Max1845 – Rainbow Electronics MAX1845 User Manual
Page 12
MAX1845
Two external factors that influence switching-frequency
accuracy are resistive drops in the two conduction
loops (including inductor and PC board resistance) and
the dead-time effect. These effects are the largest con-
tributors to the change of frequency with changing load
current. The dead-time effect increases the effective
on-time, reducing the switching frequency as one or
both dead times. It occurs only in PWM mode (SKIP =
high) when the inductor current reverses at light or neg-
ative load currents. With reversed inductor current, the
inductor’s EMF causes LX to go high earlier than nor-
mal, extending the on-time by a period equal to the
low-to-high dead time.
For loads above the critical conduction point, the actual
switching frequency is:
where V
DROP
1 is the sum of the parasitic voltage drops
in the inductor discharge path, including synchronous
rectifier, inductor, and PC board resistances; V
DROP2
is
the sum of the resistances in the charging path; and
t
ON
is the on-time calculated by the MAX1845.
Automatic Pulse-Skipping Switchover
In skip mode (SKIP = GND), an inherent automatic
switchover to PFM takes place at light loads. This
switchover is effected by a comparator that truncates
the low-side switch on-time at the inductor current’s
zero crossing. This mechanism causes the threshold
between pulse-skipping PFM and nonskipping PWM
operation to coincide with the boundary between con-
tinuous and discontinuous inductor-current operation
(also known as the critical conduction point). For a 7V
to 24V battery range, of this threshold is relatively con-
stant, with only a minor dependence on battery voltage:
I
K V
2L
V
- V
V
