Skip – Rainbow Electronics MAX1845 User Manual
Page 14
MAX1845
Dual, High-Efficiency, Step-Down
Controller with Accurate Current Limit
14
______________________________________________________________________________________
FROM
OUT
REF
FROM ZERO-CROSSING
COMPARATOR
ERROR
AMP
TON
FEEDBACK
MUX
(SEE FIGURE 9)
x2
TO DL DRIVER
SHUTDOWN
TO DH DRIVER
ON-TIME
COMPUTE
TON
1-SHOT
FROM ILIM
COMPARATOR
FROM
OPPOSITE
PWM
TO
OPPOSITE
PWM
TOFF 1-SHOT
TRIG
TRIG
Q
Q
S
R
FAULT
Q
R
Q
S
R
Q
S
TIMER
TON
V+
S
R
Q
TO PGOOD
OR-GATE
1.1V
0.9V
0.7V
0.1V
1.14V
OVP
V
CC
- 1V
UVP
FB_
OUT_
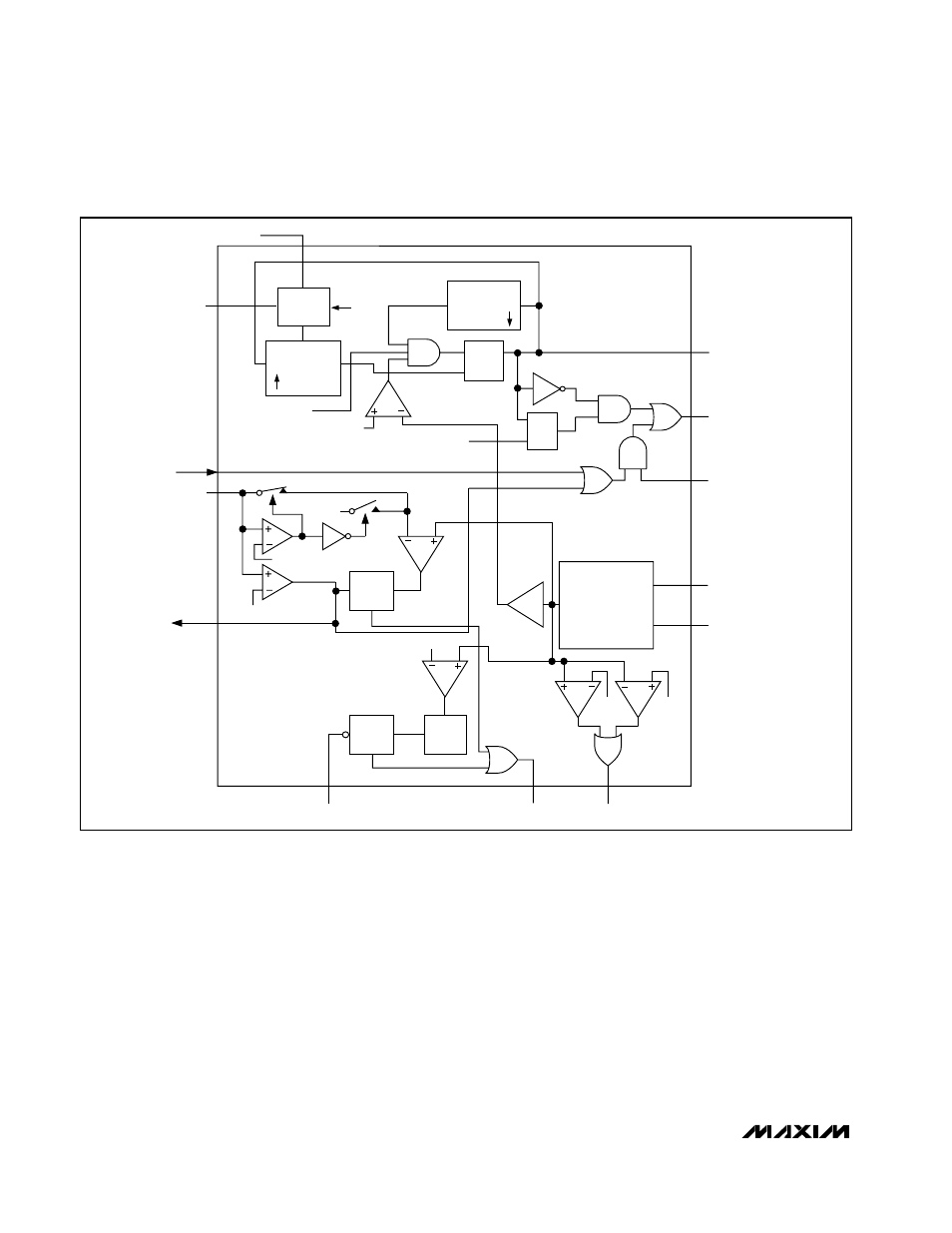
Figure 3. PWM Controller (One Side Only)
include larger physical size and degraded load-tran-
sient response (especially at low input voltage levels).
DC output accuracy specifications refer to the threshold
of the error comparator. When the inductor is in continu-
ous conduction, the output voltage will have a DC regula-
tion higher than the trip level by 50% of the ripple. In
discontinuous conduction (SKIP = GND, light-load), the
output voltage will have a DC regulation higher than the
trip level by approximately 1.5% due to slope compensa-
tion.
Forced-PWM Mode (
SKIP
= High)
The low-noise, forced-PWM mode (SKIP = high) dis-
ables the zero-crossing comparator, which controls the
low-side switch on-time. This causes the low-side gate-
drive waveform to become the complement of the high-
side gate-drive waveform. This in turn causes the
inductor current to reverse at light loads as the PWM
loop strives to maintain a duty ratio of V
OUT
/V
IN
. The
benefit of forced-PWM mode is to keep the switching
frequency fairly constant, but it comes at a cost: The
no-load battery current can be 10mA to 40mA, depend-
ing on the external MOSFETs.
Forced-PWM mode is most useful for reducing audio-
frequency noise, improving load-transient response,
providing sink-current capability for dynamic output
voltage adjustment, and improving the cross-regulation
