Rainbow Electronics MAX1181 User Manual
Page 11
noise filtering purposes, bypass REFIN with a >10nF
capacitor to GND. In internal reference mode, REFOUT,
COM, REFP, and REFN become low-impedance out-
puts.
In the buffered external reference mode, adjust the ref-
erence voltage levels externally by applying a stable
and accurate voltage at REFIN. In this mode, COM,
REFP, and REFN become outputs. REFOUT may be left
open or connected to REFIN through a >10k
Ω resistor.
In the unbuffered external reference mode, connect
REFIN to GND. This deactivates the on-chip reference
buffers for REFP, COM, and REFN. With their buffers
shut down, these nodes become high impedance and
may be driven through separate external reference
sources.
Clock Input (CLK)
The MAX1181’s CLK input accepts CMOS-compatible
clock signals. Since the interstage conversion of the
device depends on the repeatability of the rising and
falling edges of the external clock, use a clock with low
jitter and fast rise and fall times (< 2ns). In particular,
sampling occurs on the rising edge of the clock signal,
requiring this edge to provide lowest possible jitter. Any
significant aperture jitter would limit the SNR perfor-
mance of the on-chip ADCs as follows:
SNR
dB
= 20
✕
log
10
(1 / [2
π x f
IN
✕
t
AJ
]),
where f
IN
represents the analog input frequency and
t
AJ
is the time of the aperture jitter.
Clock jitter is especially critical for undersampling
applications. The clock input should always be consid-
ered as an analog input and routed away from any ana-
log input or other digital signal lines.
The MAX1181 clock input operates with a voltage thresh-
old set to V
DD
/2. Clock inputs with a duty cycle other
than 50% must meet the specifications for high and low
periods as stated in the Electrical Characteristics.
System Timing Requirements
Figure 3 depicts the relationship between the clock
input, analog input, and data output. The MAX1181
samples at the rising edge of the input clock. Output
data for channels A and B is valid on the next rising
edge of the input clock. The output data has an internal
latency of five clock cycles. Figure 4 also determines
the relationship between the input clock parameters
and the valid output data on channels A and B.
Digital Output Data, Output Data Format
Selection (T/B), Output Enable (
OE
)
All digital outputs, D0A–D9A (Channel A) and D0B–D9B
(Channel B), are TTL/CMOS logic-compatible. There is a
MAX1181
Dual 10-Bit, 80Msps, +3V, Low-Power ADC with
Internal Reference and Parallel Outputs
______________________________________________________________________________________
11
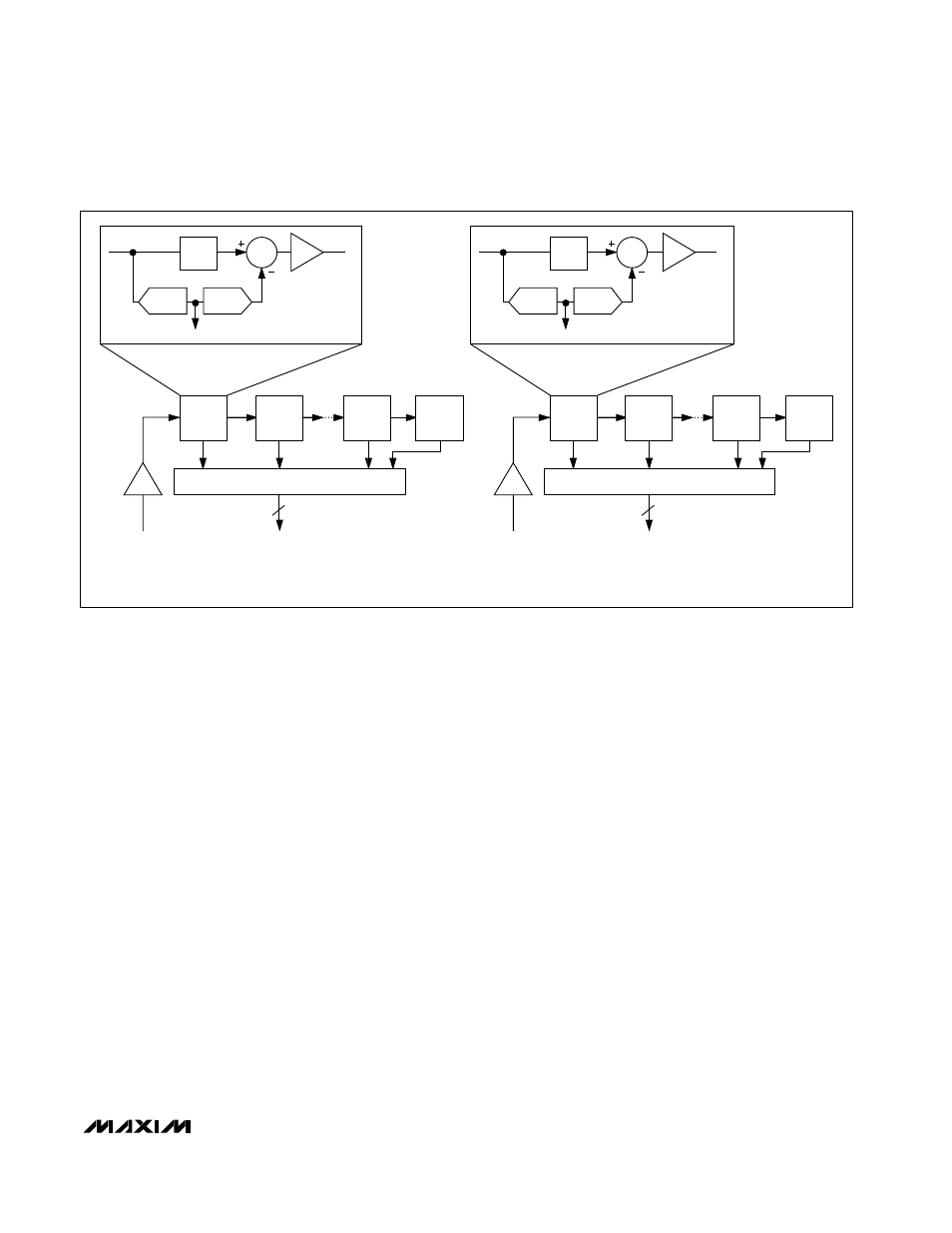
T/H
V
OUT
x2
Σ
FLASH
ADC
DAC
1.5 BITS
10
V
INA
V
IN
STAGE 1
STAGE 2
D9A–D0A
V
INA
= INPUT VOLTAGE BETWEEN INA+ AND INA- (DIFFERENTIAL OR SINGLE-ENDED)
V
INB
= INPUT VOLTAGE BETWEEN INB+ AND INB- (DIFFERENTIAL OR SINGLE-ENDED)
DIGITAL CORRECTION LOGIC
STAGE 8
STAGE 9
2-BIT FLASH
ADC
T/H
T/H
V
OUT
x2
Σ
FLASH
ADC
DAC
1.5 BITS
10
V
INB
V
IN
STAGE 1
STAGE 2
D9B–D0B
DIGITAL CORRECTION LOGIC
STAGE 8
STAGE 9
2-BIT FLASH
ADC
T/H
Figure 1. Pipelined Architecture––Stage Blocks