LOAD(SKIP)
OUT_
IN
OUT_
IN
≈
×
f
V
V
t
V
V
OUT
DROP
ON
IN
DROP
=
+
+
(
)
1
2
Dual, High-Efficiency, Step-Down
Controller with Accurate Current Limit
12
______________________________________________________________________________________
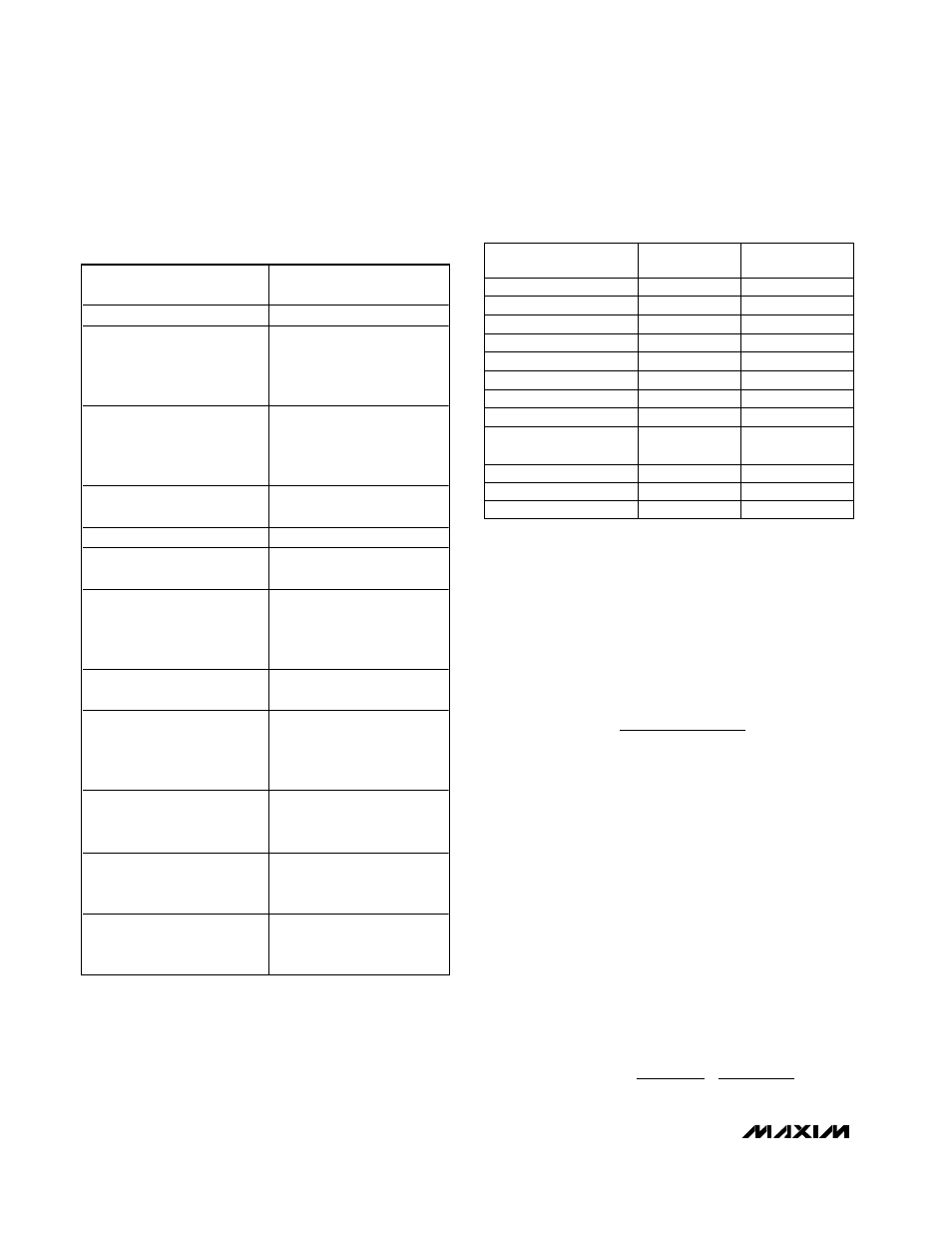
Table 1. Component Selection for
Standard Applications
Table 2. Component Suppliers
*Distributor
COMPONENT
SIDE 1: 1.8V AT 8A/
SIDE 2: 2.5V AT 4A
Input Range
4.5V to 28V
Q1 High-Side MOSFET
Fairchild Semiconductor
FDS6612A or
International Rectifier
IRF7807
Q2 Low-Side MOSFET
Fairchild Semiconductor
FDS6670A or
International Rectifier
IRF7805
Q3, Q4 High/Low-Side
MOSFETs
Fairchild Semiconductor
FDS6982A
D1, D2 Rectifier
Nihon EP10QY03
D3 Rectifier
Central Semiconductor
CMPSH-3A
L1 Inductor
2.2µH
Panasonic ETQP6F2R2SFA
or
Sumida CDRH127-2R4
L2 Inductor
4.7µH
Sumida CDRH124-4R7MC
C1 (3), C2 (2) Input
Capacitor
10µF, 25V
Taiyo Yuden
TMK432BJ106KM or
TDK C4532X5R1E106M
C3 (3), C4 Output Capacitor
470µF, 6V
Kemet T510X477M006AS or
Sanyo 6TPB330M
R
SENSE1
5m
Ω, ±1%, 1W
IRC LR2512-01-R005-F or
D
ALE
WSL-2512-R005F
R
SENSE2
10m
Ω, ±1%, 0.5W
IRC LR2010-01-R010-F or
D
ALE
WSL-2010-R010F
MANUFACTURER
USA PHONE
FACTORY FAX
[Country Code]
Central Semiconductor
516-435-1110
[1] 516-435-1824
Dale/Vishay
203-452-5664
[1] 203-452-5670
Fairchild Semiconductor
408-822-2181
[1] 408-721-1635
International Rectifier
310-322-3331
[1] 310-322-3332
IRC
800-752-8708
[1] 828-264-7204
Kemet
408-986-0424
[1] 408-986-1442
NIEC (Nihon)
805-867-2555*
[81] 3-3494-7414
Sanyo
619-661-6835
[81] 7-2070-1174
Siliconix
408-988-8000
800-554-5565
[1] 408-970-3950
Sumida
847-956-0666
[81] 3-3607-5144
Taiyo Yuden
408-573-4150
[1] 408-573-4159
TDK
847-390-4461
[1] 847-390-4405
