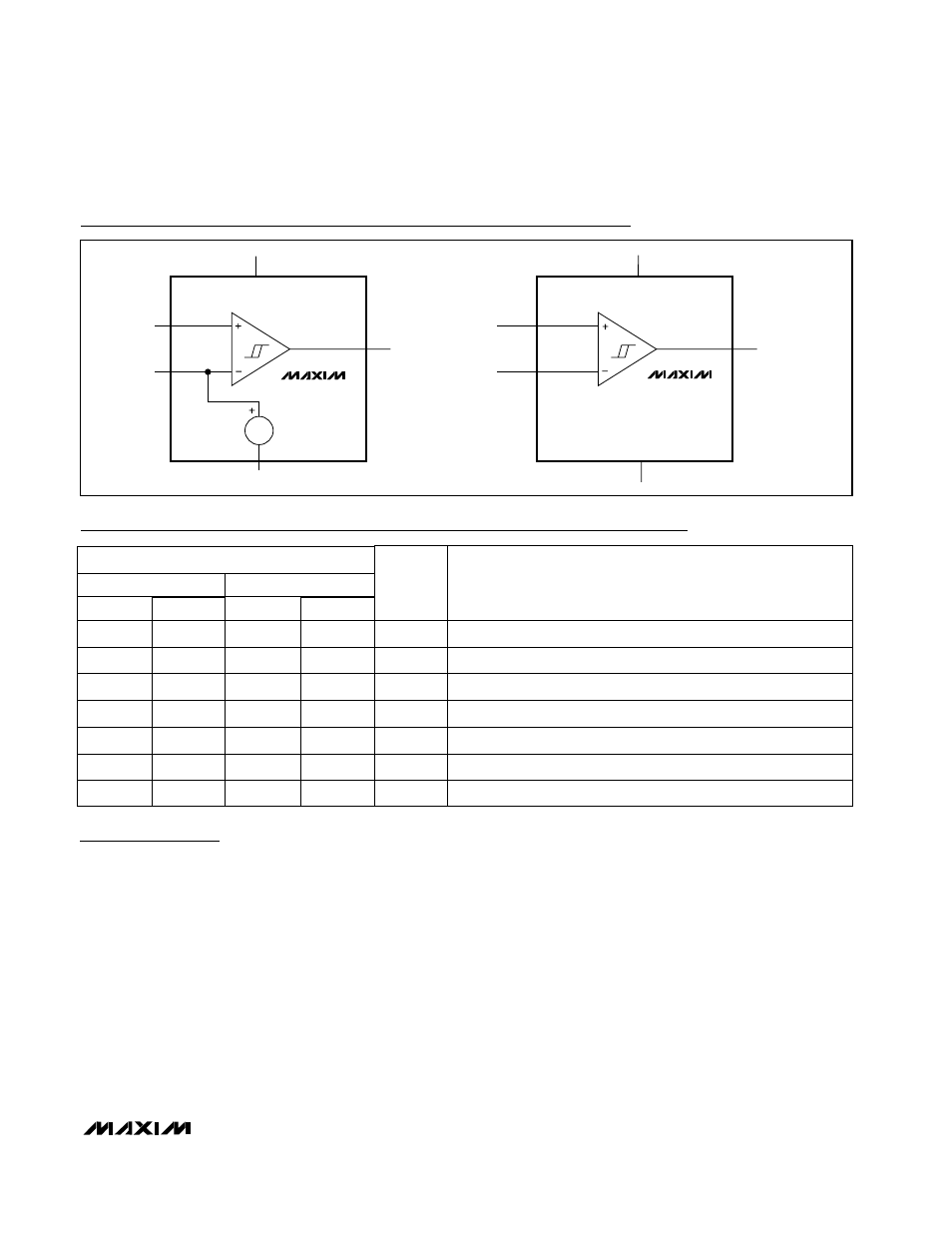
Pin Description
Functional Diagrams
MAX917
MAX918
IN+
OUT
V
CC
V
EE
REF
REF
1.245V
MAX919
MAX920
IN+
OUT
V
CC
V
EE
IN-
MAX917/MAX918
SO
PIN
SOT23-5
MAX919/MAX920
SOT23-5
SO
N.C.
V
CC
V
EE
IN-
REF
IN+
OUT
1, 5, 8
7
4
2
—
3
6
—
5
2
4
—
3
1
—
1, 5, 8
No Connection. Not internally connected.
5
7
Positive Supply Voltage
2
4
Negative Supply Voltage
—
—
Comparator Inverting Input
4
2
1.245V Reference Output and Comparator Inverting Input
3
3
Comparator Noninverting Input
1
6
Comparator Output
NAME
FUNCTION
Detailed Description
The MAX917/MAX918 feature an on-board 1.245V
±1.5% reference, yet draw an ultra-low supply current
of 750nA. The MAX919/MAX920 (without reference)
consume just 380nA of supply current. All four devices
are guaranteed to operate down to +1.8V. Their com-
mon-mode input voltage range extends 200mV
beyond-the-rails. Internal hysteresis ensures clean out-
put switching, even with slow-moving input signals.
Large internal output drivers allow rail-to-rail output
swing with up to ±8mA loads.
The output stage employs a unique design that mini-
mizes supply-current surges while switching, virtually
eliminating the supply glitches typical of many other
comparators. The MAX917/MAX919 have a push/pull
output stage that sinks as well as sources current. The
MAX918/MAX920 have an open-drain output stage that
can be pulled beyond V
CC
to an absolute maximum of
6V above V
EE
. These open-drain versions are ideal for
implementing wire-Or output logic functions.
Input Stage Circuitry
The input common-mode voltage range extends from
V
EE
- 0.2V to V
CC
+ 0.2V. These comparators operate
at any differential input voltage within these limits. Input
bias current is typically ±0.15nA if the input voltage is
between the supply rails. Comparator inputs are pro-
tected from overvoltage by internal ESD protection
diodes connected to the supply rails. As the input volt-
age exceeds the supply rails, these ESD protection
diodes become forward biased and begin to conduct.
