Transaction sequence, Net address commands – Rainbow Electronics DS2784 User Manual
Page 32
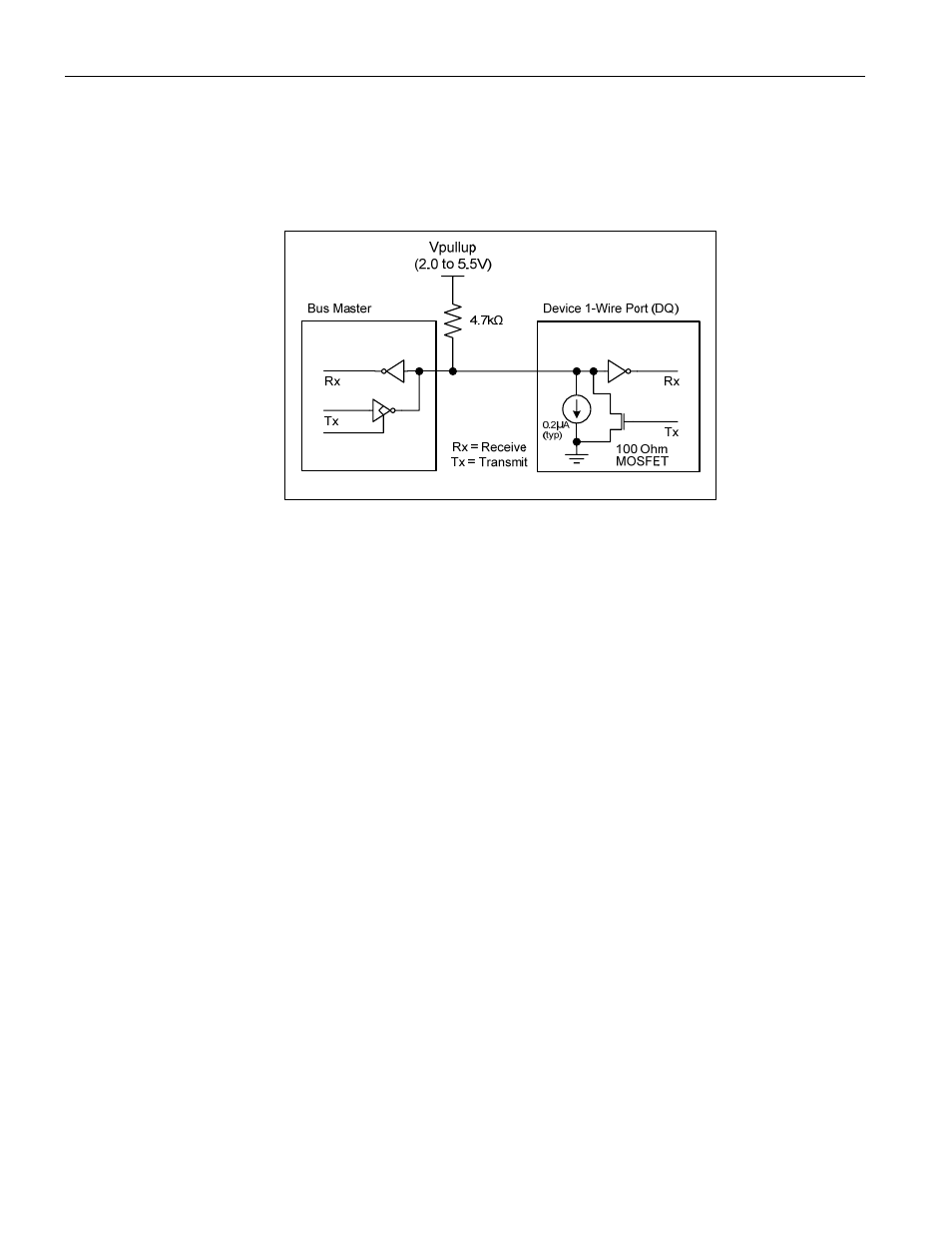
DS2784: 1-Cell Stand-Alone Fuel Gauge IC with Li+ Protector and SHA-1 Authentication
The 1-Wire bus must have a pullup resistor at the bus-master end of the bus. A value of between 2k
Ω and 5kΩ is
recommended. The idle state for the 1-Wire bus is high. If, for any reason, a bus transaction must be suspended,
the bus must be left in the idle state to properly resume the transaction later. Note that if the bus is left low for more
than t
LOW0
, slave devices on the bus begin to interpret the low period as a reset pulse, effectively terminating the
transaction.
Figure 8. 1-Wire Bus Interface Circuitry
TRANSACTION SEQUENCE
The protocol for accessing the DS2784 through the 1-Wire port is as follows:
• Initialization
• Net
Address
Command
• Function
Command(s)
• Data Transfer (not all commands have data transfer)
All transactions of the 1-Wire bus begin with an initialization sequence consisting of a reset pulse transmitted by the
bus master, followed by a presence pulse simultaneously transmitted by the DS2784 and any other slaves on the
bus. The presence pulse tells the bus master that one or more devices are on the bus and ready to operate. For
more details, see the 1-Wire Signaling section.
NET ADDRESS COMMANDS
Once the bus master has detected the presence of one or more slaves, it can issue one of the net address
commands described in the following paragraphs. The name of each net address command (ROM command) is
followed by the 8-bit op code for that command in square brackets.
Read Net Address [33h].
This command allows the bus master to read the DS2784’s 1-Wire net address. This
command can only be used if there is a single slave on the bus. If more than one slave is present, a data collision
occurs when all slaves try to transmit at the same time (open drain produces a wired-AND result).
Match Net Address [55h].
This command allows the bus master to specifically address one DS2784 on the 1-Wire
bus. Only the addressed DS2784 responds to any subsequent function command. All other slave devices ignore
the function command and wait for a reset pulse. This command can be used with one or more slave devices on
the bus.
Skip Net Address [CCh].
This command saves time when there is only one DS2784 on the bus by allowing the
bus master to issue a function command without specifying the address of the slave. If more than one slave device
is present on the bus, a subsequent function command can cause a data collision when all slaves transmit data at
the same time.
32 of 38
